Abstract
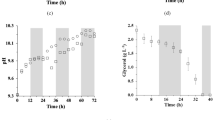
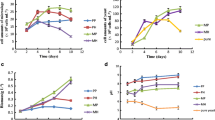
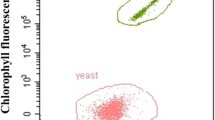
Mix cultivation of microalgae (Spirulina platensis) and yeast (Rhodotorula glutinis) for lipid production was studied. Mixing cultivation of the two microorganisms significantly increased the accumulation of total biomass and total lipid yield. Dissolved oxygen and medium components in the mixed fermentation medium were analyzed. Mix cultivation in monosodium glutamate wastewater was further studied. Result indicated 1,600 mg/L of biomass was obtained and 73% of COD were removed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keith, E. C., James, B. G., Scott, A. W., & Patrik, R. J. (1987). Journal of Microbiological Methods, 6, 333–345. doi:10.1016/0167-7012(87)90019-4.
Edward, C., Cirilo, N. H., Genta, K., Kenji, S., & Ayaaki, I. (2001). Process Biochemistry, 37, 65–71. doi:10.1016/S0032-9592(01)00178-9.
Xue, F. Y., Zhang, X., Luo, H., & Tan, T. W. (2006). Process Biochemistry, 41, 1699–1702. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2006.03.002.
Zhao, Z. B. (2005). Biotech-world (Chinese Journal), 12, 62–63.
Yan, Z., & Chen, J. (2003). Journal of Cereal & Oils (Chinese Journal), 7, 13–15.
Seraphim, P., Michael, K., & George, A. (2004). Bioresource Technology, 95, 287–291. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2004.02.016.
Lin, Y.H., et al. (2007). Biochemical Engineering Journal, 37, 166–176. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2007.04.014.
Stredansky, M., Conti, E., & Salaris, A. (2000). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 26, 304–307. doi:10.1016/S0141-0229(99)00146-5.
Peng, W. M., Wu, Q. G., Tu, P. G., & Zhao, N. M. (2001). Bioresource Technology, 80, 1–7. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00072-4.
Aaronson, S., Berner, T., & Dubinsky, Z. (1980). Microalgae. As a source of chemicals and natural products. In G. Shelef, & C. J. Soeder (Eds.), Algae biomass, production and use, (575–601). Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier-North Holland.
Kiet, P. Q., & Jean, P. D. (1997). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1346, 237–246.
Shi, A. H., & Zhou, B. (2003). Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 24, 48–51.
Jose, L. P., Gloria, Z. C., Maria, C., & Zaccaro, M. (1998). International Journal of Food Microbiology, 45, 225–228. doi:10.1016/S0168-1605(98)00151-2.
Yoshitomo, W., & David, O. H. (1995). Energy Conversion, 36, 721–724. doi:10.1016/0196-8904(95)00106-N.
Bligh, E. G., & Dyer, W. J. (1959). Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology, 35, 911–917.
Shang, F., Wen, S. H., Wang, X., & Tan, T. W. (2006). Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 101, 38–41. doi:10.1263/jbb.101.38.
Marquez, F. J. J. (1993). Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 76, 408–410. doi:10.1016/0922-338X(93)90034-6.
Chen, T. F., Zheng, W. J., Yang, F., & Bai, Y. (2006). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 39, 103–107. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.10.001.
Ragaerta, P., Devliegherea, F., Loosa, S., Dewulfb, J., Langenhoveb, H. V., & Debeverea, J. (2006). Food Microbiology, 23, 154–161. doi:10.1016/j.fm.2005.02.002.
Jorge, A., Vieira, C., Luciane, M. C., & Paulp, F. D. (2004). Bioresource Technology, 92, 237–241. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2003.09.013.
Li, Y., Zhao, Z. B., et al. (2007). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 41, 312–317. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2007.02.008.
Acknowledgements
We wish to express our thanks for the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 20576013), Nature Fund for Outstanding Youth (grant no. 20325622), Beijing WWF (grant no. 2071002), Beijing Science And Technology Projects (grant no. D0205004040211), the National Basic Research 973 Program of China (grant nos. 2007CB707804 and 2007CB714304), and the National High Technology Research and Development 863 Program of China (grant nos. 2006AA020103, 2006AA020102, and 2006AA020201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, F., Miao, J., Zhang, X. et al. A New Strategy for Lipid Production by Mix Cultivation of Spirulina platensis and Rhodotorula glutinis . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160, 498–503 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8376-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8376-z