Abstract
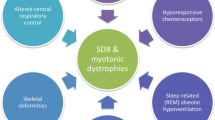
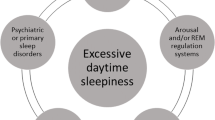
Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) represents the 1 chronic neuromuscular disease with the most prominent sleep disorders, including excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), sleep apneas, periodic leg movements during sleep, and rapid eye movement sleep dysregulation. The large majority of DM1 patients complain about EDS, which may have a deleterious impact on work, domestic responsibilities, social life, and quality of life. Here, we review the extant literature and report that studies are largely supportive of the view that DM1-related EDS is primarily caused by a central dysfunction of sleep regulation rather than by sleep-related disordered breathing (SRDB) or sleep fragmentation. The pathogenesis of EDS in DM1 still remains unclear but several arguments favor a model in which brain/brainstem nuclear accumulations of toxic expanded DM protein kinase (DMPK) gene are responsible for aberrant genes expression in modifying alternative splicing. Regarding management, early recognition, and treatment of SRDB with nocturnal noninvasive mechanical ventilation is first mandatory. However, despite its appropriate management, EDS often persists and may require a psychostimulant but no consensus has been yet established. Further studies are needed to clarify the discrepancies between daytime sleepiness/fatigue complaints and subjective/objective measurement of daytime sleepiness, the role of cognitive impairment and apathy in this relationship, and its reversibility with appropriate management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of outstanding importance
Harley HG, Brook JD, Rundle SA, Crow S, Reardon W, Buckler AJ, et al. Expansion of an unstable DNA region and phenotypic variation in myotonic dystrophy. Nature. 1992;355:545–6.
Harper PS. Myotonic dystrophy. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 2001.
Mathieu J, De Braekeleer M, Prevost C. Genealogical reconstruction of myotonic dystrophy in the Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean area (Quebec, Canada). Neurology. 1990;40:839–42.
Brunner HG, Jennekens FGI, Smeets HJM, de Visser M, Wintzen AR. Myotonic dystrophy (Steinert’s disease). In: Emery AE, editor. Diagnostic criteria for neuromuscular disorders. 2nd ed. London: Royal Society of Medicine Press; 1998.
Harley HG, Rundle SA, MacMillan JC, Myring J, Brook JD, Crow S, et al. Size of the unstable CTG repeat sequence in relation to phenotype and parental transmission in myotonic dystrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 1993;52:1164–74.
de Die-Smulders CE. Congenital and childhood-onset myotonic dystrophy. In: Harper P, van Engelen B, Eymard B, Wilcox D, editors. Myotonic dystrophy: present management, future therapy. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2004.
Arsenault ME, Prevost C, Lescault A, Laberge L, Puymirat J, Mathieu J. Clinical characteristics of myotonic dystrophy type 1 patients with small CTG expansions. Neurology. 2006;66:1248–50.
Gagnon C, Noreau L, Moxley RT, Laberge L, Jean S, Richer L, et al. Toward an integrative approach to the management of myotonic dystrophy type 1. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007;78:800–6.
Ashizawa T. Myotonic dystrophy as a brain disorder. Arch Neurol. 1998;55:291–3.
Hilton-Jones D. Myotonic dystrophy-forgotten aspects of an often neglected condition. Curr Opin Neurol. 1997;10:399–401.
Kierkegaard M, Harms-Ringdahl K, Widen Holmqvist L, Tollback A. Perceived functioning and disability in adults with myotonic dystrophy type 1: a survey according to the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health. J Rehabil Med. 2009;41:512–20.
Heatwole C, Bode R, Johnson N, Quinn C, Martens W, McDermott MP. Patient-reported impact of symptoms in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (PRISM-1). Neurology. 2012;79:348–57.
Quera Salva MA, Blumen M, Jacquette A, Durand MC, Andre S, De Villiers M, et al. Sleep disorders in childhood-onset myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neuromuscul Disord. 2006;16:564–70.
Lam EM, St.Louis EK, Slocumb SL, Milone M. Restless legs syndrome, daytime fatigue, and poor sleep quality are common in myotonic dystrophy type 2. Sleep. 2012;35:A288.
Shepard P, Lam EM, St Louis EK, Dominik J. Sleep disturbances in myotonic dystrophy type 2. Eur Neurol. 2012;68:377–80.
Tieleman AA, Knoop H, van de Logt AE, Bleijenberg G, van Engelen BG, Overeem S, et al. Poor sleep quality and fatigue but no excessive daytime sleepiness in myotonic dystrophy type 2. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2010;81:963–7.
Hilton-Jones D, Damian MS, Meola G. Somnolence and its management. In: Harper P, van Engelen B, Eymard B, Wilcox D, editors. Myotonic dystrophy: present management, future therapy. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2004.
Laberge L, Gagnon C, Jean S, Mathieu J. Fatigue and daytime sleepiness rating scales in myotonic dystrophy: a study of reliability. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2005;76:1403–5.
Laberge L, Bégin P, Montplaisir J, Mathieu J. Sleep complaints in patients with myotonic dystrophy. J Sleep Res. 2004;13:95–100.
Leygonie-Goldenberg F, Perrier M, Duizabo P, Bouchareine A, Harf A, Barbizet J, et al. Disturbances of wakefulness, sleep and respiratory function in Steinert's disease. Rev Neurol. 1977;133:255–70.
Park JD, Radtke RA. Hypersomnolence in myotonic dystrophy: demonstration of sleep onset REM sleep [letter]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1995;58:512–3.
Phemister JC, Small JM. Hypersomnia in dystrophia myotonica. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1961;24:173–5.
Kilburn KH, Eagen JT, Heyman A. Cardiopulmonary insufficiency associated with myotonic dystrophy. Am J Med. 1959;26:929–35.
Rubinsztein JS, Rubinsztein DC, Goodburn S, Holland AJ. Apathy and hypersomnia are common features of myotonic dystrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998;64:510–5.
van der Meché FG, Bogaard JM, van der Sluys JC, Schimsheimer RJ, Ververs CC, Busch HF. Daytime sleep in myotonic dystrophy is not caused by sleep apnoea. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1994;57:626–8.
• Hilton-Jones D, Bowler M, Lochmueller H, Longman C, Petty R, Roberts M, et al. Modafinil for excessive daytime sleepiness in myotonic dystrophy type 1—the patients' perspective. Neuromuscul Disord. 2012;22:597–603. This review reports the experience of a large group of DM1 patients and their clinicians concerning EDS and concludes that in spite of the limited literature there is sufficient evidence to support the use of modafinil in carefully selected patients.
Thomasen E. Myotonia. Denmark: Aarhuus Universitetsforlaget; 1948.
van Hilten JJ, Kerkhof GA, van Dijk JG, Dunnewold R, Wintzen AR. Disruption of sleep-wake rhythmicity and daytime sleepiness in myotonic dystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1993;114:68–75.
Laberge L, Prévost C, Perron M, Mathieu J, Auclair J, Gaudreault M, et al. Clinical and genetic knowledge and attitudes of patients with myotonic dystrophy type 1. Public Health Genom. 2010;13:424–30.
Chervin RD. Sleepiness, fatigue, tiredness, and lack of energy in obstructive sleep apnea. Chest. 2000;118:372–9.
Krupp LB, LaRocca NG, Muir-Nash J, Steinberg AD. The fatigue severity scale. Application to patients with multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch Neurol. 1989;46:1121–3.
Laberge L, Dauvilliers Y, Bégin P, Richer L, Jean S, Mathieu J. Fatigue and daytime sleepiness in patients with myotonic dystrophy type 1: to lump or split? Neuromuscul Disord. 2009;19:397–402.
• Hermans MC, Merkies IS, Laberge L, Blom EW, Tennant A, Faber CG, et al. Fatigue and daytime sleepiness scale in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Muscle Nerve. 2013;47:89–95. This study presents the Rasch-built Fatigue and Daytime Sleepiness Scale, developed specifically for DM1 patients. It provides interval measures on a single continuum and is recommended for future clinical trials and therapeutic follow-up.
Delaporte C. Personality patterns in patients with myotonic dystrophy. Arch Neurol. 1998;55:635–40.
Meola G, Sansone V, Perani D, Scarone S, Cappa S, Dragoni C, et al. Executive dysfunction and avoidant personality trait in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM-1) and in proximal myotonic myopathy (PROMM/DM-2). Neuromuscul Disord. 2003;13:813–21.
Winblad S, Lindberg C, Hansen S. Temperament and character in patients with classical myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM-1). Neuromuscul Disord. 2005;15:287–92.
Laberge L, Dauvilliers Y. Myotonic dystrophy and sleepiness. In: Thorpy M, Billiard M, editors. Sleepiness: causes, consequences, disorders and treatment. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 2011.
Gagnon C, Mathieu J, Noreau L. Life habits in myotonic dystrophy type 1. J Rehabil Med. 2007;39:560–6.
Phillips MF, Steer HM, Soldan JR, Wiles CM, Harper PS. Daytime somnolence in myotonic dystrophy. J Neurol. 1999;246:275–82.
Gagnon C, Mathieu J, Jean S, et al. Predictors of disrupted social participation in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2008;89:1246–55.
MacDonald JR, Hill JD, Tarnopolsky MA. Modafinil reduces excessive somnolence and enhances mood in patients with myotonic dystrophy. Neurology. 2002;59:1876–80.
Orlikowski D, Chevret S, Quera-Salva MA, Laforêt P, Lofaso F, Verschueren A, et al. Modafinil for the treatment of hypersomnia associated with myotonic muscular dystrophy in adults: a multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 4-week trial. Clin Ther. 2009;31:1765–73.
Puymirat J, Bouchard JP, Mathieu J. Efficacy and tolerability of a 20-mg dose of methylphenidate for the treatment of daytime sleepiness in adult patients with myotonic dystrophy type 1: a 2-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 3-week crossover trial. Clin Ther. 2012;34:1103–11.
Talbot K, Stradling J, Crosby J, Hilton-Jones D. Reduction in excess daytime sleepiness by modafinil in patients with myotonic dystrophy. Neuromuscul Disord. 2003;13:357–64.
Gilmartin JJ, Cooper BG, Griffiths CJ, Walls TJ, Veale D, Stone TN, et al. Breathing during sleep in patients with myotonic dystrophy and non-myotonic respiratory muscle weakness. Q J Med. 1991;78:21–31.
Guilleminault C, Philip P, Robinson A. Sleep and neuromuscular disease: bilevel positive airway pressure by nasal mask as a treatment for sleep disordered breathing in patients with neuromuscular disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1998;65:225–32.
Manni R, Zucca C, Martinetti M, Ottolini A, Lanzi G, Tartara A. Hypersomnia in dystrophia myotonica: a neurophysiological and immunogenetic study. Acta Neurol Scand. 1991;84:498–502.
•• Yu H, Laberge L, Jaussent I, Bayard S, Scholtz S, Raoul M, et al. Daytime sleepiness and REM sleep characteristics in myotonic dystrophy: a case-control study. Sleep. 2011;34:165–70. This first age-, sex-matched case-control study demonstrated higher frequency of daytime sleepiness and abnormalities in REM sleep regulation, with an increased daytime and nighttime REM sleep propensity, REM density, and PLMS. These data strongly support the hypothesis of a primary central sleep regulation dysfunction in DM1.
Giubilei F, Antonini G, Bastianello S, Morino S, Paolillo A, Fiorelli M, et al. Excessive daytime sleepiness in myotonic dystrophy. J Neurol Sci. 1999;164:60–3.
Romigi A, Izzi F, Pisani V, Placidi F, Pisani LR, Marciani MG, et al. Sleep disorders in adult-onset myotonic dystrophy type 1: a controlled polysomnographic study. Eur J Neurol. 2011;18:1139–45.
Broughton R, Stuss D, Kates M, Roberts J, Dunham W. Neuropsychological deficits and sleep in myotonic dystrophy. Can J Neurol Sci. 1990;17:410–5.
Cirignotta F, Mondini S, Zucconi M, Barrot-Cortes E, Sturani C, Schiavina M, et al. Sleep-related breathing impairment in myotonic dystrophy. J Neurol. 1987;235:80–5.
Laberge L, Bégin P, Dauvilliers Y, Beaudry M, Laforte M, Jean S, et al. A polysomnographic study of daytime sleepiness in myotonic dystrophy type 1. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009;80:642–6.
Ciafaloni E, Mignot E, Sansone V, Hilbert JE, Lin L, Lin X, et al. The hypocretin neurotransmission system in myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neurology. 2008;70:226–30.
Cummiskey J, Guilleminault C, Davis R, Duncan K, Golden J. Automatic respiratory failure: sleep studies and Leigh's disease (case report). Neurology. 1987;37:1876–8.
Gibbs 3rd JW, Ciafaloni E, Radtke RA. Excessive daytime somnolence and increased rapid eye movement pressure in myotonic dystrophy. Sleep. 2002;25:672–5.
Martinez-Rodriguez JE, Lin L, Iranzo A, Genis D, Marti MJ, Santamaria J, et al. Decreased hypocretin-1 (orexin-A) levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with myotonic dystrophy and excessive daytime sleepiness. Sleep. 2003;26:287–90.
Laberge L, Lacroix G, Bégin P, Beaudry M, Mathieu J. Psychomotor vigilance performance is associated with objective daytime sleepiness in myotonic dystrophy. J Sleep Res. 2004;13:421.
Bennett LS, Stradling JR, Davies RJ. A behavioral test to assess daytime sleepiness in obstructive sleep apnoea. J Sleep Res. 1997;6:142–5.
Bégin P, Mathieu J, Almirall J, Grassino A. Relationship between chronic hypercapnia and inspiratory-muscle weakness in myotonic dystrophy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;156:133–9.
Coccagna G, Martinelli P, Lugaresi E. Sleep and alveolar hypoventilation in myotonic dystrophy. Acta Neurol Belg. 1982;82:185–94.
Finnimore AJ, Jackson RV, Morton A, Lynch E. Sleep hypoxia in myotonic dystrophy and its correlation with awake respiratory function. Thorax. 1994;49:66–70.
Guilleminault C, Cummiskey J, Motta J, Lynne-Davies P. Respiratory and hemodynamic study during wakefulness and sleep in myotonic dystrophy. Sleep. 1978;1:19–31.
Serisier DE, Mastaglia FL, Gibson GJ. Respiratory muscle function and ventilatory control. I in patients with motor neurone disease, II in patients with myotonic dystrophy. Q J Med. 1982;51:205–26.
Kiyan E, Okumus G, Cuhadaroglu C, Deymeer F. Sleep apnea in adult myotonic dystrophy patients who have no excessive daytime sleepiness. Sleep Breath. 2010;14:19–24.
Pincherle A, Patruno V, Raimondi P, Moretti S, Dominese A, Martinelli-Boneschi F, et al. Sleep breathing disorders in 40 Italian patients with Myotonic dystrophy type 1. Neuromuscul Disord. 2012;22:219–24.
•• Minnerop M, Weber B, Schoene-Bake JC, Roeske S, Mirbach S, Anspach C, et al. The brain in myotonic dystrophy 1 and 2: evidence for a predominant white matter disease. Brain. 2011;134:3530–46. This study is notable because it compared the brain involvement of individuals with DM1 and DM2 with that of a healthy control group using structural brain magnetic resonance imaging. It revealed extensive white matter involvement in the whole brain, brainstem, and corpus callosum together with grey matter decrease in cortical areas, thalamus, and putamen in DM1. Furthermore, white matter alteration was found to be associated with age/disease duration, but not with daytime sleepiness.
Culebras A, Podolsky S, Leopold NA. Absence of sleep-related growth hormone elevations in myotonic dystrophy. Neurology. 1977;27:165–7.
Johansson A, Carlstrom K, Ahren B, Cederquist K, Krylborg E, Forsberg H, et al. Abnormal cytokine and adrenocortical hormone regulation in myotonic dystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:3169–76.
Culebras A, Feldman RG, Merk FB. Cytoplasmic inclusion bodies within neurons of the thalamus in myotonic dystrophy. A light and electron microscope study. J Neurol Sci. 1973;19:319–29.
Ono S, Kanda F, Takahashi K, Fukuoka Y, Jinnai K, Kurisaki H, et al. Neuronal loss in the medullary reticular formation in myotonic dystrophy: a clinicopathological study. Neurology. 1996;46:228–31.
Ono S, Kurisaki H, Sakuma A, Nagao K. Myotonic dystrophy with alveolar hypoventilation and hypersomnia: a clinicopathological study. J Neurol Sci. 1995;128:225–31.
Ono S, Takahashi K, Jinnai K, Kanda F, Fukuoka Y, Kurisaki H, et al. Loss of catecholaminergic neurons in the medullary reticular formation in myotonic dystrophy. Neurology. 1998;51:1121–4.
Dauvilliers Y, Baumann CR, Carlander B, Bischof M, Blatter T, Lecendreux M, et al. CSF hypocretin-1 levels in narcolepsy, Kleine-Levin syndrome, and other hypersomnias and neurological conditions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003;74:1667–73.
Timchenko LT. Myotonic dystrophy: the role of RNA CUG triplet repeats. Am J Hum Genet. 1999;64:360–4.
Jiang H, Mankodi A, Swanson MS, Moxley RT, Thornton CA. Myotonic dystrophy type 1 is associated with nuclear foci of mutant RNA, sequestration of muscleblind proteins, and deregulated alternative splicing in neurons. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13:3079–88.
Loube DI, Gay PC, Strohl KP, Pack AL, White DP, Collop NA. Indications for positive airway pressure treatment of adult obstructive sleep apnea patients: a consensus statement. Chest. 1999;115:863–6.
Nugent AM, Smith IE, Shneerson JM. Domiciliary-assisted ventilation in patients with myotonic dystrophy. Chest. 2002;121:459–64.
Morgenthaler TI, Kapur VK, Brown T, Swick TJ, Alessi C, Aurora RN, et al. Practice parameters for the treatment of narcolepsy and other hypersomnias of central origin. Sleep. 2007;30:1705–11.
Annane D, Moore DH, Barnes PR, Miller RG. Psychostimulants for hypersomnia (excessive daytime sleepiness) in myotonic dystrophy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;3:CD003218.
Disclosure
Luc Laberge declares no conflict of interest. Cynthia Gagnon declares no conflict of interest. Yves Dauvilliers has received consulting fees/honoraria from UCB, Bioprojet, Cephalon, Novartis, and JAZZ, served on advisory boards for UCB, Bioprojet, Cephalon, and JAZZ, and served on speakers’ bureaus for UCB, Bioprojet, Cephalon, and Novartis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Sleep
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laberge, L., Gagnon, C. & Dauvilliers, Y. Daytime Sleepiness and Myotonic Dystrophy. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 13, 340 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-013-0340-9
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-013-0340-9