Abstract
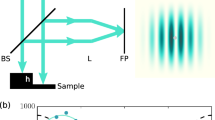
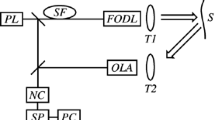
A profilometer used for 3 dimension measurement of micro-surface topography is presented. The instrument is based on the vertical scanning microscopic interferometry (VSMI). A Linnik type interference microscope is used and the interferograms which present changes of surface profile are recorded with a CCD camera. A developed nano-positioning work stage with an integrated optical grating displacement measuring system realizes the precise vertical scanning motion during profile measurement. By a white-light phase shifting algorithm of arbitrary step, frames of interferograms are processed by a computer to rebuild and evaluate the measured profile. Because of the specialty of VSMI, the profilometer is suitable for both smooth and rough surface measurement. It can also be used to measure curved surfaces, dimension of micro electro mechanical systems (MEMS), etc. The vertical resolution of the profilometer is 0.5 nm, and lateral resolution 0.5 μm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
James C W. Advance in interferometric metrology [C]//Optical Design and Testing, Shanghai. [S.l.]: SPIE, 2002, 4927: 154–162.
Kitagawa K. Recent trends in white-light interferometry [C]//Two-and Three-Dimensional Methods for Inspection and Metrology IV, Boston, MA. [S.l.]: SPIE, 2006, 6382: 134–141.
Wyko NT9100 optical profiler [EB/OL]. [2007-05-07]. http://www.veeco.com.cn/products/details.php?cat=1 & sub=5 & pid=379.
Caber P J, Martinek S J, Niemann R J. A new interferometric profiler for smooth and rough surfaces [C]//Laser Dimensional Metrology: Recent Advances for Industrial Application, Brighton. [S.l.]: SPIE, 1993, 2088: 195–203.
Gordon S K, Stanley S C C. Mirau correlation microscope [J]. Applied Optics, 1990, 29(26): 3775–3783.
Pavel P, Jan S. Theoretical measurement uncertainty of white-light interferometry on rough surfaces [J]. Applied Optics, 2003, 42(10): 1809–1813.
Peter de G, Xavier C de L, Jim K, et al. Determination of fringe order in white-light interference microscopy [J]. Applied Optics, 2002, 41(22): 4571–4578
Larkin K G. Efficient nonlinear algorithm for envelop detection in white light interferometry [J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1996, 13(4): 832–843.
Mark M, Scott B. Error sources and algorithms for white-light fringe estimation at low light levels [J]. Applied Optics, 2002, 41(14): 2655–2671.
ZHANG Hongxia. Research of Nanometer Whitelight Phase-shifting Interferometry and Instrumentation Used for Micro-surface Topography Measurement [D]. Doctoral Dissertation, Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2006 (in Chinese).
HE Yonghui, JIANG Jianfeng, ZHAO Wansheng. Surface 3D profiler based on scanning white light interferometry method [J]. Optical Technology, 2001, 27(2): 150–155 (in Chinese).
Stoilov G, Dragostinov T. Phase-stepping interferometry: five-frame algorithm with an arbitrary step [J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 1997, 28(1): 61–69.
LI Qingxiang, WANG Dongshen, LI Yuhe. Modern Precision Mechanism Design [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2004 (in Chinese).
DAI R, XIE T B, CHANG S. A micro-displacement stage for scanning white-light interferometry [C]//The 7th International Symposium on Measurement Technology and Intelligent Instruments, Huddersfield. [S.l.]: IOP Publishing, 2005, 13: 94–97.
CHEN Jianqiao. Material Mechanics [M]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2001 (in Chinese).
JIANG Xianqian, XIAO Saojun, XIE Tiebang, et al. Application of grating technology in nanometer measurement [J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 1995, 16(1): 374–377 (in Chinese).
MAO Qiguang. The Measurement and Evaluation of Surface Roughness [M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 1991 (in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.50175037)
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, R., Xie, Tb., Gong, W. et al. A high precision profilometer based on vertical scanning microscopic interferometry. J. Shanghai Univ.(Engl. Ed.) 12, 255–260 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11741-008-0312-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11741-008-0312-2