Abstract
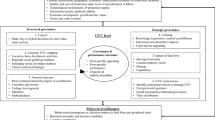
From research on Western new product development (NPD) practices a rich body of literature has emerged. However, the impact of country specific and cultural influences has not been examined in this context yet. This study is a first attempt to identify differences in NPD practices between Research and Development (R&D) subsidiaries in Germany, China and India within multinational companies. Data has been generated by qualitative interviews with R&D executives in those countries across multiple cases. The study samples strategic, organizational and operational aspects indicates definite differences in process coordination, rewarding systems, market orientation and the average age of NPD teams. Other aspects like strategic targets, the management involvement, etc. show rather slight differences across the countries. Hence, findings suggest that while some aspects are universally applicable across cultural frontiers, Western companies have to understand different expectations regarding NPD in India and China by adjusting practices accordingly.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Translated from German by the authors.
References
Agarwal N, Brem A (2012) Frugal and reverse innovation-Literature overview and case study insights from a German MNC in India and China. In: Engineering, technology and innovation (ICE), 2012 18th international ICE conference on. IEEE, pp 1–11
Ambos B, Ambos TC (2011) Meeting the challenge of offshoring R&D: an examination of firm- and location-specific factors. R&D Manag 41(2):107–119
Amsden AH, Tschang T, Goto A (2001) Do foreign companies conduct R&D in developing countries?: a new approach to analyzing the level of R&D, with an analysis of Singapore (No. 14). Tokyo. ADB Institute Working Paper. Retrieved from http://adbi.adb.org/files/2001.03.rp14.conduct.research.development.pdf
Barczak G, Griffin A, Kahn KB (2009) Perspective: trends and drivers of success in NPD practices: results of the 2003 PDMA best practices study. J Prod Innov Manag 26(1):3–23
Berét P, Mendez A, Paraponaris C, Richez-Battesti N (2003) R&D personnel and human resource management in multinational companies; between homogenization and differentiation. Int J Hum Resour Manag 14(3):449–468
Bozionelos N, Wang L (2007) An investigation on the attitudes of Chinese workers towards individually based performance-related reward systems. Int J Hum Resour Manag 18(2):284–302
Brem A, Freitag F (2014) Internationalization of new product development: Results from a multiple case study on companies with innovation processes in Germany and India. Int J Innov Manag 19(1):1550010-1–1550010-32
Brem A, Moitra D (2012) Learning from failure: Case insights into a UK–India technology transfer project. In: Technology transfer in a global economy, Springer US, pp 253–275
Brem A, Wolfram P (2014) Research and development from the bottom up-introduction of terminologies for new product development in emerging markets. J Innov Entrep 3(1):1–22
Busse R (2014) Is culture driving innovation? A multi-national quantitative analysis. Hum Syst Manag 33(3):91–98
Cantwell J, Piscitello L (2000) Accumulating technological competence: its changing impact on corporate diversification and internationalization. Ind Corp Change 9(1):21–51
Cappelli P, Sherer PD (1991) The missing role of context in OB: the need for a meso-level approach. Res Organ Behav 13:55–110
CIA [Central Intelligence Agency] (2012a) The world factbook, India. Retrieved from https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/in.html. 15 Dec 2014
CIA [Central Intelligence Agency] (2012b) The world factbook, Germany. Retrieved from https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/gm.html. 15 Dec 2014
CIA [Central Intelligence Agency] (2012c) The world factbook, China. Retrieved from https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ch.html. 15 Dec 2014
Cooper RG, Edgett SJ, Kleinschmidt EJ (2004a) Benchmarking best NPD practices—II. Res Technol Manag 47(3):50–59
Cooper RG, Edgett SJ, Kleinschmidt EJ (2004b) Benchmarking best NPD practices—III. Res Technol Manag 47(6):43–55
Cooper RG, Edgett SJ, Kleinschmidt EJ (2004c) Benchmarking best NPD practices—I. Res Technol Manag 47(1):31–43
Criscuolo P (2009) Inter-firm reverse technology transfer: the home country effect of R&D internationalization. Ind Corp Change 18(5):869–899
de Brentani U (2001) Innovative versus incremental new business services: different keys for achieving success. J Prod Innov Manag 18(3):169–187
DeSanctis G, Glass JT, Ensing IM (2002) Organizational designs for R&D. Acad Manag Exec 16(3):55–66
Dorfman PW, Howell JP (1988) Dimensions of national culture and effective leadership patterns: Hofstede revisited. Adv Int Comp Manag 3:127–150
Dunning JH, Lundan SM (2009) The internationalization of corporate R&D: a review of the evidence and some policy implications for home countries 1. Rev Policy Res 26(1–2):13–33
Ecker B, van Triest S, Williams C (2013) Management control and the decentralization of R&D. J Manag 39(4):906–927
Economist Intelligence Unit (EIU) (2004) Scattering the seeds of invention: the globalisation of research and development, Whitepaper, Economist Intelligence Unit. http://graphics.eiu.com/files/ad_pdfs/RnD_GLOBILISATION_WHITEPAPER.pdf
Ernst D (2005) The complexity and internationalization of innovation: the root causes. In: Proceedings globalization of R&D and developing countries: proceedings of the expert meeting Geneva, 24–26 January 2005, pp 61–88
Erramilli MK, Agarwal S, Kim S-S (1997) Are firm-specific advantages location-specific too? J Int Bus Stud 28(4):735–757
Farquhar JD (2012) Case study research for business. Sage Publications, London, Thousand Oaks
Flyvbjerg B (2006) Five misunderstandings about case-study research. Qual Inq 12(2):219–245
Gerhart B (2008) Cross cultural management research: assumptions, evidence and suggested directions. Internat J Cross-Cultural Manag 8(3):259–274
Gioia DA, Pitre E (1990) Multiparadigm perspectives on theory building. Acad Manag Rev 15:584–602
Giorgi S, Lockwood C, Glynn MA (2015) The many faces of culture: making sense of 30 years of research on culture in organization studies. Acad Manag Ann 9(1):1–54
Griffin A (1997) PDMA research on new product development practices: updating trends and benchmarking best practices. J Prod Innov Manag 14(6):429–458
Gulati R, Nohria N, Zaheer A (2000) Strategic networks. Strateg Manag J 21(3):203–215
Gupta V (2008) An inquiry into the characteristics of entrepreneurship in India. J Int Bus Res 7(1):53–69
Hartley J (2004) Case study research. In: Cassell C, Symon G (eds) Essential guide to qualitative methods in organizational research. Sage Publications, London, Thousand Oaks, pp 323–333
Hickson DJ, McMillan CJ (1981a) Organization and nation: the Aston programme IV. Gower, Farnborough
Hickson D, McMillan C (1981b) Concluding comments on countries, context and culture. Or-ganization and nation: the Aston programme IV. Gower, Farnborough, pp 187–196
Hofstede G (1983) National cultures in four dimensions: a research-based theory of cultural differences among nations. Int Stud Manag Organ XIII(1):46–74
Hofstede GH (2001) Culture’s consequences: comparing values, behaviors, institutions, and organizations across nations, 2nd edn. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks
Hofstede G (2007) Asian management in the 21st century. Asia Pac J Manag 24(4):411–420
Hofstede G (2013) The Hofstede centre. Retrieved from http://geert-hofstede.com/countries.html. 05 Feb 2013
Hofstede GH, Hofstede GJ, Minkov M (2010) Cultures and organizations: software of the mind, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, Maidenhead
House R, Hanges PJ, Javidan M, Dorfmann GP, Gupta V (2004) Culture, leadership, and organizations: the GLOBE study of 62 societies. SAGE Publications
Im S, Nakata C, Park H, Ha Y-W (2003) Determinants of Korean and Japanese new product performance: an interrelational and process view. J Int Mark 11(4):81–112
Johns G (2006) The essential impact of context on organizational behavior. Acad Manag Rev 31(2):386–408
Kleinschmidt EJ, de Brentani U, Salomo S (2007) Performance of global new product development programs: a resource-based view. J Prod Innov Manag 24(5):419–441
Kluckhohn C (1951) The study of culture. In: Lerner D, Lasswell HD (eds) The policy sciences. Stanford University Press, Stanford, pp 86–101
Kornai J (2010) Innovation and dynamism: interaction between systems and technical progress. Econ Transit 18(4):629–670
Leiponen A, Helfat CE (2010) Innovation objectives, knowledge sources, and the benefits of breadth. Strateg Manag J 31(2):224–236
Leonard-Barton D (1990) A dual methodology for case studies: synergistic use of a longitudinal single site with replicated multiple sites. Organ Sci 1(3):248–266
Li Y, Liu Y, Zhao Y (2006) The role of market and entrepreneurship orientation and internal control in the new product development activities of Chinese firms. Ind Mark Manag 35(3):336–347
Lin L-H (2009) Effects of national culture on process management and technological innovation. Total Qual Manag 20(12):1287–1301
Lindell M, Arvonen J (1996) The Nordic management style in a European context. Int Stud Manag Organ 26(3):73
Manning S (2008) Customizing clusters: on the role of Western multinational corporations in the formation of science and engineering clusters in emerging economies. Econ Dev Q 22(4):316–323
Mansfield E, Teece D, Romeo A (1979) Overseas research and development by U.S. multinationals. Economica 46:187–196
Mansfield E, Romeo A, Schwartz M, Teece D, Wagner S, Brach P (1983) New findings in technology transfer productivity and economic policy. Res Manag 26(2):11–20
Mayring P (2001) Kombination und integration qualitativer und quantitativer analyse. Forum Qual Soc Res 2(1, Art. 6):1–10
Miller DC (1991) Handbook of research design & social measurement. Sage Publications, Newbury Park
Moitra D (2008) Globalization of R&D: leveraging offshoring for innovative capability and organizational flexibility. ERIM Ph.D. Series Research in Management. Erasmus Research Institute of Management (ERIM)
Nakata C, Sivakumar K (1996) National culture and new product development: an integrative review. J Mark 60(1):61
OECD (2011) Education at a glance 2011: OECD indicators. OECD Publishing, Paris
Offereins A (2006) Organising R&D in globalised context: convergence or divergence? The relative influence of Dutch and foreign cultures on the organisational structure of R&D in multinational corporations. Manag Rev 17(4):466–483
Orlikowski WJ, Baroudi JJ (1991) Studying information technology in organizations: research approaches and assumptions. Inf Syst Res 2(1):1–28
Ozer M (2011) Strategic, organizational, and operational challenges of product innovation in china: Chinese firms tend to engage in a narrower range of new-product development techniques and activities compared to Western firms. Res Technol Manag 54(4):46–52
Ozer M, Chen Z (2006) Do the best new product development practices of US companies matter in Hong Kong? Ind Mark Manag 35(3):279–292
Patterson O (2014) Making sense of culture. Annu Rev Sociol 40:1–30
Persaud A, Kumar U, Kumar V (2002) Coordination structures and innovative performance in global R&D labs. Can J Adm Sci 19(1):57–75
Prakash Y, Gupta M (2007) Relationship between organisation structure and firm-level innovation in the manufacturing sector of India. Indian J Ind Relat 43(2):191–216
Rapoza K (2011) Within a generation, China middle class four times larger than America’s. Retrieved from http://www.forbes.com/sites/kenrapoza/2011/09/05/within-a-generation-china-middle-class-four-times-larger-than-americas/. 15 Dec 2014
Salomo S, Keinschmidt E, de Brentani U (2010) Managing new product development teams in a globally dispersed NPD program. J Prod Innov Manag 27(7):955–971
Sarin S, Mahajan V (2001) The effect of reward structures on the performance of cross-functional product development teams. J Mark 65(2):35–53
Schatzel K (1996) The R&D workers: managing innovation in Britain, Germany, Japan, and the United States. J Int Mark 4(2):95–97
Schwartz SH (1999) A theory of cultural values and some implications for work. Appl Psychol 48(1):23–47
Siu W-S, Lin T, Fang W, Liu Z-C (2006) An institutional analysis of the new product development process of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in China, Hong Kong and Taiwan. Ind Mark Manag 35(3):323–335
Stummer C, Günther M, Köck AM (2010) Grundzüge des Innovations- und Technologiemanagements (3., aktualisierte Aufl.). Manual. Wien: Facultas.wuv
Sun Y, Wen K (2007) Uncertainties, imitative behaviours and foreign R&D location: explaining the over-concentration of foreign R&D in Beijing and Shanghai within China. Asia Pac Bus Rev 13(3):405–424
Tahir R (2014) The impact of national and organizational cultural differences on international joint venture performance. IBA Bus Rev 9(1):47–63
Tellis GJ, Prabhu JC, Chandy RK (2009) Radical innovation across nations: the preeminence of corporate culture. J Mark 73(1):3–23
Tjosvold D, Wong ASH (2004) Innovation across cultural boundaries. Applying conflict theory to develop a common approach. Int Negot 9:291–313
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) (2005) World investment report 2005: transnational corporations and the internationalization of R&D. World investment report: Vol. 2005. United Nations, New York, Geneva
United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) (2011) World investment report 2011: non-equity modes of international production and development. World investment report: Vol. 2011. United Nations, New York, Geneva
Von Zedtwitz M (2004) Managing foreign R&D laboratories in China. R&D Management 34(4):439–452
Wahyuni D (2012) The research design maze: understanding paradigms, cases, methods and methodologies. J Appl Manag Acc Res 10(1):69–80
Wang S, Guidice RM, Tansky JW, Wang Z-M (2010) When R&D spending is not enough: the critical role of culture when you really want to innovate. Hum Resour Manag 49(4):767–792
Witzel A (2000) Das problemzentrierte interview. Forum Qualitative Sozialforschung/Forum: Qual Soc Res, 1(1, Art. 22). Retrieved from http://nbn-resolving.de/urn:nbn:de:0114-fqs0001228
Yin RK (2003) Applications of case study research, vol 34., Applied social research methods seriesSage Publications, California
Zeng SX, Xie XM, Tam CM, Sun PM (2009) Identifying cultural difference in R&D project for performance improvement: a field study. J Bus Econ Manag 10(1):61–70
Zeschky M, Widenmayer B, Gassmann O (2011) Frugal innovation in emerging markets: the case of Mettler Toledo: successful frugal innovation requires a strong local presence in the emerging markets that are demanding affordable, good-enough products. Res Technol Manag 54(4):38–45
Zhang X, Williams A (2008) Strategic new product development in Chinese organizations: a case study in the high technology sector. Des Manag J 3(1):69–78
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Hans–Frisch–Stiftung (Nürnberg, Germany) for their financial support of this project. In addition, this research project would not have been possible without the support of Florian Freitag and Tamara Kürzdörfer, which is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Interview guideline
Appendix: Interview guideline



Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brem, A., Wolfram, P. Organisation of new product development in Asia and Europe: results from Western multinationals R&D sites in Germany, India, and China. Rev Manag Sci 11, 159–190 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-015-0183-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-015-0183-7
Keywords
- New product development (NPD)
- Research and Development (R&D)
- Culture
- Developing markets
- Developed markets
- Case study