Abstract
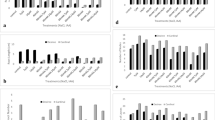
The effect of auxin, GA and BAP on potato shoot growth and tuberization was investigated under in vitro condition. The shoot length of potato explants increased with the increasing of concentrations (0.5 – 10 mg dm−3) of IAA treatment especially with the addition of GA3 (0.5 mg dm−3), but was inhibited by BAP (5 mg dm−3). The root number and root fresh weight of potato explants increased with the increasing of IAA levels either in the presence of GA3 (treatment IAA+GA) or not (IAA alone). However, no root was observed in the treatment IAA+BAP, instead there were brown swollen calli formed around the basal cut surface of the explants. The addition of GA3 remarkably increased the fresh weight and diameter of calli. Microtubers were formed in the treatments of IAA+BAP and IAA + GA + BAP but not observed in the treatments of IAA alone or IAA + GA. IAA of higher concentrations (2.5 – 10 mg dm−3) was helpful to form sessile tubers. With the increasing of IAA levels, the fresh weight and diameter of microtubers increased progressively. At 10 mg/L IAA, the fresh weight and diameter of microtubers in the treatment of IAA + GA + BAP were 409.6 % and 184.4 % of that in the treatment of IAA + BAP respectively, indicating the interaction effect of GA and IAA in potato microtuberization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Estrada R., Tovar P., Dodds J. H. 1986. Induction of in vitro tubers in a broad range of potato genotypes. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult., 7: 3–10.
FAO. 1995. Potatoes in the 1990s. Situations and Prospects of World Potato Economy. Publ. No. M-71, FAO, Rome: 39.
Haga K., Iino M. 1998. Auxin-growth relationships in maize coleoptiles and pea internodes and control by auxin of the tissue sensitivity to auxin. Plant Physiol., 117: 1473–1486.
Harvey B. M. R., Crothers S. H., Evans N. E., Selby C. 1991. The use of growth retardants to improve microtuber formation by potato (Solanum tuberosum). Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult., 27: 59–64.
Hooley R. 1994. Gibberellins: perception, transduction and responses. Plant Mol. Biol., 26: 1529–1555.
Hussey G., Stacey N. J. 1984. Factors affecting the formation of in vitro of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Ann. Bot., 53: 565–578.
Kende H., Zeevaart J. A. D. 1997. The five ‘classical’ plant hormones. Plant Cell 9: 1197–1210.
Lopez-Delgado H., Scott I. M. 1997. Induction of in vitro tuberization of potato plants by acetylsalicylic acid. J. Plant Physiol., 151: 74–78.
Mauk C. S., Langille A. R. 1978. Physiology of tuberization in Solanum tuberosum L. Plant Physiol., 62: 438–442.
Menzel C. M. 1980. Tuberization in potato at high temperatures: response to gibberellin and growth inhibitors. Ann. Bot., 46: 259–265.
Murashige T., Skoog F. 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant., 15: 473–479.
Obata-Sasamoto H., Suzuki H. 1979. Activities of enzymes relating to starch synthesis and endogenous levels of growth regulators in potato stolon tips during tuberization. Physiol. Plant., 45: 320–324.
Palmer C.E., Smith O. E. 1969. Cytokinins and tuber initiation in the potato Salanum tuberosum L. Nature, 221: 279–280.
Radmacher W. 2000. Growth retardants: effects on gibberellin biosynthesis and other metabolic pathways. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 51: 501–531.
Ross J. J., O’Neill D. P. 2001. New interactions between classical plant hormones. Trends Plant Sci., 6: 2–4.
Ross J. J., O’Neill D. P., Smith J. J., Kerckhoffs L. H. J., Elliott R. C. 2000. Evidence that auxin promotes gibberellin A1 biosynthesis in pea. Plant J., 21: 547–552.
Ross J. J., O’Neill D. P., Wolbang C. M., Symons G. M., Reid J. 2002. Auxin — Gibberillin interactions and their role in plant growth. J. Plant Growth Regul., 20: 346–353.
Sharma N., Kaur N., Gupta A. K. 1998. Effects of gibberellic acid and chlorocholine chloride on tuberisation and growth of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). J. Sci. Food Agric., 78: 466–470.
SPSS. 1999. SPSS for Windows, version 10.0, SPSS Inc, Chicago, 233S, Wacker Drive, Chicago, Illinois, USA.
Struik P. C., Vreugdenhil D., Vaneck H. J., Bachem C. W., Visser R. G. F. 1999. Physiological and genetic control of tuber formation. Potato Res., 42: 313–331.
Tang G. X., Zhou W. J., Li H. Z., Mao B. Z., He Z. H., Yoneyama K. 2003. Medium, explant and genotype factors influencing shoot regeneration in oilseed Brassica spp. J. Agron. Crop Sci., 189: 351–358.
Vreugdenhil D., Struik P. C. 1989. An intergrated view of the hormonal regulation of tuber formation in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Physiol. Plant., 75: 525–531.
Yang, T., Davies, P. J., Reid J. B. 1996. Genetic dissection of the relative roles of auxin and gibberellin in the regulation of stem elongation in intact light grown peas. Plant Physiol., 110: 1029–1034.
Zhang G. Q., Zhou W. J., Gu H. H., Song W. J., Momoh E. J. J. 2003. Plant regeneration from the hybridization of Brassica napus and B. juncea through embryo culture. J. Agron. Crop Sci., 189: 347–350.
Zhang Z. J., Li H. Z., Li Z. M., Zhou W. J. 2003. Effect of jasmonic acid on explant growth and tuberization in potato. In: Research and Industrial Exploitation of Potato in China, ed. by Chen Y. L., D. Y. Qu. Harbin Engineering University Press, Harbin: 158–163.
Zhou W. J., Yoneyama K., Takeuchi Y., Iso S., Rungmekarat S., Chae S. H., Sato D., Joel D. M. 2004. In vitro infection of host roots by differentiated calli of the parasitic plant Orobanche. J. Exp. Bot., 55: 899–907.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Zhou, W. & Li, H. The role of GA, IAA and BAP in the regulation of in vitro shoot growth and microtuberization in potato. Acta Physiol Plant 27, 363–369 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-005-0013-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-005-0013-7