Abstract
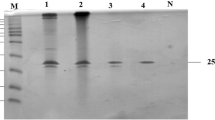
An aerobic xylanolytic moderately halophilic and alkali-tolerant bacterium, Gracilibacillus sp. TSCPVG, produces multiple xylanases of unusual halo-acid-alkali-thermo-stable nature. The purification of a major xylanase from TSCPVG culture supernatant was achieved by hydrophobic and gel permeation chromatographic methods followed by electroelution from preparatory PAGE. The molecular mass of the purified xylanase was 42 kDa, as analyzed by SDS-PAGE, with a pI value of 6.1. It exhibited maximal activity in 3.5 % NaCl and retained over 75 % of its activity across the broad salinity range of 0–30 % NaCl, indicating a high halo-tolerance. It showed maximal activity at pH 7.5 and had retained 63 % of its activity at pH 5.0 and 73 % at pH 10.5, signifying the tolerance to broad acid to alkaline conditions. With birchwood xylan as a substrate, K m and specific activity values were 21 mg/ml and 1,667 U/mg, respectively. It is an endoxylanase that degrades xylan to xylose and xylobiose and had no activity on p-nitrophenyl-β-d-xylopyranoside, p-nitrophenyl-β-d-glucopyranoside, p-nitrophenyl acetate, carboxymethylcellulose, and filter paper. Since it showed remarkable stability over different salinities, broad pH, and temperature ranges, it is promising for application in many industries.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mortimer, J. C., Miles, G. P., Brown, D. M., Zhang, Z. N., Segura, M. P., Weimar, T., et al. (2010). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107, 17409–17414.
Kim, D. Y., Han, M. K., Lee, J. S., Oh, H.-W., Park, D.-S., Shin, D.-H., et al. (2009). Process Biochemistry, 44, 1055–1059.
Chen, X., Vega-Sánchez, M. E., Verhertbruggen, Y., Chiniquy, D., Canlas, P. E., Fagerström, A., et al. (2012). Molecular Plant, 6, 570–573.
Ahmed, S., Riaz, S., & Jamil, A. (2009). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 84, 19–35.
Badhan, A. K., Chadha, B. S., Kaur, J., Saini, H. S., & Bhat, M. K. (2007). Bioresource Technology, 98, 504–510.
Zhang, G. M., Huang, J., Huang, G. R., Ma, L. X., & Zhang, X. E. (2007). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 74, 339–346.
Wang, K., Luo, H., Tian, J., Turunen, O., Huang, H., Shi, P., et al. (2014). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80, 2158–2165.
Collins, T., Gerday, C., & Feller, G. (2005). FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 29, 3–23.
St. John, F. J., Gonzalez, J. M., & Pozharski, E. (2010). FEBS Letters, 584, 4435–4441.
Lenartovicz, V., Souza, C. G. M., Moreira, F. G., & Peralta, R. M. (2002). Journal of Basic Microbiology, 42, 388–395.
Carmona, E. C., Fialho, M. B., Buchgnani, E. B., Coelho, G. D., Brocheto-Braga, M. R., & Jorge, J. A. (2005). Process Biochemistry, 40, 359–364.
Tachaapaikoon, C., Kyu, K. L., & Ratanakhanokchai, K. (2006). Process Biochemistry, 41, 2441–2445.
Dhillon, A., Gupta, J. K., & Khanna, S. (2000). Process Biochemistry, 35, 849–856.
Merchant, R., Merchant, F., & Margaritis, A. (1988). Biotechnology Letters, 10, 513–516.
Zheng, H., Liu, Y., Sun, M., Han, Y., Wang, J., Sun, J., et al. (2014). Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 41, 153–162.
Wejse, P. L., Ingvorsen, K., & Mortensen, K. K. (2003). Extremophiles, 7, 423–431.
Waino, M., & Ingvorsen, K. (2003). Extremophiles, 7, 87–93.
Wejse, P. L., Ingvorsen, K., & Mortensen, K. K. (2003). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 32, 721–727.
Prakash, S., Veeranagouda, Y., Kyoung, L., & Sreeramulu, K. (2009). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 25, 197–204.
Giridhar, P. V., & Chandra, T. S. (2010). Process Biochemistry, 45, 1730–1737.
Wang, C. Y., Chan, H., Lin, H. T., & Shyu, Y. T. (2010). Annals of Applied Biology, 156, 187–197.
Hung, K. S., Liu, S. M., Tzou, W. S., Lin, F. P., Pan, C. L., Fang, T. Y., et al. (2011). Process Biochemistry, 46, 1257–1263.
Menon, G., Mody, K., Keshri, J., & Jha, B. (2010). Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 15, 998–1005.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. C., & Randall, R. J. (1951). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 193, 265–275.
Sa-Pereira, P., Duarte, J., & Costa-Ferreira, M. (2000). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 27, 95–99.
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Nature (London), 227, 680–685.
Breccia, J. D., Baigori, M. D., Castro, G. R., & Sineriz, F. (1995). Biotechnology Techniques, 9, 145–148.
Shrinivas, D., Savitha, G., Raviranjan, K., & Naik, G. R. (2010). Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162, 2049–2057.
Beg, Q. K., Kapoor, M., Mahajan, L., & Hoondal, G. S. (2001). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 56, 326–338.
Thiagarajan, S., Jeya, M., & Gunasekaran, P. (2006). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 22, 487–492.
Wong, K. K. Y., Tan, L. U. L., & Saddler, J. N. (1988). Microbiological Reviews, 52, 305–317.
Basaran, P., Basaran, N., & Hang, Y. D. (2000). World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 16, 545–550.
Bataillon, M., Cardinali, A. P. N., Castillon, N., & Duchiron, F. (2000). Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 26, 187–192.
Khasin, A., Alchnati, I., & Shoam, Y. (1993). Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 59, 1725–1730.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poosarla, V.G., Chandra, T.S. Purification and Characterization of Novel Halo-Acid-Alkali-Thermo-stable Xylanase from Gracilibacillus sp. TSCPVG. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173, 1375–1390 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0939-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0939-6