Abstract
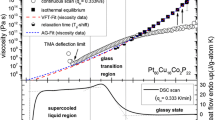
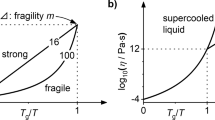
Bulk metallic glass-forming liquids are alloys with typically three to five metallic components that have a large atomic-size mismatch and a composition close to a deep eutectic. They are dense liquids with small free volumes and viscosities that are several orders of magnitude higher than in pure metals or previously known alloys. In addition, these melts are energetically closer to the crystalline state than other metallic melts due to their high packing density in conjunction with a tendency to develop short-range order. These factors lead to slow crystallization kinetics and high glass-forming ability. Crystallization kinetics is very complex, especially in the vicinity of the glass transition, due to the influence of phase separation and the decoupling of the diffusion constants of the different species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Inoue, T. Zhang, and T. Masumoto, Mater. Trans. JIM, 31 (1991), p. 425.
T. Zhang, A. Inoue, and T. Masumoto, Mater. Trans. JIM, 32 (1991), p. 1005.
A. Inoue et al., Mater. Trans. JIM, 32 (1991), p. 609.
A. Peker and W. L. Johnson, Appl. Phys. Lett., 63 (1993), p. 2342.
W.L. Johnson, MRS Bull., 24 (1999), p. 42.
W. Klement, R. Willens, and P. Duwez, Nature, 187 (1960), p. 869.
H.S. Chen and D. Tumbull, J. Chem. Phys., 48 (1968), p. 2560.
H.S. Chen and D. Turnbull, Acta Metall., 17 (1969), p. 1021.
R.W. Cahn, Mater. Sci. Technol., vol. 9, ed. R.W. Cahn, P. Haasen, and E. Kramer (Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH, 1991).
Y.J. Kim et al., Appl. Phys Lett., 68 (1996), p. 1057.
A. Masuhr et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 82 (1999), p. 2290.
D. Turnbull, J. Appl. Phys., 21 (1950), p. 1022.
C.V. Thompson and F. Spaepen, Acta Metall., 27 (1979), p. 1855.
K.S. Dubey and P. Ramachandrarao, Acta Metall., 32 (1984), p. 323.
L. Battezzati and E. Garrone, Z. Metallkde, 75 (1984), p. 305.
R. Bormann and K. Zöltzer, Phys. Stat. Sol., 131 (1992), p. 691.
R. Busch, unpublished.
M.C. Lee et al., Mater. Sci. Eng., 89 (1988), p. 301.
R. Busch, Y.J. Kim, and W.L. Johnson, J. Appl. Phys., 77 (1995), p. 4039.
R. Busch, W. Liu, and W.L. Johnson, J. Appl. Phys., 83 (1998), p. 4134.
G. Wilde et al., Appl. Phys. Lett., 65 (1994), p. 397.
I.R. Lu et al., J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 252 (1999), p. 577.
S.C. Glade et al., J. Appl. Phys., 87 (2000), p. 7242.
F. Gärtner, private communication.
K. Ohsaka et al., Appl. Phys. Lett., 70 (1997), p. 726.
S.S. Tsao and F. Spaepen, Acta Metall., 33 (1985), p. 1355.
C.A. Volkert and F. Spaepen, Acta Metall., 37 (1989), p. 1355.
E. Bakke, R. Busch, and W.L. Johnson, Appl. Phys. Lett., 67 (1995), p. 3260.
R. Busch, E. Bakke, and W.L. Johnson, Acta Mater., 46 (1998), p. 4725.
T.A. Waniuk et al., Acta Mater., 46 (1998), p. 5229.
C.A. Angell, Science, 267 (1995), p. 1924.
G.S. Grest and M.H. Cohen, Adv. Chem. Phys., 48 (1981), p. 455.
C.A. Angell, B.E. Richards, and V. Velikov, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter., 11 (1999), p. A75.
A. Meyer et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 80 (1998), p. 4454.
A. Meyer, R. Busch, and H. Schober, Phys. Rev. Lett., 85 (1999), p. 5027.
M. Weiss, M. Moske, and K. Samwer, Appl. Phys. Lett., 69 (1996), p. 3200.
K. Samwer, R. Busch, and W.L. Johnson, Phys. Rev. Lett., 82 (1999), p. 580.
M.K. Miller et al., J. de Physique IV, 6 (C5) (1996), p. 217.
R. Busch et al., Appl. Phys. Lett., 67 (1995), p. 1544.
S. Schneider, P. Thiyagarajan, and W.L. Johnson, Appl. Phys. Lett., 68 (1996), p. 493.
F. Faupel, P.W. Hüppe, and K. Rätzke, Phys. Rev. Lett., 65 (1990), p. 1219.
K. Rätzke, P.W. Hüppe, and F. Faupel, Phys. Rev. Lett., 68 (1992), p. 2347.
U. Geyer et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 75 (1995), p. 2364.
F. Wenwer et al., Defect and Diffusion Forum, 143–147 (1997), p. 831.
E. Budke et al., Defect and Diffusion Forum, 143–147 (1997), p. 825.
H. Ehmler et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 80 (1998), p. 4919.
W.L. Johnson, Prog. Mat. Sci., 30 (1986), p. 81.
A.L. Greer, N. Karpe, and J. Bottiger, J. Alloys and Compounds, 194 (1993), p. 199.
U. Geyer et al., Appl. Phys. Lett., 69 (1996), p. 2492.
X.P. Tang et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 81 (1998), p. 5358.
X.P. Tang et al., Nature, 402 (1999), p. 160.
R. Busch et al., Appl. Phys. Lett., 67 (1996), p. 1544.
S. Schneider, P. Thiyagarajan, and W.L. Johnson, Appl. Phys. Lett., 68 (1996), p. 493.
W.H. Wang et al., Appl. Phys. Lett., 71 (1997), p. 1053.
W.H. Wang, Q. Wei, and S. Friedrich, Phys. Rev. B, 57 (1998), p. 8211.
J. Schroers et al., Phys. Rev. B, 60 (1999), p. 11855.
J. Schroers et al., Appl. Phys. Lett., 76 (2000), p. 2343.
K.F. Kelton, Philos. Mag. Lett., 77 (1997), p. 337.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Editor’s Note: A hypertext-enhanced version of this article is available on-line at www.tms.org/pubs/journals/JOM/0007/Busch-0007.html.
For more information, contact R. Busch, Oregon State University, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Rogers Hall 204, Corvallis, Oregon 97331; (541) 737-2648; fax (541) 737-2600; e-mail ralf.busch@orst.edu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Busch, R. The thermophysical properties of bulk metallic glass-forming liquids. JOM 52, 39–42 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-000-0160-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-000-0160-7