Abstract
Objective
Our previous study has showed that ΔDNMT3B is the predominant form of DNMT3B in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In this study, we aimed to explore the expression patterns of the ΔDNMT3B variants in breast cancer and to identify whether the pattern was similar to that in NSCLC or not and its clinical significance.
Methods
Expression of seven ΔDNMT3B variants in 59 breast cancer and the corresponding normal tissue was measured using RT-PCR. The correlations between the expressions of ΔDNMT3B variants and the clinical parameters including ER/PR status, clincopathologic feature and survivals were analyzed.
Results
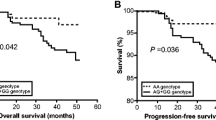
There were significant differences in the expression ratios of ΔDNMT3B1-7 variants between breast cancer tissues and normal tissues (P<0.001). The positive ratio of ΔDNMT3B1-7 variants were 66%, 71%, 17%, 51%, 76.2%, 50% and 61% in tumor tissue, respectively; while 16%, 8.4%, 3.38%, 3.38%, 11.8%, 13.5% and 5.08% in the corresponding normal tissue, which was different from the pattern of ΔDNMT3B1-7 expression in NSCLC (62%, 76%, 2.5%, 46%, 18%, 27% and 16% in tumor tissue, respectively; while 18%, 11%, 0%, 3.3%, 0%, 0% and 0% in normal lung tissue, respectively; P<0.0001). Expressions of ΔDNMT3B2, 3B4 and 3B7 were higher in the patients with negative estrogen receptor (ER) than those with positive estrogen receptor (P=0.035, P=0.0141 and P=0.0219, respectively). ΔDNMT3B7 expression was higher for the patients with negative progestogen receptor (PR) compared to those with positive progestogen receptor (P=0.0379). Expression ratio of ΔDNMT3B5 in stage III tumors is lower than that in stage I/II ones (P= 0.041). But we did not find any relation between the ΔDNMT3B variants and the patients’ survival.
Conclusion
The pattern of ΔDNMT3B variants in breast cancer is different from that in NSCLC. Expressions of ΔDNMT3B2, 3B4 and 3B7 are associated with estrogen receptors status. While ΔDNMT3B7 is associated with progestogen receptor. No relation between the ΔDNMT3B variants and the patients’ survival were found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Robertson KD, Uzvolgyi E, Liang G, et al. The human DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs) 1, 3a and 3b: coordinate mRNA expression in normal tissues and overexpression in tumors [J]. Nucleic Acids Res 1999; 27:2291–2298.
Girault I, Tozlu S, Lidereau R, et al. Expression analysis of DNA methyltransferases 1, 3A, and 3B in sporadic breast carcinomas [J]. clin cancer Res 2003; 9:4415–4422.
Oue N, Kuraoka K, Kuniyasu H, et al. DNA methylation status of hMLH1, p16(INK4a), and CDH1 is not associated with mRNA expression levels of DNA methyltransferase and DNA demethylase in gastric carcinomas. [J]. Oncol Rep 2001; 8:1085–1089.
Yakushiji T, Uzawa K, Shibahara T, et al. Over-expression of DNA methyltransferases and CDKN2A gene methylation status in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. [J]. Int J Oncol 2003; 22:1201–1207.
Sato M, Horio Y, Sekido Y, et al. The expression of DNA methyltransferases and methyl-CpG-binding proteins is not associated with the methylation status of p14(ARF), p16(INK4a) and RASSF1A in human lung cancer cell lines. [J]. Oncogene 2002; 21:4822–4829.
wang L, wang J, Sun S, et al. A novel DNMT3B subfamily, DeltaDNMT3B, is the predominant form of DNMT3B in non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Int J Oncol 2006; 29:201–207.
WANG Shu-hang, LIU Ning-hong, WANG Jie, et al. Critical role of ΔDNMT3B4/2 in regulating RASSF1A promoter specific DNA methylation in non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Chin Med J 2008; 121:1712–1721.
Feinberg AP. The epigenetics of cancer etiology [J]. Semin Cancer Biol 2004; 14:427–432.
Herman JG. Epigenetics in lung cancer: focus on progression and early lesions [J]. Chest 2004; 125(5 Suppl):119S–122S
Herman JG, Baylin SB. Gene silencing in cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation [J]. N Engl J Med 2003; 349:2042–2054.
Goffin J, Eisenhauer E. DNA methyltransferase inhibitors-state of the art [J]. Ann Oncol 2002; 13:1699–1716.
Liang G, Chan MF, Tomigahara Y, et al. Cooperativity between DNA methyltransferases in the maintenance methylation of repetitive elements [J]. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22:480–491.
Rhee I, Bachman KE, Park BH, et al. DNMT1 and DNMT3B cooperate to silence genes in human cancer cells [J]. Nature 2002; 416:552–556.
Wang J, Walsh G, Liu DD, et al. Expression of DeltaDNMT3B variants and its association with promoter methylation of p16 and RASSF1A in primary non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Cancer Res 2006; 66:8361–8366.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.30572104, 30772472).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Nh., Yang, L., Zhuo, Ml. et al. Expression of ΔDNMT3B variants and its association with estrogen/progestogen receptor status in breast cancer. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 21, 229–234 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-009-0229-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11670-009-0229-y