Abstract
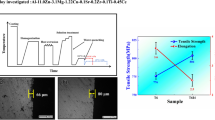
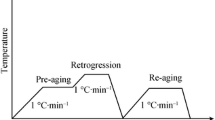
The mechanical properties and stress corrosion cracking (SCC) resistance of an Al-Zn-Cu-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy under different aging conditions were investigated. The dependence of microstructure and mechanical properties on aging parameters was evaluated by tensile test, hardness test and conductivity measurement. The results show that for the alloys with retrogression and re-aging treatment (RRA), the conductivity increases with the retrogression time and temperature, while the tensile strength decreases. The transmission electron microscopy (TEM) results show that the precipitates η(MgZn2) at grain boundary aggregate apparently with retrogression time and the precipitates inside the matrix exhibit the similar distribution to T6 temper, which comprises fine GP zones, large η′(MgZn2) and η(MgZn2) phases. According to the mechanical properties and microstructure observations, the optimal RRA regime is recommended to be 120 °C, 24 h + 180 °C, 30 min + 120 °C, 24 h. The strength level of the alloy after the optimum RRA treatment is similar to that in T6 condition and the SCC resistance is improved obviously in contrast to T6 condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
KIM K T, KIM J M, SUNG K D, JUN J H, JUNG W J. Effect of alloying elements on the strength and casting characteristics of high strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys [J]. Materials Science Forum, 2005, 475/476/477/478/479(3): 2539–2542.
YOU Jiang-hai, LIU Sheng-dan, ZHANG Xin-ming, ZHANG Xiao-yan. Influence of quench transfer time on microstructure and mechanical properties of 7055 aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2008, 15(2): 153–158.
NING Ai-lin, LIU Zhi-yi, PENG Bai-shan, ZENG Su-min. Redistribution and re-precipitation of solute atom during retrogression and reaging of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2007, 17(5): 1005–1011.
SENKOV O N, BHAT R B, SENKOVA S V, SCHLOZ J D. Microstructure and properties of cast ingots of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys modified with Sc and Zr [J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2005, 36(8): 2115–2126.
FENG Chun, LIU Zhi-yi, NING Ai-lin, LIU Yan-bin, ZENG Su-min. Retrogression and re-aging treatment of Al-9.99%Zn-1.72%Cu-2.5%Mg-O.13%Zr aluminum alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16(5): 1163–1170.
HE Yong-dong, ZHANG Xin-ming, YOU Jiang-hai. Effect of minor Sc and Zr on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16(5): 1228–1235.
COSTELLO F A, ROBSON J D, PRANGNELL P B. The effect of small scandium additions to AA7050 on the as-cast and homogenized microstructure [J]. Materials Science Forum, 396/402: 757–762.
YUAN Zhi-shan, LU Zheng, XIE You-hua, DAI Sheng-long, LIU Chang-sheng. Effects of RRA treatments on microstructures and properties of a new high-strength aluminum-lithium alloy—2A97 [J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2007, 20(2): 187–192.
CINA B. Reducing the susceptibility of alloy, particular aluminum alloys to stress corrosion cracking: US Patent 3856584 [P]. 1974.
NORMAN A F, HYDE K, COSTELLO F, THOMPSON S, BIRLEY S, PANGNELL P B. Examination of the effect of Sc on 2000 and 7000 series aluminium alloy castings: For improvements in fusion welding [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2003, 354(1/2): 188–198.
LI Hong-ying, GENG Jin-feng, DONG Xian-juan, WANG Chang-jian, ZHENG Feng. Effect of aging on fracture toughness and stress corrosion cracking resistance of forged 7475 aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology: Materials Science Edition, 2007, 22(2): 191–195.
OLIVEIRA A F, DE BARROS M C, CARDOSO K R, TRAVESSA D N. The effect of RRA on the strength and SCC resistance on AA7050 and AA7150 aluminum alloys [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 379(1/2): 321–326.
LI Wen-bin, PAN Qing-lin, ZOU Liang, LIANG Wen-jie, HE Yun-bin, LIU Jun-sheng. Effects of minor Sc on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr based alloys [J]. Rare Metals, 2009, 28(1): 102–106.
LI Wen-bin, PAN Qing-lin, LIU Jun-sheng, LIU Xiao-yan, GUO Yun-shu, ZHANG Xin-ming. Optimum retrogression and reaging heat treatment of super-high strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy containing Sc [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2009, 19(9): 1533–1538. (in Chinese)
BUHA J, LUMLEY R N, CROSKY A G. Secondary ageing in an aluminium alloy 7050 [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 492(1/2): 1–10.
FENG Chun, LIU Zhi-yi, NING Ai-lin, ZENG Su-min. Effect of retrogression and reaging treatment on stress corrosion cracking resistance of super high strength aluminum alloy [J]. Journal of Central South University: Science and Technology, 2006, 37(6): 1054–1059. (in Chinese)
REDA Y, ABDEL-KARIM R, ELMAHALLAWI I. Improvements in mechanical and stress corrosion cracking properties in Al-alloy 7075 via retrogression and reaging [J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008, 485(1/2): 468–475.
ZHENG Zi-qiao, LI Hong-ying, MO Zhi-min. Retrogression and reaging treatment of a 7055 type aluminum alloy [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2001, 11(5): 771–776.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Project(2006AA03Z523) supported by the National High-tech Research and Development Program of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Wb., Pan, Ql., Xiao, Yp. et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Zn-Cu-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy after retrogression and re-aging treatments. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 18, 279–284 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-011-0691-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-011-0691-9