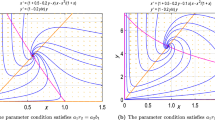
Abstract
We investigate the effect of dispersal and spatial heterogeneity of the environment on the dynamics of a predator–prey model. In contrast with the homogeneous environment, the dynamics of the model in spatially heterogeneous environment is more complex. For instance, for certain ranges of death and dispersal rates of the predator, the semi-trivial steady state of the model in the heterogeneous case could change its stability multiple times as the dispersal rate of the prey varies from small to large, whereas the stability of the semi-trivial steady state is unaffected by the dispersal rates of the predator and prey in the homogeneous case.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Averill, I., Lam, K.-Y., Lou, Y.: The role of advection in a two-species competition model: a bifurcation approach. Mem. Am. Math. Soc. 245(1161) (2017) (in press)
Bai, X.L., He, X.Q., Li, F.: An optimization problem and its application in population dynamics. Proc. AMS 144, 2161–2170 (2016)
Cantrell, R.S., Conser, C.: Diffusive logistic equations with indefinite weights: population models in disrupted environments. Proc. R. Soc. Edin. Sect. A 112, 293–318 (1989)
Cantrell, R.S., Conser, C.: The effects of spatial heterogeneity in population dynamics. J. Math. Bio. 29, 315–338 (1991)
Cantrell, R.S., Conser, C.: Spatial Ecology via Reaction-diffusion Equations. Series in Mathematical and Computational Biology. Wiley, Chichester (2003)
Cantrell, R.S., Conser, C., Hutson, V.: Permanence in ecological systems with spatial heterogeneity. Proc. R. Soc. Edin. Sect. A 123, 533–559 (1993)
Cosner, C.: Reaction-diffusion-advection models for the effects and evolution of dispersal. Discr. Cont. Dyn. Syst. 34, 1701–1745 (2014)
Chen, X.F., Hambrock, R., Lou, Y.: Evolution of conditional: a reaction-diffusion-advection model. J. Math. Biol. 57, 3687–3703 (2008)
Cui, R.H., Lou, Y.: Spatial SIS epidemic models in advective environments. J. Differ. Equations 261, 3305–3343 (2016)
Dancer, E.N., Du, Y.H.: Effects of certain degeneracies in the predator-prey model. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 34, 292–314 (2002)
DeAngelis, D., Ni, W.-M., Zhang, B.: Dispersal and spatial heterogeneity: single species. J. Math. Biol. 72, 239–254 (2016)
Du, Y.H., Hsu, S.B.: A diffusive predator-prey model in heterogeneous environment. J. Differ. Equations 203, 331–364 (2004)
Y.H. Du, J.P. Shi, Some recent results on diffusive predator-prey models in spatially heterogeneous envionment. In: Nonlinear Dynamics and Evolution Equations, in: Fields Inst. Commun., vol. 48, pp. 95–135. American Mathematical Society, Providence, R.I. (2006)
Du, Y.H., Shi, J.P.: Allee effect and bistability in a spatially heterogenous predator-prey model. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 359, 4557–4593 (2007)
He, X.Q., Ni, W.M.: The effects of diffusion and spatial variation in Lotka-Volterra competition-diffusion system I: Heterogeneity vs. homogeneity. J. Differ. Equations 254, 528–546 (2013)
He, X.Q., Ni, W.-M.: The effects of diffusion and spatial variation in Lotka-Volterra competition-diffusion system II: The general case. J. Differ. Equations 254, 4088–4108 (2013)
He, X.Q., Ni, W.-M.: Global dynamics of the Lotka-Volterra competition-diffusion system: Diffusion and spatial heterogeneity. I. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 69, 981–1014 (2016)
Lam, K.-Y., Lou, Y., Lutscher, F.: The emergence of range limits in advective environments. SIAM J. Appl. Math 76, 641–662 (2016)
Lam, K.-Y., Lou, Y., Lutscher, F.: Evolution of dispersal in closed advective environments. J. Biol. Dyn. 9(Supplement 1), 188–212 (2015)
Lam, K.-Y., Ni, W.-M.: Uniquenss and complete dynamics of the Lotka-Volterra competition diffusion system. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 72, 1695–1712 (2012)
Liang, S., Lou, Y.: On the dependence of population size upon random dispersal rate. Discr. Cont. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B. 17, 2771–2788 (2012)
Lou, Y.: On the effects of migration and spatial heterogeneity on single and multiple species. J. Differ. Equations 223, 400–426 (2006)
Lou, Y.: Some challenging mathematical problems in evolution of dispersal and population dynamics. In: Friedman, A. (ed.) Tutor. Math. Biosci. vol IV: Evolution and Ecology, Lect. Notes Mathematics vol. 1922, pp. 171–205. Springer, New York (2007)
Lou, Y.: Some reaction diffusion models in spatial ecology. Sci. Sin. Math. 45(10), 1619–1634 (2015)
Medvinsky, A.B., Petrovskii, S.V., Tikhonova, I.A., Malchow, H., Li, B.-L.: Spatiotemporal complexity of plankton and fish dynamics. SIAM Rev. 44, 311–370 (2002)
W.-M. Ni, The Mathematics of Diffusion, CBMS-NSF Regional Conf. Ser. In: Appl. Math. vol. 82. SIAM, Philadelphia (2011)
Peng, R., Shi, J.P.: Non-existence of non-constant positive steady states of two Holling type-II predator-prey systems: strong interaction case. J. Differ. Equations 247, 866–886 (2009)
Wang, J.F., Wei, J.J., Shi, J.P.: Global bifurcation analysis and pattern formation in homogeneous diffusive predator-prey systems. J. Differ. Equations 260, 3495–3523 (2016)
Yi, F.Q., Wei, J.J., Shi, J.P.: Bifurcation and spatiotemporal patterns in a homogeneous diffusive predator-prey system. J. Differ. Equations 246, 1944–1977 (2009)
Acknowledgments
We thank the referee for his helpful comments and suggestions. We thank Dr. Renhao Cui for his help with the figures and Ms. Rui Li for her helpful comments. This research is partially supported by NSFC Grants Nos. 11571364 and 11571363 (YL), NSF Grant DMS-1411476 (YL) and China Scholarship Council (BW). Part of this work was done during the visit of YL to Tokyo Institute of Technology and the visit of BW to Ohio State University. We thank both institutions for the hospitality.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor Paul Rabinowitz on the occasion of his 77th birthday.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, Y., Wang, B. Local dynamics of a diffusive predator–prey model in spatially heterogeneous environment. J. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 19, 755–772 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11784-016-0372-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11784-016-0372-2