Abstract
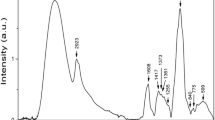
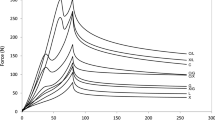
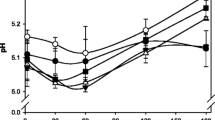
In attempts to produce a low-fat cheese with a rheology and texture similar to that of a full-fat cheese, guar gum (within 0.0025–0.01%; w/v, final concentration) was added to low-fat milk. The obtained cheeses were characterised regarding their physicochemical, thermal, rheological and textural properties. Control cheeses were also produced with low and full-fat milk. The physicochemical properties of the guar gum modified cheeses were similar to those of the low-fat control. No significant differences were detected in the thermal properties (concerning the enthalpy and profile of water desorption) among all types of cheeses. The rheological behaviour of the 0.0025% modified cheese was very similar to the full-fat control. Overall, no trend was observed in the texture profile (hardness, cohesiveness, gumminess and elasticity) of the modified cheeses versus guar gum concentration, as well as in comparison with the control groups, suggesting that none of the studied polysaccharide concentrations simulated the textural functions of fat in Edam cheese.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC (1980) Official methods of analysis, 13th ed. In: W. Horwitz Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Arlington, VA. pp 376–384.
Bourriot, S., Garnier, C., & Doublier, J.-L. (1999). Phase separation, rheology and microstructure of micellar casein–guar gum mixtures. Food Hydrocolloids, 13(1), 43–49.
Bullens, C., Krawczyk, G., & Geithman, L. (1994). Reduced-fat cheese products using carrageenan and microcrystalline cellulose. Food Technology, 48(1), 79–81.
Clark, A. H., & Ross-Murphy, S. B. (1987). Structural and mechanical properties of biopolymer gels. Advance in Polymer Science, 83, 55–192.
Dourado, F., Mota, M., Pala, H., & Gama, F. M. (1999). Effect of Cellulase adsorption on the surface and interfacial properties of cellulose. Cellulose, 6(4), 265–282.
Dourado, F., Bastos, M., Mota, M., & Gama, F. M. (2002). Studies on the properties of Celluclast/Eudragit L-100 conjugate. Journal of Biotechnology, 99(2), 21–131.
Fox, J. E. (1992). Seed gums. In A. Imerson (Ed.), Thickening and gelling agents for food (pp. 153–170). Glasgow: Blackie.
INE (2002) Estatísticas Agro-Industriais – Leite e Derivados 1996-2000. In http://www.ine.pt/xportal/xmain?xpid=INE&xpgid=ine_publicacoes&PUBLICACOESpub_boui=140523&PUBLICACOESmodo=2
Kailasapathy, K. (1998). Effect of adding carrageenan and gellan gums on yield and textural quality of Caerphilly cheese. Milchwissenschaft, 53(8), 446–449.
Kanombirira, S., & Kailasapathy, K. (1995). Effects of interactions of carrageenan and gellan gum on yields, textural and sensory attributes of Cheddar cheese. Milchwissenschaft, 50(8), 452–458.
Kavas, G., Oysun, G., Kinik, O., & Uysal, H. (2004). Effect of some fat replacers on chemical, physical and sensory attributes of low-fat white pickled cheese. Food Chemistry, 88(3), 381–388.
Küçüköner, E., & Haque, Z. U. (2003). Physico-chemical and rheological properties of full fat and low fat Edam cheeses. European Food Research and Technology, 217(3), 281–286.
Lobato-Calleros, C., Robles-Martinez, J. C., Caballero-Perez, J. F., & Aguirre-Mandujano, E. (2001). Fat replacers in low-fat Mexican Manchego cheese. Journal of Texture Studies, 32(1), 1–14.
Ma, L., Drake, M. A., Barbosa-Cánovas, G. V., & Swanson, B. G. (1997). Rheology of full-fat and low-fat Cheddar cheeses as related to type of fat mimetic. Journal of Food Science, 62(4), 748–752. Emmental cheese. Lait, 84, 343-358.
Mistry, V. V. (2001). Low fat cheese technology. International Dairy Journal, 11(4–7), 413–422.
Raju, N. P., & Pal, D. (2009). The Physico-chemical, Sensory, and Textural Properties of Misti Dahi Prepared from Reduced Fat Buffalo Milk. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2(1), 101–108.
Robinson, G., Ross-Murphy, S. B., & Morris, E. R. (1982). Viscosity-molecular weight relationships, intrinsic chains flexibility, and dynamic solution properties of guar galactomannan. Carbohydrate Research, 107(1), 17–32.
Romieh, E. A., Michaelidou, A., Biliaderis, C. G., & Zerfiridis, G. K. (2002). Low-fat white-brined cheese made from bovine milk and two commercial fat mimetics: chemical, physical and sensory attributes. International Dairy Journal, 12(6), 525–540.
Saldo, J., Sendra, E., & Guamis, B. (2002). Changes in water binding in high-pressure treated cheese, measured by TGA (thermogravimetrical analysis). Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies, 3(3), 203–207.
Srivastava, M., & Kapoor, V. P. (2005). Seed galactomannans: an overview. Chemistry & Biodiversity, 2(3), 295–317.
Tan, Y. L., Ye, A., Singh, H., & Hemar, Y. (2007). Effects of biopolymer addition on the dynamic rheology and microstructure of renneted skim milk systems. Journal of Texture Studies, 38(3), 404–422.
Tunick, M. H. (2000). Rheology of dairy foods that gel, stretch, and fracture. Journal of Dairy Science, 83(8), 1892–1898.
Volikakis, P., Biliaderis, C. G., Vamvakas, C., & Zerfiridis, G. K. (2004). Effects of a commercial oat-β-glucan concentrate on the chemical, physico-chemical and sensory attributes of a low-fat white-brined cheese product. Food Research International, 37(1), 83–94.
Zisu, B., & Shah, N. P. (2005). Textural and functional changes in low-fat Mozzarella cheeses in relation to proteolysis and microstructure as influenced by the use of fat replacers, pre-acidification and EPS starter. International Dairy Journal, 15(6–9), 957–972.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliveira, N.M., Dourado, F.Q., Peres, A.M. et al. Effect of Guar Gum on the Physicochemical, Thermal, Rheological and Textural Properties of Green Edam Cheese. Food Bioprocess Technol 4, 1414–1421 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0324-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11947-010-0324-6