Abstract
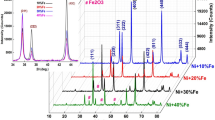
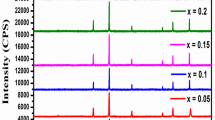
The semiconducting polycrystalline ferrite materials with the general formula Ni1−x Mg x Fe2O4 were synthesized by using the solid state reaction method. X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectrographs, and atomic force microscopy techniques were utilized to study the structural parameters. XRD confirms the formation of single phase cubic spinel structure of the ferrites. The crystallite sizes of ferrites determined using the Debye–Scherer formula ranges from 0.963 μm to 1.069 μm. The cation distribution of ferrite shows that Mg2+ ions occupy a tetrahedral site (A-site) and the Ni2+ ion occupy an octahedral site (B-site) whereas Fe3+ ions occupies an octahedral as well as a tetrahedral site. The study of elastic parameters such as the longitudinal modulus, rigidity modulus, Young’s modulus, bulk modulus, and Debye temperature were estimated using the FTIR technique. The decrease of direct current (DC) resistivity with increase in temperature indicates the semiconducting nature of ferrites. The dielectric constant as well as loss tangent decreases with increase in frequency, and at still higher frequencies, they are almost constant. This shows usual dielectric dispersion behavior attributed to the Maxwell–Wagner type of interfacial polarization and is in accordance with Koop’s phenomenological theory. The linear increase of alternating current conductivity with increase of frequency shows the small polaron hopping type of conduction mechanism in all the ferrites. The magnetic properties such as saturation magnetization (M s ), magnetic moment, coercivity, remnant magnetization (M r ), and the ratio of M r /M s was estimated using the M–H loop.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q.A. Pankhurst, J. Connolly, S.K. Jones, and J. Dobson, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 36, 167 (2003).
J. Kulikowski, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 41, 56 (1990).
M.A. El Hiti, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 29, 501 (1999).
A. Largeteau, J.M. Reau, and J. Raves, Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 111, 627 (1990).
A.M. Abdeen, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 192, 121 (1999).
C.G. Koops, Phys. Rev. 83, 121 (1951).
F. Haberey and H. Wijn, Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 26, 231 (1968).
V.R.K. Murthy and J. Sobhanadri, Phys. Stat. Sol. (a) 3, 647 (1976).
M. Naeem, N.A. Shah, I.H. Gul, and A. Maqsood, J. Alloys Compd. 487, 739 (2009).
M.A. Gabal and Y.M. Al Angari, Mater. Chem. Phys. 118, 153 (2009).
P.B. Belavi, G.N. Chavan, L.R. Naik, R. Somashekar, and R.K. Kotnala, Mater. Chem. Phys. 132, 138 (2012).
T.J. Shinde, A.B. Gadkari, and P.N. Vasambekar, Mater. Chem. Phys. 111, 87 (2008).
R.D. Waldron, Phys. Rev. 99, 1727 (1955).
V.A.M. Brabers, Phys. Status Sol. 33, 563 (1969).
P.P. Hankare, V.T. Vader, N.M. Patil, S.D. Jadhav, U.B. Sankpal, M.R. Kadam, B.K. Chougule, and N.S. Gajbhiye, Mater. Chem. Phys. 113, 233 (2009).
N.M. Mahmoodi, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 44, 322 (2013).
R.S. Gaikwad, S.-Y. Chae, R.S. Mane, S.-H. Han, O.-S. Joo, SAGE-Hindawi Access to Res. Int. J. Electrochem. 2011, 1 (2011).
R.S. Devan, B.K. Chougule, and Y.D. Kolekar, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 18, 9809 (2006).
E.J.W. Verwey, F. de Boer, and J.H. van Santen, J. Chem. Phys. 16, 1091 (1948).
G.N. Chavan, P.B. Belavi, L.R. Naik, B.K. Bammannavar, K.P. Ramesh, and S. Kumar, Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2, 82 (2013).
R.C. Kambale, P.A. Shaikh, S.S. Kamble, and Y.D. Kolekar, J. Alloys Compd. 478, 599 (2009).
A.M. El-Sayed, Mater. Chem. Phys. 82, 583 (2003).
M.U. Islam, T. Abbas, S.B. Niazi, Z. Ahmad, S. Sabeen, and M.A. Chaudhry, Solid State Commun. 130, 353 (2004).
G.M. Kale and T. Asokan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 62, 2324 (1993).
N. Rezlescuu and E. Cuciureanu, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 32, 1096 (1971).
P. Chavan and L.R. Naik, Int. J. Eng. Sci. Res. 6, 29 (2016).
R.F.G. Gardner, R.L. Moss, and D.W. Tanner, Br. J. Appl. Phys. 17, 55 (2002).
N. Sivakumar, A. Narayanasamy, J.M. Greneche, R. Murugaraj, and Y.S. Lee, J. Alloys Compd. 504, 395 (2010).
K. Iwauchi, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 10, 1520 (1971).
D.R. Patil and B.K. Chougule, J. Alloys Compd. 458, 335 (2008).
H.H. Qiu, M. Kudo, and H. Sakata, Mater. Chem. Phys. 51, 233 (1997).
D. Adler and J. Feinleib, Phys. Rev. B 2, 3112 (1970).
S.L. Kadam, K.K. Patankar, C.M. Kanamadi, and B.K. Chougule, Mater. Res. Bull. 39, 2265 (2004).
K.B. Modi, M.K. Rangolia, M.C. Chhantbar, and H.H. Joshi, J. Mater. Sci. 41, 7308 (2006).
L. Said Jan and M. Ahmed Siddig, Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 29, 181 (2011).
A.I. Ahmed, M.A. Siddig, A.A. Mirghni, M.I. Omer, and A.A. Elbadawi, Adv. Nanopart. 4, 45 (2015).
A.E. Berkowitz, W.J. Schuele, and P.J. Flanders, J. Appl. Phys. 39, 1261 (1968).
A.B. Gadkari, T.J. Shinde, and P.N. Vasambekar, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 21, 96 (2010).
A. Verma and R. Chatterjee, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 306, 313 (2006).
M. Siva Ram Prasad, B.B.V.S.V. Prasad, B. Rajesh, K.H. Rao, and K.V. Ramesh, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2115 (2011).
Y.P. Irkin and E.A. Turor, Sovt. Phys. JEPT. 33, 673 (1957).
Acknowledgement
The author (Pradeep Chavan) expresses his gratitude to Dr. Jyoti Shah, National Physical Laboratory, New Delhi, for providing an opportunity to carry out magnetic measurements at their laboratory. The author is thankful to staff of University Science Instrumentation Centre (USIC), Karnatak university Dharwad for their help during the measurement of AFM, UV, and FTIR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chavan, P., Naik, L.R., Belavi, P.B. et al. Studies on Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Mg-Substituted Nickel Ferrites. J. Electron. Mater. 46, 188–198 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4886-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-016-4886-6