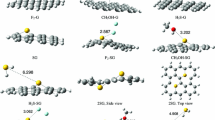
Abstract
Based on first-principles computations, the adsorption ability of hydrogen on heteroatom (B, N)-doped porous graphene has been illustrated. It is found that the adsorption energy (− 0.117 ~ − 0.173 eV) of hydrogen on heteroatom (B, N)-doped porous graphene meets the optimal adsorption energy (− 0.1 ~ − 0.2 eV) on high-performance adsorbent, indicating that the porosity and heteroatom dopant would be the important role for the H2 adsorption. In addition, the interaction is found to be enhanced by applying positive and negative charges into the system. More important, we demonstrate that the adsorption energy can be dramatically increased to − 0.738 eV on the B-doped porous graphene with one positive charge. The H2 adsorption/desorption process on the positively charged B-doped porous graphene is spontaneous, reversible, and readily controlled by injecting/removing the additional positive charge. The gravimetric density is predicted to be 10.8 wt % on the positively charged B-doped porous graphene.
Graphic abstract

Based on density functional theory computations, we investigate the adsorption ability of hydrogen on heteroatom (B, N)-doped porous graphene. Calculation results show that the H2 adsorption/desorption process on the positively charged B-doped porous graphene is spontaneous and reversible with fast kinetics and readily controlled by the adding/removing the additional positive charge.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bieri M, Treier M, Cai JM, Aı¨tMansour K, Ruffieus P, Gro¨ning O, Gro¨ning P, Kastler M, Rieger R, Feng XL, Mu¨llen K, Fasel R (2009) Porous graphenes: two-dimensional polymer synthesis with atomic precision. Chem Commun 45:6919–6921
Bieri M, Nguyen M, Gro¨ning O, Cai JM, Treier M, Aı¨tMansour K, Ruffieus P, Pignedoli C, Passerone D, Kastler M, Mu¨llen K, Fasel R (2010) Two-dimensional polymer formation on surfaces: insight into the roles of precursor mobility and reactivity. J Am Chem Soc 132:16669
Bodrenko IV, Avdeenkov AV, Bessarabov DG, Bibikov AV, Nikolaev AV, Taran MD, Tkalya EV (2012) Hydrogen storage in aromatic carbon ring based molecular materials decorated with alkali or alkali-earth metals. J Phys Chem C 116:25286–25292
Bromley BP (2002) Tomorrow’s energy: hydrogen, fuel cell, and the prospects for a clean plant. Health Phys 82(3):401
Côté AP, Benin AI, Ockwig NW, O’Keeffe M, Matzger AJ, Yaghi OM (2005) Porous, crystalline, covalent organic frameworks. Science 310:1166–117
Delley B (1990) An all-electron numerical method for solving the local density functional for polyatomic molecules. J Chem Phys 92:508
Delley B (2003) From molecules to solids with the DMol3 approach. J Chem Phys 113:7756
Dillon AC, Jones KM, Bekkedahl TA, Klang CH, Bethune DS, Heben MJ (1997) Storage of hydrogen in single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nature 386:377–379
Ding Y, Wang YL, Shi SQ, Tang WH (2011) Electronic structures of porous graphene, BN, and BC2N sheets with one- and two-hydrogen passivations from first principles. J Phys Chem C 115:5334–5343
Du A, Zhu Z, Smith SC (2010) Multifunctional porous graphene for nanoelectronics and hydrogen storage: new properties revealed by first principle calculation. J Am Chem Soc 132:2876–2877
Furukawa H, Yaghi OM (2009) Storage of hydrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide in highly porous covalent organic frameworks for clean energy applications. J Am Chem Soc 131:8875–8883
Furukawa H, Ko N, Go YB, Aratani N, Chio SB, Chio E, Yazaydin AÖ, Snurr RQ, O’Keeffe M, Kim J, Yaghi OM (2010) Ultrahigh porosity in metal-organic frameworks. Science 329:424–428
Grimme S (2006) Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction. J Comput Chem 27:1787–1799
Hehre WJ (1976) Ab initio molecular orbital theory. Acc Chem Res 9:399–406
Heine T, Zhechkov L, Seifert G (2004) Hydrogen storage by physisorption on nanostructured graphite platelets. Phys Chem Chem Phys 6:980–984
Huang H-W, Hsieh H-J, Lin I-H, Tong Y-J, Chen H-T (2014) Hydrogen adsorption and storage in heteroatoms (B, N) modified carbon-based materials decorated with alkali metals: a computational study. J Phys Chem C 119:7662–7669
Hubner O, Gloss A, Fichtner M, Klopper W (2004) On the interaction of dihydrogen with aromatic systems. J Phys Chem A 108:3019–3023
Kim Y, Zhao Y, Williamson A, Heben M, Zhang S (2006) Nondissociative adsorption of H2 molecules in light-element-doped fullerenes. Phys Rev Lett 96:016102
Lee H, Ihm J, Cohen ML, Louie SG (2010) Calcium-decorated graphene-based nanostructures for hydrogen storage. Nano Lett 10:793–798
Lin I-H, Tong Y-J, Hsieh H-J, Huang H-W, Chen H-T (2016) Hydrogen adsorption and storage in boron-substituted and nitrogen-substituted nano-carbon materials decorated with alkaline earth metals. Int J Energy Res 40:230–240
Liu C, Fan YY, Liu M, Cong HT, Cheng HM, Dresselhaus MS (1999) Hydrogen storage in single-walled carbon nanotubes at room temperature. Science 286:1127–1129
Liu Y, Liang C, Wei Z, Jiang Y, Gao M, Pan H, Wang Q (2010) Hydrogenstorage reaction over a ternary imide Li2Mg2N3H3. Phys Chem Chem Phys 12:3108
Mao WL, Koh CA, Sloan ED (2007) Clathrate hydrates under pressure. Phys Today 60:42–47
Monkhorst HJ, Pack JD (1976) Special points for brillouin-zone integrations. Phys Rev B 13:5188–5192
Ning GQ, Xu CG, Mu L, Chen GG, Wang G, Gao J, Fan ZG, Qian WH, Wei F (2012) High capacity gas storage in corrugated porous graphene with a specific surface area-lossless tightly stacking manner. Chem Commun 48:6815–6817
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1996) Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys Rev Lett 77:3865–3868
Reunchan P, Jhi SH (2011) Metal-dispersed porous graphene for hydrogen storage. Appl Phys Lett 98:093103
Rosi NL, Eckert J, Eddaoudi M, Vodak DT, Kim J, O’Keeffe M, Yaghi OM (2003) Hydrogen storage in microporous metal-organic frameworks. Science 300:1127–1129
Sankaran M, Viswanathan B (2006) The role of heteroatoms in carbon nanotubes for hydrogen storage. Carbon 44:2816–2821
Sankaran M, Viswanathan B (2007) Hydrogen storage in boron substituted carbon nanotubes. Carbon 45:1628–1635
Sankaran M, Viswanathan B, Srinivasa Murthy S (2008) Boron substituted carbon nanotubes—how appropriate are they for hydrogen storage? Int J Hydrog Energy 33:393–403
Schlapbach L, Zuttel A (2001) Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications. Nature 414:353–358
Su F, Bray CL, Carter BO, Overend G, Vropper C, Iggo JA, Khimyak YZ, Fogg AM, Cooper AI (2009) Reversible hydrogen storage in hydrogel clathrate hydrates. Adv Mater 21:2382–2386
Tan X, Kou L, Tahini HA, Smith SC (2015) Charge modulation in graphitic carbon nitride as a switchable approach to high-capacity hydrogen storage. ChemsusChem 8:3626–3631
Tan X, Tahini HA, Smith SC (2016) Conductive boron-doped graphene as an ideal material for electrocatalytically switchable and high-capacity hydrogen storage. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:32815–32822
Wang L, Yang RT (2008) New sorbents for hydrogen storage by hydrogen spillover: a review. Energy Environ Sci 1:268–279
Wang L, Yang RT (2009) Hydrogen storage properties of N-doped microporous carbon. J Phys Chem C 113:21883–21888
Wang L, Yang FH, Yang RT (2009) Hydrogen storage properties of B- and N-doped microporous carbon. AIChE J 55:1823–1833
Winter CJ, Nitsch J (1988) Hydrogen as an energy carrier: technologies, systems, economy, 1st edn. Springer, Berlin
Wu X, Gao Y, Zeng XC (2008) Hydrogen storage in pillared li-dispersed boron carbide nanotubes. J Phys Chem C 112:8458–8463
Wu HY, Fan XF, Kuo JL, Deng WQ (2010) Carbon doped boron nitride cages as competitive candidates for hydrogen storage materials. Chem Commun 46:883
Yuan L, Chen Y, Kang L, Zhang C, Wang D, Wang C, Zhang M, Wu X (2017) First-principles investigation of hydrogen storage capacity of Y-decorated porous graphene. Appl Surf Sci 399:463–468
Zhou J, Wang Q, Sun Q, Jena P, Chen XS (2010) Electric field enhanced hydrogen storage on polarizable materials substrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:2801–2806
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST), Taiwan, under Grant Numbers of MOST 110-2113-M-033-009, MOST 109-2113-M-033-001, MOST 108-2113-M-033-001, and MOST 107-2113-M-033-004, and Chung Yuan Christian University (CYCU) for the financial support and the National Center for High-Performance Computing, Taiwan, for the use of facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, CW., Wu, SY. & Chen, HT. The interaction of hydrogen with heteroatoms (B, N)-doped porous graphene: A computational study. Chem. Pap. 76, 1009–1017 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01901-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01901-7