Abstract
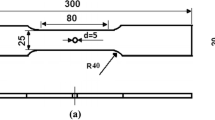
The effects of traction load, plate thickness, and pin radius on stress and deformation distribution were investigated by simulation symmetrical pin traction experiment and analytical calculation methods. At the beginning of traction, both contact angle and maximum stress increase with the traction load. As the traction continues, maximum stress is steady and only the contact angle increases with the traction load. The stress concentration increases with the decrease of pin radius and does not change with other parameters under the same pin radius. The increase of specimen thickness can only reduce the contact angle but does not lessen the stress concentration, and thicker specimens can bear more traction load when reaching the same contact angle. Strengthening during deformation is caused not only by the increase of dislocation density in martensite matrix but also by retained austenite (RA) strain-induced martensite transformation (SIMT), which is conducive to the transfer of plastic deformation.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \(D\) :
-
Diameter of the hole
- \(\Delta D\) :
-
Diameter increase along the direction of the traction
- \(F\) :
-
Traction force
- \(h\) :
-
Thickness of the specimen
- \(\Delta {h}_{0}\) :
-
Maximum unilateral thickening of the specimen
- \(p\) :
-
Normal edge force
- \({p}_{0}\) :
-
Force resultant amplitude
- \(r\) :
-
Radius of the pin
- \(R\) :
-
Radius of the hole
- \(t\) :
-
Length of thickening area
- \(\Delta \theta \) :
-
Contact angle between pin and hole
References
F. Gamdani, R. Boukhili, and A. Vadean, Mater. Des. 88, 702. (2015).
H. Bazvandi and E. Poursaeidi, Eng. Fail. Anal. 111, 104443 (2020).
Y. Xu, H. Zhu, W. Xu, and C. Liu, Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf. 125, 629. (2018).
R. Karakuzu, N. Taylak, B.M. İçten, and M. Aktaş, Compos. Struct. 85, 1. (2008).
V. Fiore, L. Calabrese, T. Scalici, and A. Valenza, Compos. B. Eng. 187, 107864 (2020).
Z. Zhang, W. Wang, C. Rans, and R. Benedictus, Procedia Struct. Integr. 2, 3361. (2016).
B. Grüber, W. Hufenbach, L. Kroll, M. Lepper, and B. Zhou, Compos. Sci. Technol. 67, 1439. (2007).
T.S. Kim, and H. Kuwamura, Mater. Des. 32, 3942. (2011).
O. Aluko, and H.A. Whitworth, Compos. Struct. 86, 308. (2008).
C. Echavarría, P. Haller, and A. Salenikovich, Compos. Struct. 79, 107. (2007).
T. Wu, K. Zhang, H. Cheng, P. Liu, D. Song, and Y. Li, Compos. B. Eng. 100, 176. (2016).
E. Persson, E. Madenci, and I. Eriksson, Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 30, 87. (1998).
Z. Wang, Y. Wang, Y. Zhang, L. Gardner, and Y. Ouyang, Eng. Struct. 200, 109675 (2019).
R. Karakuzu, C.R. Çalışkan, M. Aktaş, and B.M. İçten, Compos. Struct. 82, 225. (2008).
V. Fiore, L. Calabrese, T. Scalici, P. Bruzzaniti, and A. Valenza, Polym. Test. 69, 310. (2018).
R. Karakuzu, O. Demirgoren, B.M. Icten, and M.E. Deniz, Mater. Des. 31, 3029. (2010).
Z.Z. Zhao, R.H. Cao, J.H. Liang, F. Li, C. Li, and S.F. Yang, JOM-US 70, 700. (2018).
G.Q. Su, X.H. Gao, D.Z. Zhang, L.X. Du, J. Hu, and Z.G. Liu, JOM-US 70, 672. (2018).
R. Alturk, L.G. Hector Jr., M. Enloe, F. Abu-Farha, and T.W. Brown, JOM-US 70, 894. (2018).
R. Rana, E. De Moor, J.G. Speer, and D.K. Matlock, JOM-US 70, 706. (2018).
S. Pani, S.K. Singh, and B.K. Mohapatra, JOM-US 68, 1525. (2016).
J. Zhao, and Z. Jiang, Prog. Mater. Sci. 94, 174. (2018).
Y.K. Lee, and J. Han, Mater. Sci. Technol. 31, 843. (2015).
J. Hu, L.X. Du, W. Xu, J.H. Zhai, Y. Dong, Y.J. Liu, and R.D.K. Misra, Mater. Charact. 136, 20. (2017).
H. Liu, L.X. Du, J. Hu, H.Y. Wu, and R.D.K. Misra, J. Alloys Compd. 695, 2072. (2017).
X.Y. Qi, L.X. Du, J. Hu, and R.D.K. Misra, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 718, 471. (2018).
H. Luo, J. Shi, C. Wang, W. Cao, X. Sun, and H. Dong, Acta Mater. 59, 4002. (2011).
B.B. He, B.M. Huang, S.H. He, Y. Qi, H.W. Yen, and M.X. Huang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 724, 11. (2018).
H. Lee, M.C. Jo, S.S. Sohn, A. Zargaran, and S. Lee, Acta Mater. 147, 247. (2018).
J. Hu, L. Du, G. Sun, H. Xie, and R.D.K. Misra, Scr. Mater. 104, 87. (2015).
Y. Du, X. Gao, L. Lan, X. Qi, H. Wu, L. Du, and R.D.K. Misra, Int. J. Hydrog. Energ. 44, 32292. (2019).
P.D. Mangalgiri, T.S. Ramamurthy, B. Dattaguru, and A.K. Rao, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 29, 577. (1987).
F. Chang, R.A. Scott, and G.S. Springer, J. Compos. Mater. 16, 470. (1982).
Y.H. Fan, B. Zhang, H.L. Yi, G.S. Hao, Y.Y. Sun, J.Q. Wang, E.H. Han, and W. Ke, Acta Mater. 139, 188. (2017).
B. Zhang, L.X. Du, Y. Dong, D.X. Han, H.Y. Wu, F.H. Lu, and R.D.K. Misra, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 771, 138643 (2020).
Acknowledgements
The authors at NEU gratefully appreciate the financial support by the National High-tech R&D Program (863 Program) (No. 2015AA03A501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Y., Gao, X.H., Du, Z.W. et al. Stress and Deformation Distribution and Microstructure Changes Around Pin-Loaded Holes in Medium Manganese Steel Plates. JOM 73, 3301–3311 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04881-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04881-x