Abstract
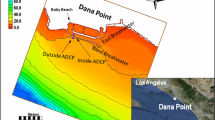
Sedimentation in artificial ports and harbors is a common issue throughout the world. Based on an assessment of the coastal fishing harbors in Egypt, the El-Burullus fishing harbor has been found to suffer severely from siltation. Sediment deposits are concentrated at the harbor entrance, which threatens navigation through this area. Although the harbor authority has constructed a perpendicular extension on the main breakwater to mitigate these siltation issues, fishing boats are still suffering from the siltation at the harbor entrance. Dredging is required every year to maintain continuity of navigation through the harbor; the cost of dredging is a critical element which impacts the economic feasibility of the harbor. Therefore, the need to investigate new solutions for the siltation issue is critical. In this study, a two-dimensional calibrated and validated model using the Coastal Modeling System package is used to understand the coastal processes within the study area. It is also used to investigate the effects of the proposed breakwater extension on the siltation at the harbor outlet. Field data such as hydrographic surveys, waves, tides, and lake outlet discharge data were collected and included in the model. The results obtained for the current breakwater conditions confirmed the claims of the fishermen that the sedimentation problem still occurs at the entrance. Thus, five possible solutions to mitigate the problem were proposed and simulated considering the following parameters: sediment deposition rate to the west of the main breakwater, the erosion rate in front of the seawall in the eastern part of the harbor, and the morphological changes within the El-Burullus lake outlet. According to the simulation results, reducing the length of the upper edge of the middle jetty by 90 m improves the stability of the harbor entrance. Alternatively, replacing the perpendicular extension by an inclined extension of 60 m in length and shortening the middle jetty by 60 m reduces the accretion and erosion rates around the harbor which promotes the long-term stability for the coastal area in addition to favorable conditions to the El-Burullus harbor entrance.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abayazid H, El-Shinnawy I (2012) Coastal lake sustainability: threats and opportunities with climate change. IOSR journal of mechanical and. Civ Eng 1(5):33–41. Available at https://www.iosrjournals.org/iosr-jmce/papers/vol1-issue5/G0153341.pdf
AbdAllah AM, Sharaf El-Din S, Shereet SM (2006) Analysis of wave observation and wave transformation in Abu-Qir bay, Egypt. Egypt J Aquat Res 32(1):22–33
Ahmed AS (2006) Numerical model as a toolto investigate coastal problems in Egypt. In: Proceeding of the tenth international water technology conference, IWTC10 2006, Alexandria, Egypt, pp 933–944
Bottin Jr R, Markle DG (1992) Small-boat harbor design experience (lessons learned) through physical modeling and subsequent prototype performance. US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station Vicksburg
Cáceres RA, Zyserman JA, Perillo GM (2016) Analysis of sedimentation problems at the entrance to Mar del Plata harbor. Journal of Coastal Research 32(2):301–314 Coconut Creek (Florida) https://doi.org/10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-14-00056.1
Donnelly P, MacInnis I (1968) Experience with self-dredging harbour entrances. In: Coastal engineering, pp 1283–1294
El-Asmar HM, White K (2002) Changes in coastal sediment transport processes due to construction of new Damietta harbour, Nile Delta, Egypt. Coast Eng 46(2):127–138
El-Shinnawy IA (2003) Reservoir hydrologic routing for water balance of Al-Burullus wetland, Egypt. In: Proceedings of the seventh international water technology conference IWTC7, pp 867–877
Fanos AM, Khafagy AA, Dean RG (1995) Protective works on the Nile delta coast. J Coast Res 11(2):516–528
Frihy OE (2001) The necessity of environmental impact assessment (EIA) in implementing coastal projects: lessons learned from the Egyptian Mediterranean coast. Ocean Coast Manag 44(7):489–516
Frihy OE, Deabes EA (2011) Beach and nearshore morphodynamics of the central-bulge of the Nile delta coast, Egypt. International Journal of Environmental protection, IJEP 1(2):33–46
Frihy OE, Abd-ElMoniem AB, Hassan MS (2002) Sedimentation processes at the navigation channel of the Damietta harbour on the northeastern Nile delta coast of Egypt. J Coast Res 18(3):459–469
Frihy OE, Deabes EA, El Gindy AA (2010) Wave climate and nearshore processes on the Mediterranean coast of Egypt. J Coast Res 261(261):103–112
Frihy OE, Deabes EA, Helmy EE (2016) Compatibility analysis of dredged sediments from routine pathways and maintenance of harbor’s channels for reuse in nearshore nourishment in the Nile delta, Egypt. J Coast Res 32(3):555–566. Available at https://www.bioone.org/, https://doi.org/10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-14-00181.1
Ghosh LK, Prasad N, Joshi VB, Kunte SS (2001) A study on siltation in access channel to a port. Coast Eng 43(1):59–74
Gunbak AR, Gokce KT, Guler I (1992) Sedimentation and erosion problems of Yakakent fishery harbor. In: Coastal engineering, pp 3081–3092 https://doi.org/10.1061/9780872629332.235
Iskander MM (2013) Wave climate and coastal structures in the Nile delta coast of Egypt. Emirates Journal for Engineering Research 18(1):43–57
Johnson HN, McAnally WH, Ortega-Achury S (2010) Sedimentation management alternatives for the Port Of Pascagoula. Report no. FHWA/MS-DOT-RD-10-199. Prepared for Mississippi Department of Transportation
Khafagy AA, Naffaa MG, Fanos AM, Dean RG (1992) Nearshore coastal changes along the Nile delta shores. In: Coastal engineering, vol 23, pp 3260–3272
Khalifa MA (2012) Adoption of recent formulae for sediment transport calculations applied on the Egyptian Nile delta coastal area. J Coast Conserv 16(1):37–49
Kuijper C, Christiansen H, Cornelisse JM, Winterwerp JC (2005) Reducing harbor siltation. ΙΙ: case study of Parkhafen in Hamburg. J Waterw Port Coast Ocean Eng 121(6):267–276
Lakhan VC, editor (2003) Advances in coastal modeling. Elsevier Oceanography Series 67. School of Physical Sciences, Windsor, Canada, Preface
Lin L, Demirbilek Z (2010) CMS: A coastal modeling system for inlets and navigation projects. In proceedings of the 5th International Ocean-Atmosphere Conference
Masria AA, Negm AM, Iskander MM, Saavedra OC (2013) Hydrodynamic modeling of outlet stability case study Rosetta promontory in Nile delta. Water Science 27(54):39–47. Available at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1110492913000052
Mcanally WH, Haydel JF, Savant G (2004) Port sedimentation solutions for the Tennessee-Tombigbee waterway in Mississippi. Report 1. Department of Civil Engineering, James Worth Bagely College of Engineering, Mississipi State University
Mojabi M, Hejazi K, Karimi M (2013) Numerical investigation of effective harbor geometry parameters on sedimentation inside square harbors. Int. J.MAr. Sci Eng 3(2):57–68
Ouellet Y, Anctil F, Desjardins L (1989) Solving a harbor accretion problem: the case of Millerand, IIes-de-la-Madeleine, Quebec. Can J Civ Eng 16(6):924–935
PIANC (2008) Minimising harbour siltation, Tech. Rep. 102. World Association for Waterborne Transport Infrastructure, Brussels, Be
Reed CW, Brown ME, Sanchez A, Wu W, Buttolph AM (2011) The coastal modeling system flow model (CMS-Flow): past and present. Journal of Coastal Research. SI(59):1–6
Sanchez A, Brown M, Beck T, Styles R, Li H (2015) Long-term morphological modeling at coastal inlets. Army Engineer Research and Development Center, Coastal and Hydraulic Laboratory, Vicksburg, pp 1–11
Sharaan M, Negm A, Iskander M, Nadaoka K (2016) Egyptian fishing ports challenges and opportunities, case study Mediterranean Sea ports. In: Proceedings of ports 2016 conference, pp 540–549. Available at https://www.ascelibrary.org/, https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784479919.055
Sharaan M, Negm A, Iskander M, Nadaoka K (2017) Questionnaire-based assessment of Mediterranean fishing ports, Nile delta, Egypt. Mar Policy 81:98–108. Available at https://www.linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0308597X16305498
van Rijn LC (2005) Estuarine and coastal sedimentation problems. International Journal of Sediment Research 20(1):39–51
van Rijn LC (2016) Harbour siltation and control measures. https://www.leovanrijn-sediment.com/papers/Harboursiltation2012.pdf
Winterwerp JC (2005) Reducing harbor siltation I : methodology. J Waterw Port Coast Ocean Eng 131(6):258–266. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(2005)131:6(258)
Yin J, Falconer RA, Chen Y, Probert SD (2000) Water and sediment movements in harbours. Appl Energy 67(3):341–352
Yuksek O (1995) Effects of breakwater parameters on shoaling of fishery harbors. J Waterw Port Coast Ocean Eng 121(1):13–22
Zeydan BA, Elshinnawy IA (2003) Impact of the catchment area on water and sediment quality of Al Burullus Lake, Egypt. WIT Trans Ecol Environ 61:265–275
Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank the Egyptian Ministry of Higher Education (MOHE) for providing the financial support (Ph.D. scholarship) for this research as well as the Egypt-Japan University of Science and Technology (E-JUST) for offering the software, facilities, and tools needed to conduct this work. We would like to express special thanks to Dr. Ali Masria, Lecturer at Faculty of Engineering, Mansoura University for his contribution, guides during using and training for CMS software. Also, we would express our thanks to the Coastal Research Institute, National Water Research Center, Ministry of Water Resources and Irrigation, Egypt for technical support and providing different field data and measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharaan, M., Ibrahim, M.G., Iskander, M. et al. Analysis of sedimentation at the fishing harbor entrance: case study of El-Burullus, Egypt. J Coast Conserv 22, 1143–1156 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-018-0624-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11852-018-0624-y