Abstract
Purpose
Genotyping of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus for polymorphisms in deltamethrin-resistant loci of sodium channel gene by allele-specific PCR (AS-PCR).
Methods
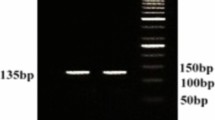
Adult R. (B.) microplus ticks were collected from naturally infested cattle in Kerala. The larval packet test (LPT) was performed with deltamethrin and dose response data were analysed by probit method. Adult and larval tick DNA were amplified by PCR and later sequenced to identify mutations, if any, in the domain II S4-5 linker and domain III S6 regions in para voltage-gated sodium channel gene, at loci that were previously documented to be associated with deltamethrin resistance. Allele-specific PCR was performed for the amplification of target gene locus (C190A and T2134C) to genotype 1000 larvae each, at these loci. Genotype frequency was statistically analysed by Chi-square test.
Results
Bioassay using LPT revealed that LC50 and LC95 values of all the R. (B.) microplus isolates in this study were more than double the reported values of reference susceptible strain. Sequence analysis of the PCR amplicons of domain II S4-5 linker of voltage-gated sodium channel gene revealed C190A mutation, A271G mutation as well as A–G mutation at 217th position. AS-PCR done to genotype C190A mutations revealed a frequency of 6%, 15% and 64%, respectively for homozygous-susceptible (SS), heterozygous (RS) and homozygous-resistant (RR) genotypes. In domain III S6 region of the gene, C2121T and A2102T mutations were observed. AS-PCR to genotype the previously reported T2134C mutation revealed 100% SS genotype in R. (B.) microplus isolates of Kerala.
Conclusions
Genotyping of R. (B.) microplus isolates of Kerala for target site mutations reportedly associated with deltamethrin resistance revealed a significantly high frequency of resistant genotypes at II S4–5 linker of voltage-gated sodium channel gene. This study forms the first report of such mutations in Kerala, south India and demands serious attention in the light of increased prevalence of tick-borne haemoparasitic infection.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
All the data supporting the conclusions of this article are available within the article. The sequences obtained in this study are available in GenBank under the accession numbers MT328784, MT328785, MT328786.
Code Availability
None.
References
Haque M, Singh NK, Rath SS (2014) Effect of various acaricides on hatchability of eggs of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/425423
Rani S, D’Souza PE, Byregowda SM, Veeregowda BM, Sengupta PP, Chandranaik BM, Thimmareddy PM (2018) In vitro acaricidal efficacy of deltamethrin, cypermethrin and amitraz against sheep ticks in Karnataka. Exp Parasitol 201:42–48
Ahmed J, Alp H, Aksin M, Seitzer U (2007) Current status of ticks in Asia. Parasitol Res 101:159–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0696-3
Kumar S, Paul S, Sharma AK, Kumar R, Tewari SS, Chaudhuri P, Ray DD, Rawat AK, Ghosh S (2011) Diazinon resistant status in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus collected from different agro-climatic regions of India. Vet Parasitol 181:274–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.04.030
Abbas RZ, Zaman MA, Colwell DD, Gilleard J, Iqbal Z (2014) Acaricide resistance in cattle ticks and approaches to its management: the state of play. Vet Parasitol 203:6–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.03.006
Singh NK, Haque M, Singh H, Rath SS, Ghosh S (2014) A comparative study on cypermethrin resistance in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus and Hyalomma anatolicum from Punjab (India). Ticks Tick-Borne Dis 5:90–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.08.002
Singh NK, Gelot IS, Bhat SA, Singh H, Singh V (2015) Detection of acaricidal resistance in Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum from Banaskantha district, Gujarat. J Parasit Dis 39:563–566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12639-013-0397-z
FAO (2004) Guidelines resistance management and integrated parasite control in ruminants. FAO, Rome, p 216
McCosker PJ (1979) Global aspects of the management and control of ticks of veterinary importance. Recent Adv Acarol 2:45–53
Ghosh S, Nagar G (2014) Problem of ticks and tick-borne diseases in India with special emphasis on progress in tick control research: a review. J Vector Borne Dis 51:259
Ravindran R, Ramankutty SA, Juliet S, Palayullaparambil AK, Gopi J, Gopalan AK, Nair SN, Ghosh S (2014) Comparison of in vitro acaricidal effects of commercial preparations of cypermethrin and fenvalerate against Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus. Springerplus 3:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-3-90
Du Y, Nomura Y, Zhorov B, Dong K (2016) Sodium channel mutations and pyrethroid resistance in Aedes aegypti. Insects 7:60. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects7040060
Klafke GM, Miller RJ, Tidwell J, Barreto R, Guerrero FD, Kaufman PE, Pérez de Leon AA (2017) Mutation in the sodium channel gene corresponds with phenotypic resistance of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato (Acari: Ixodidae) to pyrethroids. J Med Entomol 54:1639–1642. https://doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjx060
Domingues LN, Brasil BDSAF, de Paiva Bello ACP, da Cunha AP, de Barros ATM, Leite RC, Silaghi C, Pfister K, Passos LMF (2012) Survey of pyrethroid and organophosphate resistance in Brazilian field populations of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus: detection of C190A mutation in domain II of the para-type sodium channel gene. Vet Parasitol 189:327–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.04.031
Yessinou RE, Akpo Y, Adoligbe C, Adinci J, Assogba MN, Koutinhouin B, Karim IY, Farougou S (2016) Resistance of tick Rhipicephalus microplus to acaricides and control strategies. J Entomol Zool Stud 4:408–414
Guerrero FD, Lovis L, Martins JR (2012) Acaricide resistance mechanisms in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet 21:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-29612012000100002
Coles TB, Dryden MW (2014) Insecticide/acaricide resistance in fleas and ticks infesting dogs and cats. Parasite Vector 7:8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-7-8
Vatsya S, Yadav CL (2011) Evaluation of acaricide resistance mechanisms in field populations of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus collected from India. Int J Acarol 37:405–410. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647954.2010.521518
Sharma AK, Kumar R, Kumar S, Nagar G, Singh NK, Rawat SS, Dhakad ML, Rawat AKS, Ray DD (2012) Deltamethrin and cypermethrin resistance status of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus collected from six agro-climatic regions of India. Vet Parasitol 188:337–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.03.050
Shyma KP, Kumar S, Sangwan AK, Sharma AK, Nagar G, Ray DD, Ghosh S (2013) Acaricide resistance status of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus and Hyalomma anatolicum collected from Haryana. Indian J Anim Sci 83:591–594
Jyothimol G, Ravindran R, Juliet S, Ajithkumar KG, Suresh NN, Vimalkumar MB, Lenka DR, Varghese S, Ghosh S (2014) Low level deltamethrin resistance in ticks from cattle of Kerala, a south Indian state. Vet Parasitol 204:433–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.04.028
Kumar S, Sharma AK, Ray DD, Ghosh S (2014) Determination of discriminating dose and evaluation of amitraz resistance status in different field isolates of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus in India. Exp Appl Acarol 63:413–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-014-9789-8
Lenka DR, Ravindran R, Jyothimol G, Udaykumar M, Reddy PMT, Sathish N, Palla I, Chandramohan B, Ajithkumar KG, Nair SN, Chandrasekhar L (2016) Deltamethrin resistance in south Indian isolates of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Vet Parasitol Reg Stud Rep 5:37–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vprsr.2016.09.002
Sen SK, Fletcher TB (1962) Veterinary entomology and acarology in India. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi
Finney DJ (1952) Probit analysis: a statistical treatment of the sigmoid response curve. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Green MR, Sambrook J (2012) Molecular cloning, a Laboratory Manual. Cold spring harbor laboratory press
Klafke GM, Miller RJ, Tidwell JP, Thomas DB, Sanchez D, Arroyo TPF, de León AAP (2019) High-resolution melt (HRM) analysis for detection of SNPs associated with pyrethroid resistance in the southern cattle fever tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Res 9:100–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpddr.2019.03.001
Morgan JA, Corley SW, Jackson LA, Lew-Tabor AE, Moolhuijzen PM, Jonsson NN (2009) Identification of a mutation in the para-sodium channel gene of the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus associated with resistance to synthetic pyrethroid acaricides. Int J Parasitol 39:775–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2008.12.006
Tucker NS, Kaufman PE, Weeks EN, Rowland J, Tidwell J, Miller RJ (2017) Characterization of a sodium channel mutation in permethrin-resistant Rhipicephalus sanguineus (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol 54:1633–1638. https://doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjx127
Lovis L, Guerrero FD, Miller RJ, Bodine DM, Betschart B, Sager H (2012) Distribution patterns of three sodium channel mutations associated with pyrethroid resistance in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus populations from North and South America, South Africa and Australia. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Res 2:216–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpddr.2012.08.001
Stone NE, Olafson PU, Davey RB, Buckmeier G, Bodine D, Sidak-Loftis LC, Giles JR, Duhaime R, Miller RJ, Mosqueda J, Scoles GA (2014) Multiple mutations in the para-sodium channel gene are associated with pyrethroid resistance in Rhipicephalus microplus from the United States and Mexico. Parasit Vectors 7(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-014-0456-z
Kumar R, Nagar G, Sharma AK, Kumar S, Ray DD, Chaudhuri P, Ghosh S (2013) Survey of pyrethroids resistance in Indian isolates of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus: identification of C190A mutation in the domain II of the para-sodium channel gene. Acta Trop 125:237–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2012.10.006
Ghosh S, Kumar R, Nagar G, Kumar S, Sharma AK, Srivastava A, Kumar S, Kumar KA, Saravanan BC (2015) Survey of acaricides resistance status of Rhipiciphalus (Boophilus) microplus collected from selected places of Bihar, an eastern state of India. Ticks Tick-borne Dis 6:668–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2015.05.013
Yessinou RE, Akpo Y, Ossè R, Adoligbe C, Cassini R, Akogbeto M, Farougou S (2018) Molecular characterization of pyrethroids resistance mechanisms in field populations of Rhipicephalus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) in district of Kpinnou and Opkara, Benin. Int J Acarol 44:198–203. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647954.2018.1491623
Bandara KJ, Karunaratne SP (2017) Mechanisms of acaricide resistance in the cattle tick Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus in Sri Lanka. Pesticide Biochem Physiol 139:68–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2017.05.002
Rosario-Cruz R, Guerrero FD, Miller RJ, Rodriguez-Vivas RI, Tijerina M, Dominguez-Garcia DI, Hernandez-Ortiz R, Cornel AJ, McAbee RD, Alonso-Diaz MA (2009) Molecular survey of pyrethroid resistance mechanisms in Mexican field populations of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Parasitol Res 105:1145–1153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-009-1539-1
He H, Chen AC, Davey RB, Ivie GW, George JE (1999) Identification of a point mutation in the para-type sodium channel gene from a pyrethroid-resistant cattle tick. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 261:558–561. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1999.1076
Guerrero FD, Davey RB, Miller RJ (2001) Use of an allele-specific polymerase chain reaction assay to genotype pyrethroid resistant strains of Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol 38:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1603/0022-2585-38.1.44
Sandhu HS (2006) Veterinary pharmacology and Therapeutics. Kalyani publisher, New Delhi
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the technical support of Kerala Veterinary and Animal Sciences University, Pookode, Kerala, India for conducting the research.
Funding
No external grants were received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AA performed the experiment. LB planned the research work and drafted the manuscript. JS provided support for genotyping studies. TVA critically reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
The work has been done as per the guidelines of institutional ethical committee. The article does not contain any experimental studies on animals and the protocols followed using ticks are ethical.
Consent to Participate
The ticks were collected from dogs upon pre-informed consent of clients.
Consent for Publication
The authors guarantee that the work has not been previously published elsewhere and also agreed to the terms and conditions of publications in this journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amrutha, A., Bindu, L., Siju, J. et al. Genotyping of Deltamethrin Resistance in Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus Population in Kerala, South India. Acta Parasit. 66, 1031–1038 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-021-00378-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11686-021-00378-4