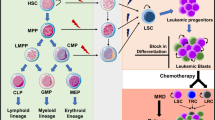
Opinion statement
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), also known as chronic myelocytic or chronic myeloid leukemia, is a clonal disorder of hematopoiesis that arises in a hematopoietic stem cell or early progenitor cell. This is characterized by the dysregulated production of mature non-lymphoid cells with normal differentiation. Eventually, in spite of the term chronic, there is progression to acute leukemia, usually of the myeloid variety, which is highly resistant to current therapies. Despite recent improvements in the treatment of early-stage disease, CML blast crisis (CMLBC) remains a therapeutic challenge. CMLBC is highly refractory to standard induction chemotherapy, with a response rate in myeloid blast crisis of less than 30%. Conventional chemotherapy has been much less successful in this disease compared with de novo acute leukemia, with a mean survival after diagnosis of blast crisis of only 2 to 4 months for nonresponders. Many regimens of chemotherapies have been tried in CMLBC, with minor success. Although imatinib was evaluated in patients with CMLBC, most CMLBC cases today arise in patients already on imatinib-based therapy and developing blastic phase on that therapy; thus there is no standard therapy for patients with CMLBC. Further studies of the mechanisms of transformation of chronic-phase CMLBC at a molecu-lar level, and methods to target these molecular abnormalities, will determine the future direction of new treatment modalities. The prognosis of CML in blast crisis remains dis-appointing, despite great efforts. Currently, the most successful strategy for improving survival in CML is by prolonging the chronic phase and delaying the onset of blast crisis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References and Recommended Reading
Faderl S, Talpaz M, Estrov Z, et al.: Chronic myelogenous leukemia: biology and therapy. Ann Intern Med 1999, 131:207–219; and The biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 1999, 341:164. This study provides a useful overview of switching treatment of CML from chemotherapy to targeted therapy based on the biology of the disease.
Deininger MW, Goldman JM, Melo JV: The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2000, 96:3343–3356.
Giles FJ, Cortes JE, Kantarjian HM, et al.: Accelerated and blastic phases of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2004, 18:753–774.
Axdorph U, Stenke L, Grimfors G, et al.: Intensive chemotherapy in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) in accelerated or blastic phase--a report from the Swedish CML group. Br J Haematol 2002, 118:1048–1054.
Bolaman Z, Koseoglu M, Ayyildiz O, et al.: Treatment of blastic phase chronic myeloid leukemia with mitox-antrone, cytosine arabinoside and high dose methyl-prednisolone. Hematologica 2002, 32:49–57.
Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, Kantarjian HM, et al.: Activity of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in the blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the Philadelphia chromosome. N Engl J Med 2001, 344:1038–1042. This pilot study is one of the pioneer studies that evaluated the effect of tyrosine kinase inhibition in patients with CMLBC and Ph-positive ALL.
Soverini S, Martinelli G, Rosti G, et al.: ABL mutations in late chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients with up-front cytogenetic resistance to ima-tinib are associated with a greater likelihood of pro-gression to blast crisis and shorter survival: a study by the GIMEMA Working Party on Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2005, 23:4100–4109.
Ilaria RL Jr: Pathobiology of lymphoid and myeloid blast crisis and management issues. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2005, 188–194.
Goldman JM, Melo JV: Chronic myeloid leukemia--advances in biology and new approaches to treat-ment. N Engl J Med 2003, 349:1451–1464.
Kurzrock R, Kantarjian HM, Druker BJ, Talpaz M: Phila-delphia chromosome-positive leukemias: from basic mechanisms to molecular therapeutics. Ann Intern Med 2003, 138:819–830.
Warmuth M, Danhauser-Riedl S, Hallek M: Molecular pathogenesis of chronic myeloid leukemia: implica-tions for new therapeutic strategies. Ann Hematol 1999, 78:49–64.
Melo JV, Deininger MW: Biology of chronic myeloge-nous leukemia--signaling pathways of initiation and transformation. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2004, 18:545–568.
Gordon MY, Dowding CR, Riley GP, et al.: Altered adhe-sive interactions with marrow stroma of hematopoietic progenitor cells in chronic myeloid leukemia. Nature 1987, 328:342–344.
Verfaillie CM, McCarthy JB, McGlave PB: Mechanisms underlying abnormal trafficking of malignant progen-itors in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Decreased adhesion to stroma and fibronectin but increased adhesion to the basement membrane components laminin and collagen type IV. J Clin Invest 1992, 90:1232–1241.
Van Etten RA: Cycling, stressed-out and nervous: cellular functions of c-Abl. Trends Cel l Bi ol 1999, 9:179–186.
Calabretta B, Prerotti D: The biology of CML blast crisis. Blood 2004, 103: 4010.
Deininger MW, Goldman JM, Melo JV: The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2000, 96:3343–3356.
Jamieson CH, Ailles LE, Dylla SJ, et al.: Granulocyte-macrophage progenitors as candidate leukemic stem cells in blast-crisis CML. N Engl J Med 2004, 351:657–667.
Sinclair PB, Nacheva EP, Leversha M, et al.: Large dele-tions at the t(9;22) breakpoint are common and may identify a poor-prognosis subgroup of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2000, 95:738–743.
Dutcher JP, Wiernik PH: Accelerated and blastic phase of chronic myeloid leukemia. Curr Treat Options Oncol 2000, 1:51–52.
Ottmann OG, Druker BJ, Sawyers CL, et al.: A phase 2 study of imatinib in patients with relapsed or refractory Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoid leukemias. Blood 2002, 100: 1965.
Kantarjian HM, Walters RS, Keating MJ, et al.: Treatment of blastic phase of chronic myelogenous leukemia with mitoxantrone and high-dose cytosine arabino-side. Cancer 1988, 62:672–676.
Kantarjian HM, Talpaz M, Gutterman J, et al.: Treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia in accelerated and blastic phases with daunorubicin, high dose cytara-bine, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Clin Oncol 1992, 10: 398–405.
Morris EL, Dutcher JP, Paietta E, et al.: A pilot study of carboplatin and mitoxantrone in blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2006, Submitted.
Robak T, Gora-Tybor J: Cladribine combined with mitoxantrone in the treatment of blastic phase of chronic myeloid leukemia. Neoplasm 2001, 48:203–207.
Koller CA, Miller DM: Preliminary observations on the therapy of the myeloid blast phase of chronic granu-locytic leukemia with plicamycin and hydroxyurea. N Engl J Med 1986, 315: 1433–1438.
Kantarjian HM, Keating MJ, Talpaz M, et al.: Chronic myelogenous leukemia in blast crisis. Analysis of 242 patients. Am J Med 1987, 83:445–454.
Schiffer CA, De Bellis R, Kasdorf H, et al.: Treatment of the blast crisis of chronic myelogenous leukemia with 5-azacitidine and VP-16-213. Cancer Treat Rep 1982, 66:267–271.
Dutcher JP, Eudey L, Wiernik PH, et al.: Phase II study of mitoxantrone and 5-azacytidine for accelerated and blast crisis of chronic myelogenous leukemia: a study of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Leukemia 1992, 6:770–775.
Dutcher JP, Coletti D, Paietta E, et al.: A pilot study of alpha-interferon and plicamycin for accelerated phase of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res 1997, 21: 375–380.
Dutcher JP, Lee S, Paietta E, et al.: Phase II study of car-boplatin in blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study (E 1992). Leukemia 1998, 12:1037–1040.
Dutcher JP, Lee S, Wiernik PH, et al.: Phase II study of All-Trans retinoic acid (ATRA) in accelerated phase or early blastic phase of chronic myeloid leukemia. A study of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (E1993). Leuk Lymphoma 2005, 46:377–385.
Cervantes F, Villamor N, Esteve J, et al.: "Lymphoid" blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukaemia is associated with distinct clinicohaematological features. Br J Haematol 1998, 100:123–128.
Specchia G, Palumbo G, Pastore D, et al.: Extra-medullary blast crisis in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res 1996, 20:905–908.
Neylon AJ, O'Brien SG: Diagnosis and treatment of CML. In Neoplastic Diseases of the Blood, edn 4. Edited by Wiernik PH. New York: Cambridge University Press; 2003:53–69. This chapter provides a comprehensive review of CML and CMLBC disease, including pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment.
Goldman JM, Apperley JF, Jones L, et al.: Bone marrow transplantation for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 1986, 314: 202–207.
Fefer A, Clift RA, Thomas ED: Allogeneic marrow trans-plantation for chronic granulocytic leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst 1986, 76:1295–1299.
Kantarjian HM, Cortes JE, O'Brien S, et al.: Long-term survival benefit and improved complete cytogenetic and molecular response rates with imatinib mesylate in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia after failure of interferon-alpha. Blood 2004, 104: 1979–1988.
Marin D, Marktel S, Bua M, et al.: The use of imatinib (STI571) in chronic myeloid leukemia: some practical considerations. Haematologica 2002, 87:979–988.
Sureda A, Carrasco M, de Miguel M, et al.: Imatinib mesylate as treatment for blastic transformation of Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloge-nous leukemia. Haematologica 2003, 88:1213–1220.
Deininger MW, Goldman JM, Melo JV: The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2000, 96:3343–3356.
Druker BJ, Lydon NB: Lessons learned from the devel-opment of an Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor for chronic myelogenous leukemia. J Clin Invest 2000, 105: 3–7.
Marin D, Marktel S, Bua M, et al.: The use of imatinib (STI571) in chronic myeloid leukemia: some practical considerations. Haematologica 2002, 87:979–988.
Kantarjian HM, Cortes J, O'Brien S, et al.: Imatinib mesylate (STI571) therapy for Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia in blast phase. Blood 2002, 99:3547–3553.
Sawyers CL, Hochhaus A, Feldman E, et al.: Imatinib induces hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in mye-loid blast crisis: results of a phase II study. Blood 2002, 99:3530–3539.
Zhang GC, Zheng D, Li QH, et al.: Efficacy of imatinib mesylate, a specific inhibitor of BCR/ABL tyrosine kinase, on chronic myeloid leukemia in blast phase. Ai Zheng 2004, 23:1696–1699.
Weisberg E, Griffin JD: Resistance to imatinib (Glivec): update on clinical mechanisms. Drug Resist Updat 2003, 6:231–238.
Pfeifer H, Wassmann B, Hofmann WK, et al.: Risk and prognosis of central nervous system leukemia in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute leukemias treated with imatinib mesylate. Clin Cancer Res 2003, 9:4674–4681.
Bujassoum S, Rifkind J, Lipton JH: Isolated central ner-vous system relapse in lymphoid blast crisis chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia in patients on imatinib therapy. Leuk Lymphoma 2004, 45:401–403.
Wolff NC, Richardson JA, Egorin M, et al.: The CNS is a sanctuary for leukemic cells in mice receiving imatinib mesylate for BCR-ABL-induced leukemia. Blood 2003, 101: 5010.
Tsao AS, Kantarijian H, Talpaz M: STI-571 in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2002, 11 9 : 15.
Breccia M, Nanni M, Mancini F, et al.: Extramedullary blast crisis occurring in a Philadelphia-positive chronic myeloid leukemia patient with major cyto-genetic response to imatinib. Haematologica 2004, 89:ECR11.
Graham SM, Jorgensen HG, Allan E, et al.: Primitive, quiescent Philadelphia-positive stem cells from patients with CML are insensitive to ST1571 in vitro. Blood 2002, 99:319.
Yoshida C, Melo JV: Biology of chronic myeloid leukemia and possible therapeutic approaches to imatinib-resistant disease. Int J Hematol 2004, 79:420–433.
Talpaz M, Rousselot P: A phase II study of dasatinib in patients with CMLBC who are resistant or intolerant to imatinib: first results of the CA 180006 ‘START-B’ study [abstract 40]. http://www.abstracts2view.com/hem_ash05atlanta/. Accessed February 6, 2006. This study describes the first phase II trial of dasatinib, with significant success rate in IM-R CMLBC patients.
Guilhot F, Apperley JF, Shah N, et al.: A phase II study of dasatinib in patients with accelerated-phase CML who are resistant or intolerant to imatinib: first results of the CA 180005 ‘START-A’ study [abstract 39]. http://www.abstracts2view.com/hem_ash05atlanta/. Accessed February 6, 2006. This study describes the first phase II trial of dasatinib in accelerated phase of CML. The results are important because the patients were all resistant or intolerant to imatinib.
Guzman ML, Rossi RM, Karnischky L, et al.: The sesquit-erpene lactone parthenolide induces apoptosis of human acute myelogenous leukemia stem and pro-genitor cells. Blood 2005, 105:4163–4169.
Yu C, Rahmani M, Conrad D, et al.: The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib interacts synergistically with histone deacetylase inhibitors to induce apoptosis in Bcr/Abl+ cells sensitive and resistant to STI571. Blood 2003, 10: 3765–3774.
Dai Y, Rahmani M, Pei XY, et al.: Bortezomib and flavo-piridol interact synergistically to induce apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells resistant to imatinib mesylate through both Bcr/Abl-dependent and -inde-pendent mechanisms. Blood 2004, 104: 509–518.
Morris EL, Dutcher JP: Blastic phase of chronic myel-genous leukemia. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 2005, 3:547–552. This is an important review of the molecular biology and evolution of treatment of the blastic phase of CML.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esfahani, M.K., Morris, E.L., Dutcher, J.P. et al. Blastic phase of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Curr. Treat. Options in Oncol. 7, 189–199 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-006-0012-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11864-006-0012-y