Abstract
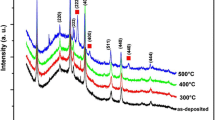
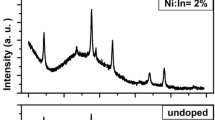
Undoped and Sn-doped (1, 1.5 and 2 at.%) indium oxide (In2O3) thin films have been grown by the chemical spray pyrolysis technique on cleaned glass substrates using indium nitrate [In(NO3)3] and stannic tetrachloride hydrated (SnCl4·5H2O) as the host and dopant precursors, respectively, and deionized water as the solvent. Structural characterization using x-ray diffraction reveals that the films possess cubic structure, with the average crystallite size in the range 10-14 nm. The surface morphology and roughness of the films have been investigated by means of an atomic force microscope. UV-Vis measurements indicate an enhancement in the optical transmittance in the visible region on Sn doping. Further, the doping effect has been found to substantially reduce the electrical resistance to a few orders of magnitude of the undoped In2O3 film. We report a simultaneous improvement in both the optical and electrical properties of indium oxide thin film due to the doping of Sn ions. These results indicate that Sn-doped In2O3 thin film can be a potential candidate for use in various optoelectronic devices. Among all the films examined, the 1 at.% Sn-doped film shows the maximum response (~91%) at 300 °C for 80 ppm concentration of formaldehyde in air.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Beena, K.J. Lethy, R. Vinodkumar, V.P. Mahadevan Pillai, V. Ganesan, D.M. Phase, and S.K. Sudheer, Effect of Substrate Temperature on Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of Pulsed Laser Ablated Nanostructured Indium Oxide Films, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2009, 255, p 8334-8342
A. Walsh, J.L.F. Da Silva, S.-H. Wei, C. Korber, A. Klein, L.F.J. Piper, A. DeMasi, K.E. Smith, G. Panaccione, P. Torelli, D.J. Payne, A. Bourlange, and R.G. Egdell, Nature of the Band Gap of In2O3 Revealed by First-Principles Calculations and X-ray Spectroscopy, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2008, 100, p 167402
P.K. Manoj, K.G. Gopchandran, P. Koshy, V.K. Vaidyan, and B. Joesph, Growth and Characterization of Indium Oxide Thin Films Prepared by Spray Pyrolysis, Opt. Mater., 2006, 28, p 1405-1411
C.H. Lee and C.S. Huang, Spray Pyrolysis Deposition for Indium Oxide Doped with Different Impurities, Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 1994, 22, p 233-240
C. Wang, V. Cimalla, G. Cherkashinin, H. Romanus, M. Ali, and O. Ambacher, Transparent Conducting Indium Oxide Thin Films Grown by Low-Temperature Metal Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition, Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515, p 2921-2925
V.S. Vaishnav, P.D. Patel, and N.G. Patel, Preparation and Characterization of Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films for Their Application as Gas Sensors, Thin Solid Films, 2005, 487, p 277-282
B.-C. Kim, J.-Y. Kim, D.-D. Lee, J.-O. Lim, and J.-S. Huh, Effect of Crystal Structures on Gas Sensing Properties of Nanocrystalline ITO Thick Films, Sens. Actuators B, 2003, 89, p 180-186
S. Parthiban, V. Gokulakrishnan, K. Ramamurthi, E. Elangovan, R. Martins, E. Fortunato, and R. Ganesan, High Near-Infrared Transparent Molybdenum-Doped Indium Oxide Thin Films for Nanocrystalline Silicon Solar Cell Applications, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2009, 93, p 92-97
E. Elangovan, G. Gonçalves, R. Martins, and E. Fortunato, RF Sputtered Wide Work Function Indium Molybdenum Oxide Thin Films for Solar Cell Applications, Sol. Energy, 2009, 83, p 726-731
Q. Zhang, X. Li, and G. Li, Dependence of Electrical and Optical Properties on Thickness of Tungsten-Doped Indium Oxide Thin Films, Thin Solid Films, 2008, 517, p 613-616
J.K. Kim and Y.G. Choi, Eu-Doped Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films Fabricated by Sol-Gel Technique, Thin Solid Films, 2009, 517, p 5084-5086
B. Zhang, X. Dong, X. Xu, P. Zhao, and J. Wu, Characteristics of Zirconium-Doped Indium Tin Oxide Thin Films Deposited by Magnetron Sputtering, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2008, 92, p 1224-1229
A. Moses Ezhil Raj, V. Senthilkumar, V. Swaminathan, J. Wollschläger, M. Suendorf, M. Neumann, M. Jayachandran, and C. Sanjeeviraja, Studies on Transparent Spinel Magnesium Indium Oxide Thin Films Prepared by Chemical Spray Pyrolysis, Thin Solid Films, 2008, 517, p 510-516
N.G. Pramod, S.N. Pandey, and P.P. Sahay, Structural, Optical and Methanol Sensing Properties of Sprayed In2O3 Nanoparticle Thin Films, Ceram. Int., 2012, 38, p 4151-4158
D. Beena, K.J. Lethy, R. Vinodkumar, A.P. Detty, V.P. Mahadevan Pillai, and V. Ganesan, Photoluminescence in Laser Ablated Nanostructured Indium Oxide Thin Films, J. Alloy. Compd., 2010, 489, p 215-223
C. Coutal, A. Azema, and J.-C. Roustan, Fabrication and Characterization of ITO Thin Films Deposited by Excimer Laser Evaporation, Thin Solid Films, 1996, 288, p 248-253
B. Radha Krishna, T.K. Subramanyam, B. Srinivasulu Naidu, and S. Uthanna, Effect of Substrate Temperature on the Electrical and Optical Properties of dc Reactive Magnetron Sputtered Indium Oxide Films, Opt. Mater., 2000, 15, p 217-224
I. Hotovy, J. Pezoldt, M. Kadlecikova, T. Kups, L. Spiess, J. Breza, E. Sakalauskas, R. Goldhahn, and V. Rehacek, Structural Characterization of Sputtered Indium Oxide Films Deposited at Room Temperature, Thin Solid Films, 2010, 518, p 4508-4511
M.A. Flores-Mendoza, R. Castanedo-Perez, G. Torres-Delgado, J. Marquez Marin, and O. Zelaya-Angel, Influence of the Annealing Temperature on the Properties of Undoped Indium Oxide Thin Films Obtained by the Sol-Gel Method, Thin Solid Films, 2008, 517, p 681-685
S. Jana and P.K. Biswas, Effect of Zr (IV) Doping on the Optical Properties of Sol-Gel Based Nanostructured Indium Oxide Films on Glass, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2009, 117, p 511-516
M.-M. Bagheri-Mohagheghi and M. Shokooh-Saremi, The Effect of High Acceptor Dopant Concentration of Zn2+ on Electrical, Optical and Structural Properties of the In2O3 Transparent Conducting Thin Films, Semicond. Sci. Technol., 2003, 18, p 97-103
M. Girtan, Investigations on the Optical Constants of Indium Oxide Thin Films Prepared by Ultrasonic Spray Pyrolysis, Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2005, 118, p 175-178
C.S. Prajapati, S.N. Pandey, and P.P. Sahay, Sensing of LPG with Nanostructured Zinc Oxide Thin Films Grown by Spray Pyrolysis Technique, Physica B, 2011, 406, p 2684-2688
V. Gupta and A. Mansingh, Influence of Postdeposition Annealing on the Structural and Optical Properties of Sputtered Zinc Oxide Film, J. Appl. Phys., 1996, 80, p 1063-1073
A. Goswami, Thin Film Fundamentals, New Age International, New Delhi, 1996
P.D.C. King, T.D. Veal, F. Fuchs, Ch.Y. Wang, D.J. Payne, A. Bourlange, H. Zhang, G.R. Bell, V. Cimalla, O. Ambacher, R.G. Egdell, F. Bechstedt, and C.F. McConville, Band Gap, Electronic Structure, and Surface Electron Accumulation of Cubic and Rhombohedral In2O3, Phys. Rev. B, 2009, 79, p 205211
K. Arshak and I. Gaiden, Development of a Novel Gas Sensor Based on Oxide Thick Films, Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2005, 118, p 44-49
K.W. Zhou, X.L. Ji, N. Zhang, and X.R. Zhang, On-Line Monitoring of Formaldehyde in Air by Cataluminescence-Based Gas Sensors, Sens. Actuators B, 2006, 119, p 392-397
H. Gonga, J.Q. Hua, J.H. Wang, C.H. Onga, and F.R. Zhub, Nano-Crystalline Cu-Doped ZnO Thin Film Gas Sensor for CO, Sens. Actuators B, 2006, 115, p 247-251
N. Han, Y. Tian, X. Wu, and Y. Chen, Improving Humidity Selectivity in Formaldehyde Gas Sensing by a Two-Sensor Array Made of Ga-Doped ZnO, Sens. Actuators B, 2009, 138, p 228-235
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Institute Instrumentation Centre, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, India, for providing XRD and AFM facilities. Financial support provided by the University Grants Commission, New Delhi, India, in the form of a major research project (No. 40-450/2011 (SR)) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pramod, N.G., Pandey, S.N. & Sahay, P.P. Sn-Doped In2O3 Nanocrystalline Thin Films Deposited by Spray Pyrolysis: Microstructural, Optical, Electrical, and Formaldehyde-Sensing Characteristics. J Therm Spray Tech 22, 1035–1043 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-013-9933-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-013-9933-8