Abstract
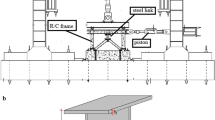
Isolation bearings and dampers are often installed between piers and superstructures to reduce the seismic responses of bridges under large earthquakes. This paper presents a novel steel damper for bridges. The damper employs steel plates as energy dissipation components, and adopts a vertical free mechanism to achieve a large deformation capacity. Quasi-static tests using displacement-controlled cyclic loading and numerical analyses using a finite element program called ABAQUS are conducted to investigate the behavior of the damper, and a design methodology is proposed based on the tests and numerical analyses. Major conclusions obtained from this study are as follows: (1) the new dampers have stable hysteresis behavior under large displacements; (2) finite element analyses are able to simulate the behavior of the damper with satisfactory accuracy; and (3) simplified design methodology of the damper is effective.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai KQ and Huang LZ (2002), “The Design and Application of the TADAS Structure,” Progress in Steel Building Structure, 4(2): 16–23. (in Chinese)
CCCC Highway Consultants CO., Ltd (2004), General Code f or Design of Highway Bridges and Culverts, JTG D60-2004. (in Chinese)
Chen G, Mu H and Bothe ER (2001), Metallic Dampers for Seismic Design and Retrofit of Brid ges, University of Missouri.
Clark PW, Aiken ID, Kasai K, Ko E and Kimura I (1999), “Design Procedures for Buildings Incorporating Hysteretic Damping Devices,” in Proc. Int.-Post-SMiRT Conf. Seminar on Seismic Isolation, Passive Energy Dissipation and Active Control of Vibrations of Structures, Cheju, South Korea.
Li XM (1989), “Optimization of the Stochastic Response of a Bridge Isolation System with Hysteretic Dampers,” Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 18(7): 951–964.
Liu LB (2009), “Bridge Design Concepts and Methods of Seismic and Wind Resistent,” Ph.D Thesis, Chang’an University. (in Chinese)
Maleki S and Bagheri S (2010), “Pipe Damper, Part II: Application to Bridges,” Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 66(8): 1096–1106.
Ministry of Construction of the People Republic of China (2003), Code for Design of Steel Structures, GB50017-2003. (in Chinese)
Ministry of Housing and Urban-rural Development of the People Republic of China (2012), Technical Specification for Building with Energy Dissipa tion Devices, JGJ xxx-2012 (in Chinese and in publication).
Pan P, Yan H, Cao HY and Wang T (2011), “Development of S teel Dampers for Bridges,” 2011 International Conference on Electric Technology and Civil Engineering (ICETCE), IEEE, 231–234.
Sun F, Zhou Y, Yu GH and Li XP (1999), “Experimental Study of Properties of Added Stiffness Circular Ring Energy Dissipater,” Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 19(3): 116–120. (in Chinese)
Tsai KC, Chen HW, Hong CP and Su YF (1993), “Design of S teel Triangular Plate Energy Absorbers for S eismic-Resistant Construction,” Earthquake Spectra, 9(3): 505–528.
Yasushi K, Mitsuo S and Toshikazu Y (1998), “Structural Design of a Tall Building with Elastic-plastic Steel Dampers for the Attenuation of Torsional and Lateral Motions,” Structure Design Tall Build, 7: 21–32.
Zhang JP, Li XP and Zhou FL (1998), “Development of Brid ge Vibration Control and its Existing Problems,” World Information on Earthquake Engineering, 14(2): 9–16. (in Chinese)
Zhang LH (2007), “The Comparative Studies on Seismic Dam age Prediction Methods of Bridge Structure,” Ph.D Thesis, Dalian University of Technology. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by: Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 51178250 and 51261120377 and Tsinghua University of China under Grant No. 2010Z01001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, P., Yan, H., Wang, T. et al. Development of steel dampers for bridges to allow large displacement through a vertical free mechanism. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 13, 375–388 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11803-014-0249-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11803-014-0249-6