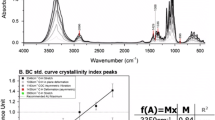
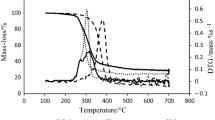
Abstract
Based on the investigation of the polysaccharide structure of cellulose by using Fourier transform spectrum analysis, the pyrolysis behaviour of cellulose was studied at a heating rate of 20 K/min by thermogravimetric (TG) analysis coupled with Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. Experimental results show that the decomposition of cellulose mainly occurs at the temperature range of 550–670 K. The weight loss becomes quite slow when the temperature increases further up to 680 K and the amount of residue reaches a mass percent of 14.7%. The FTIR analysis shows that free water is released first during cellulose pyrolysis, followed by depolymerization and dehydration. Glucosidic bond and carbon-carbon bond break into a series of hydrocarbons, alcohols, aldehydes, acids, etc. Subsequently these large-molecule compounds decompose further into gases, such as methane and carbon monoxide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antal M J, Varhegyi G. Cellulose pyrolysis kinetics: The current state of knowledge. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1995, 34(3): 703–717
Bradbury A W, Sakai Y, Shafizadeh F. A kinetic model for pyrolysis of cellulose. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 1979, 23(11): 3 271–3 280
Fisher T, Hajaligol M, Waymack B, et al. Pyrolysis behavior and kinetics of biomass derived materials. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2002, 62(2): 331–349
Bassilakis R, Carangelo R M, Wojtowicz M A. TG-FTIR analysis of biomass pyrolysis. Fuel, 2001, 80(12): 1 765–1 786
Pan W P, Richards G N. Influence of metal ions on volatile products of pyrolysis of wood. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 1989, 16(2): 117–126
De Jong W, Pirone A, Wojtowicz M A. Pyrolysis of Miscanthus Giganteus and wood pellets: TG-FTIR analysis and reaction kinetics. Fuel, 2003, 82(9): 1 139–1 147
Arthur J C. Cellulose Chemistry and Technology. Washington: American Chemical Society, 1977
Moldoveanu S C. Analytical Pyrolysis of Natural Organic Polymers. New York: ELSEVIER, 1998
Broido A, Nolson M A. Char yield on pyrolysis of cellulose. Combustion and Flame, 1975, 24: 263–268
Liao Y F, Wang S R, Luo Z Y, et al. Research on cellulose rapid pyrolysis. Journal of Zhejiang University: Engineering Science, 2003, 37(5): 582–587, 601 (in Chinese)
Li S, Lyons-Hart J, Banyasz J, et al. Real-time evolved gas analysis by FTIR method: An experimental study of cellulose pyrolysis. Fuel, 2001, 80(12): 1 809–1 717
Shafizadeh F, Lai Y Z, Mcintyre C R. Thermal degradation of 6-chlorocellulose and cellulose-zinc chloride mixture. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 1978, 22(5): 1 183–1 193
Maschio G, Koufopanos C, Lucchesi A. Pyrolysis, a promising route for biomass utilization. Bioresource Technology, 1992, 42(3): 219–231
Koufopanos C A, Maschio G, Lucchesi A. Kinetic modeling of the pyrolysis of biomass and biomass components. Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 1989, 67(1): 75–84
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2006, 40(7): 1 154–1 158 [译自: 浙江大学学报 (工学版)]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Liu, Q., Luo, Z. et al. Mechanism study on cellulose pyrolysis using thermogravimetric analysis coupled with infrared spectroscopy. Front. Energy Power Eng. China 1, 413–419 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-007-0060-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-007-0060-8