Abstract
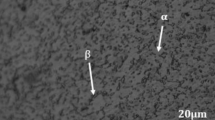
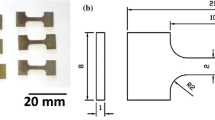
Titanium alloy Ti-3Al-2.5V is cheaper to produce and has the potential of improved ductility and formability compared to the Ti-6Al-4V alloy. Various heat treatments were performed on cylindrical tensile test bars in order to optimize the mechanical properties of Ti-3Al-2.5V. The tensile properties of heat-treated Ti-3Al-2.5V were determined at four annealing temperatures with different quenching methods and five different solution treatments and five different aging treatments for varying hours. The samples were tensile tested. The results indicated that optimum properties of high strength and ductility were reached at 926 °C of solution treatment and 480 °C of aging.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Boyer, G. Welsch, and E.W. Collings, Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1994, p 3–9
R.R. Boyer, An Overview on the Use of Titanium in the Aerospace Industry, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1996, 213, p 103–114
R. Boyer, G. Welsch, and E.W. Collings, Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1994, p 263–286
Haynes Ti-3Al-2.5V Alloy, Tube and Pipe Products, Haynes International, http://www.haynesintl.com/pdf/h5000.pdf, Accessed 7 February 2015
Bikes/T/Titanium Strength Comparison, http://www.bmxmuseum.com/bikes/info/104, Accessed 11 April 2013
R.W. Davies, M.A. Khaleel, W.C. Kinsel, and H.M. Zbib, Anisotropic Yield Locus Evolution During Cold Pilgering of Titanium Alloy Tubing, J. Eng. Mater. Technol., 2002, 2002(124), p 125–134
B. Li and M.C. Gupta, Crack Growth Life of Ti-3Al-2.5V Tubes Under Internal Impulse Pressure, Mater. Sci. Eng., 2006, A431, p 146–151
Y. Lin, M.C. Gupta, R.E. Taylor, C. Lei, W. Stone, T. Speidel, M. Yu, and R. Williams, Nanosecond Pulsed Laser Micromachining for Experimental Fatigue Life Study of Ti-3Al-2.5V Tubes, Opt. Lasers Eng., 2009, 47(1), p 118–122
S. Gollipudi, I. Charit, and K.L. Murty, Creep Mechanisms in Ti-3Al-2.5V Alloy Tubing Deformed Under Closed-End Internal Gas Pressurization, Acta Mater., 2008, 56(10), p 2406–2419
V. Venkatesan, D.S. Sarma, and K.L. Murty, On the Origin of Creep Anisotropy in a Ti-3Al-2.5V Alloy, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1991, 10(16), p 984–986
H. Li, H. Yang, F.F. Song, M. Zahn, and G.J. Li, Springback Characterization and Behaviors of High-Strength Ti-3Al-2.5V Tube in Cold Rotary Draw Bending, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2012, 212, p 1973–1987
H. Li, H. Yang, F.-F. Song, and G.-J. Li, Springback Nonlinearity of High-Strength Titanium Alloy Tube upon Mandrel Bending, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., 2013, 14(3), p 429–438
A. Salam and C. Hammond, Superplasticity in Ti-3Al-2.5V, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 2000, 19, p 1731–1733
F. Javidrad, M. Farghadani, and M. Hedari, The MPAW of Ti-3Al-2.5V Thin Sheets and Its Effect on Mechanical and Microstructural Properties, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2014, 23(2), p 666–672
P.Y. Lim, P.L. She, and H.C. Shih, Microstructure Effect on Microtopography of Chemically Etched α + β Alloys, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2006, 253, p 449–458
B. Sarrail, C. Schrupp, S. Babakhanyan, K. Muscare, J. Foyos, J. Ogren, P. Stoyanov, S. Sparkowich, R. Sutherlong, R. Clark, Jr., and O.S. Es-Said, Quenching Methods for Ti-325 Alloy, Eng. Fail. Anal., 2007, 14, p 1402–2405
Aircraft Materials, Titanium alloy Grade 9 / Ti-3Al-2.5V, http://aircraftmaterials.com/data/titanium/ti3al2-5v.html, Accessed 20 April 2015
Heat Treating of Titanium and Titanium Alloys, www.keytometals.com/Article97.htm, Accessed 19 April 2013
L. Zeng, and L. Haylock, An Evaluation of Microstructure, Texture, and Oxidation Behaviors of Ti-3Al-2.5V, Alcoa Fastening Systems, Torrance, CA, AeroMat 2011, Long Beach, CA, May 2011
Titanium Ti-6Al-4V, (Grade 5) Annealed, ASM Material Data Sheet, http://asm.matweb.com/search/SpecificMaterial.asp?bassnum=MTP641, Accessed 25 February 2015
Titanium Ti-3Al-2.5V, (Grade 5) STA, ASM Material Data Sheet, http://asm.matweb.com/search/SpecificMaterial.asp?bassnum=MTP642, Accessed 25 February 2015
Y.N. Wang and J.C. Huang, Texture Analysis in Hexagonal Materials, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2003, 81(1), p 11–26
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, M., Chavez, T., Dearborn, M. et al. Effect of Heat Treatments on the Mechanical Properties of Ti-3Al-2.5V Alloy. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 24, 3277–3290 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1628-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-015-1628-5