Abstract
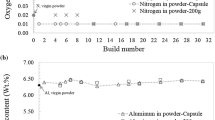
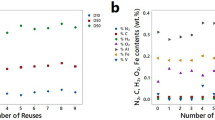
An advantage of the powder-bed-based metal additive manufacturing (AM) processes is that the powder can be reused. The powder reuse or recycling times directly affect the affordability of the additively manufactured parts, especially for the AM of titanium parts. This study examines the influence of powder reuse times on the characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V powder, including powder composition, particle size distribution (PSD), apparent density, tap density, flowability, and particle morphology. In addition, tensile samples were manufactured and evaluated with respect to powder reuse times and sample locations in the powder bed. The following findings were made from reusing the same batch of powder 21 times for AM by selective electron beam melting: (i) the oxygen (O) content increased progressively with increasing reuse times but both the Al content and the V content remained generally stable (a small decrease only); (ii) the powder became less spherical with increasing reuse times and some particles showed noticeable distortion and rough surfaces after being reused 16 times; (iii) the PSD became narrower and few satellite particles were observed after 11 times of reuse; (iv) reused powder showed improved flowability; and (v) reused powder showed no measurable undesired influence on the AM process and the samples exhibited highly consistent tensile properties, irrespective of their locations in the powder bed. The implications of these findings were discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM F3049-14, Standard Guide for Characterizing Properties of Metal Powders Used for Additive Manufacturing Processes (West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM, 2014).
AMETEK Inc., Metal Powders, http://www.readingalloys.com/Products/Metal-Powders.aspx.
J. Withers, J. Laughlin, and R. Loutfy (Paper presented at PM2014 World Congress, Orlando, FL, 2014).
X. Lu, C.C. Liu, L.P. Zhu, and X.H. Qu, Powder Tech. 254, 235 (2014).
Y.Y. Sun, S. Gulizia, C.H. Oh, C. Doblin, Y.F. Yang, and M. Qian, JOM 67 (2015), doi:10.1007/s11837-015-1301-3.
S.M. Gaytan, L.E. Murr, F. Medina, E. Martinez, M.I. Lopez, and R.B. Wicker, Mater. Tech. 24, 180 (2009).
J.A. Slotwinski, E.J. Garboczi, P.E. Statzman, C.F. Ferraris, S.S. Watson, and M.A. Peltz, J. Res. NIST 119, 460 (2014).
ASTM F3001-14, Standard Specification for Additive Manufacturing Titanium-6 Aluminum-4 Vanadium ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) with Powder Bed Fusion (West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM, 2014).
ASTM F2924-14, Standard Specification for Additive Manufacturing Titanium-6 Aluminum-4 Vanadium with Powder Bed Fusion (West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM, 2014).
H.B. Qi, Y.N. Yan, F. Lin, W. He, and R.J. Zhang, Proc. Inst. Mechan. Eng. Part B 220, 1845 (2006).
ASTM B215, Practices for Sampling Metal Powders (West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM, 2015).
ISO 4490:2001, Metallic Powders—Determination of Flow Time by Means of a Calibrated Funnel (Hall Flowmeter) (Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization).
ISO 3923-1:2008, Metallic Powders—Determination of Apparent Density (Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization).
ISO 3953:1993, Metallic Powders—Determination of Tap Density (Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization).
ISO 2738:1999, Sintered Metal Materials, Excluding Hardmetals—Permeable Sintered Metal Materials—Determination of Density, Oil Content and Open Porosity (Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization).
ISO 22963:2008, Titanium and Titanium Alloys—Determination of Oxygen—Infrared Method After Fusion Under Inert Gas (Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization).
ASTM E2371-13, Standard Test Method for Analysis of Titanium and Titanium Alloys by Direct Current Plasma and Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry (Performance-Based Test Methodology) (West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM, 2014).
C. Eschey, S. Lutzmann, and M.F. Zaeh (Paper presented at the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, Austin, TX, 2009), pp. 3–5.
M. Kahnert, S. Lutzmann, and M.F. Zaeh, (Paper presented at the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium Proceedings, vol. 18, Austin, TX, 2007), pp. 88–99.
E. Ocholla, Arcam Level 3 Training: Smoke Theory (Arcam: Cambridge, UK, 2013).
J. Karlsson, A. Snis, H.K. Engqvist, and J. Lausmaa, J. Mater. Proc. Tech. 213, 2109 (2013).
M. Yan, W. Xu, M.S. Dargusch, H.P. Tang, M. Brandt, and M. Qian, Powder Metall. 57, 251 (2014).
M. Yan, M.S. Dargusch, T. Ebel, and M. Qian, Acta Mater. 68, 196 (2014).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Ministry of Science and Technology China under the International Science & Technology Cooperation Program (2011DFA5290) and the National High Technology Research Program (No. 2013AA031103). M. Qian and H.P. Tang further acknowledge the support from the Australian Research Council (ARC) through the Linkage Projects program under ARC LP140100607. Useful comments and suggestions from the reviewers are acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, H.P., Qian, M., Liu, N. et al. Effect of Powder Reuse Times on Additive Manufacturing of Ti-6Al-4V by Selective Electron Beam Melting. JOM 67, 555–563 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1300-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-015-1300-4