Abstract
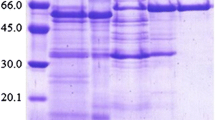
An alpha-galactosidase was purified from Pseudobalsamia microspora (PMG) to 1224.1-fold with a specific activity of 11,274.5 units/mg by ion-exchange chromatography and gel filtration. PMG is a monomeric protein with a molecular mass of 62 kDa as determined by SDS-PAGE and by gel filtration. Chemical modification using N-bromosuccinimide (NBS) resulted in a complete abrogation of the activity of PMG, suggesting that Trp is an amino acid essential to its activity. The activity was strongly inhibited by Hg2+, Cd2+, Cu2+, and Fe3+ ions. Three inner peptide sequences for PMG were obtained by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS–MS) analysis. When 4-nitrophenyl α-d-glucopyranoside (pNPGal) was used as substrate, the optimum pH and temperature of PMG were 5.0 and 55 °C, respectively. The Michaelis constant (K m) value of the alpha-galactosidase on pNPGal was 0.29 mM, and the maximal velocity (V max) was 0.97 μmol ml−1 min−1. Investigation by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) demonstrated its ability to hydrolyze raffinose and stachyose. Hence, it can be exploited in degradation of non-digestible oligosaccharides from food and feed industries.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Glasscock, H. H., & Ware, W. M. (1941). Investigations on the invasion of mushroom beds by Pseudobalsamia microspora. Annals of Applied Biology, 28, 85–90.
Sampietro, D., Quiroga, E., Sgariglia, M., Soberon, J., & Vattuone, M. A. (2012). A thermostable alpha-galactosidase from Lenzites elegans (Spreng.) ex Pat. MB445947: purification and properties. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 102, 257–267.
Liu, C. Q., & He, G. Q. (2012). Multiple alpha-galactosidases from Aspergillus foetidus ZU-G1: purification, characterization and application in soybean milk hydrolysis. European Food Research and Technology, 234, 743–751.
Shen, W., Li, Y., Chen, H., Jin, Z., Xu, X., Zhao, J., & Xie, Z. (2009). Purification and application of alpha-galactosidase from germinating coffee beans (Coffea arabica). European Food Research and Technology, 228, 969–974.
Cox, T. M. (1996). The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease: Vols I, II and III (7th edn). Trends in Genetics, 12, 78–79.
Liu, Q. P., Sulzenbacher, G., Yuan, H., Bennett, E. P., Pietz, G., Saunders, K., Spence, J., Nudelman, E., Levery, S. B., White, T., Neveu, J. M., Lane, W. S., Bourne, Y., Olsson, M. L., Henrissat, B., & Clausen, H. (2007). Bacterial glycosidases for the production of universal red blood cells. Nature Biotechnology, 25, 454–464.
Singh, N., & Kayastha, A. M. (2013). A novel application of Cicer alpha-galactosidase in reduction of raffinose family oligosaccharides in soybean flour. Journal of Plant Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 22, 353–356.
Brown, R. E., Jarvis, K. L., & Hyland, K. J. (1989). Protein measurement using bicinchoninic acid—elimination of interfering substances. Analytical Biochemistry, 180, 136–139.
Laemmli, U. K., & Favre, M. (1973). Maturation of head of bacteriophage-T4. 1. DNA packaging events. Journal of Molecular Biology, 80, 575–599.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Dwevedi, A., & Kayastha, A. M. (2009). Stabilization of beta-galactosidase (from peas) by immobilization onto amberlite MB-150 beads and its application in lactose hydrolysis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 57, 682–688.
Katrolia, P., Jia, H., Yan, Q., Song, S., Jiang, Z., & Xu, H. (2012). Characterization of a protease-resistant alpha-galactosidase from the thermophilic fungus Rhizomucor miehei and its application in removal of raffinose family oligosaccharides. Bioresource Technology, 110, 578–586.
Shibuya, H., Kobayashi, H., Sato, T., Kim, W. S., Yoshida, S., Kaneko, S., Kasamo, K., & Kusakabe, I. (1997). Purification, characterization, and cDNA cloning of a novel alpha-galactosidase from Mortierella vinacea. Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, 61, 592–598.
Du, F., Liu, Q., Wang, H., & Ng, T. (2014). Purification an alpha-galactosidase from Coriolus versicolor with acid-resistant and good degradation ability on raffinose family oligosaccharides. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 30, 1261–1267.
Wang, H., Shi, P., Luo, H., Huang, H., Yang, P., & Yao, B. (2014). A thermophilic alpha-galactosidase from Neosartorya fischeri P1 with high specific activity, broad substrate specificity and significant hydrolysis ability of soymilk. Bioresource Technology, 153, 361–364.
Ramalingam, Saraswathy, N., Sadasivam, S., Subha, K., & Poorani, N. (2007). Purification and properties of alpha-galactosidase from white-rot fungus Pleurotus florida. Indian Journal of Biochemistry & Biophysics, 44, 76–81.
Wang, H., Luo, H., Li, J., Bai, Y., Huang, H., Shi, P., Fan, Y., & Yao, B. (2010). An alpha-galactosidase from an acidophilic Bispora sp. MEY-1 strain acts synergistically with beta-mannanase. Bioresource Technology, 101, 8376–8382.
Mi, S., Meng, K., Wang, Y., Bai, Y., Yuan, T., Luo, H., & Yao, B. (2007). Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel alpha-galactosidase gene from Penicillium sp. F63 CGMCC 1669 and expression in Pichia pastoris. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 40, 1373–1380.
Shankar, S. K., Dhananjay, S. K., & Mulimani, V. H. (2009). Purification and characterization of thermostable alpha-galactosidase from Aspergillus terreus GR. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 152, 275–285.
Shibuya, H., Nagasaki, H., Kaneko, S., Yoshida, S., Park, G. G., Kusakabe, I., & Kobayashi, H. (1998). Cloning and high-level expression of alpha-galactosidase cDNA from Penicillium purpurogenum. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64, 4489–4494.
Garro, M. S., DeValdez, G. F., Oliver, G., & DeGiori, G. S. (1996). Purification of alpha-galactosidase from Lactobacillus fermentum. Journal of Biotechnology, 45, 103–109.
Falkoski, D. L., Guimaraes, V. M., Callegari, C. M., Reis, A. P., de Barros, E. G., & de Rezende, S. T. (2006). Processing of soybean products by semipurified plant and microbial alpha-galactosidases. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54, 10184–10190.
Zhou, J., Pan, L., Li, J., Tang, X., & Huang, Z. (2012). A novel alpha-galactosidase from Arthrobacter sp. GN14 isolated from Grus nigricollis feces: gene cloning, heterologous expression and characterization. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao = Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 52, 611–619.
Gote, M. M., Khan, M. I., & Khire, J. M. (2007). Active site directed chemical modification of α-galactosidase from Bacillus stearothermophilus (NCIM 5146): involvement of lysine, tryptophan and carboxylate residues in catalytic site. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 40, 1312–1320.
Ferreira, J. G., Reis, A. P., Guimaraes, V. M., Falkoski, D. L., Fialho, L. D. S., & de Rezende, S. T. (2011). Purification and characterization of Aspergillus terreus alpha-galactosidases and their use for hydrolysis of soymilk oligosaccharides. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 164, 1111–1125.
Singh, N., & Kayastha, A. M. (2012). Purification and characterization of alpha-galactosidase from white chickpea (Cicer arietinum). Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 60, 3253–3259.
Xu, H., Qin, Y., Huang, Z., & Liu, Z. (2014). Characterization and site-directed mutagenesis of an alpha-galactosidase from the deep-sea bacterium Bacillus megaterium. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 56, 46–52.
Du, F., Zhu, M., Wang, H., & Ng, T. (2013). Purification and characterization of an alpha-galactosidase from Phaseolus coccineus seeds showing degrading capability on raffinose family oligosaccharides. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 69, 49–53.
Goundar, R., & Mulimani, V. H. (2004). Purification and characterization of guar galactomannan degrading alpha-galactosidase from Aspergillus oryzae DR-5. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 14, 863–867.
Mulimani, V. H., & Ramalingam (1995). Enzymic hydrolysis of raffinose and stachyose in soymilk by alpha-galactosidase from Gibberella fujikuroi. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology International, 36, 897–905.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Grants of China (Biomass dissociation and low-molecular fragment green monomerization and transformation, 2010CB732202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, D., Tian, G., Du, F. et al. A Fungal Alpha-Galactosidase from Pseudobalsamia microspora Capable of Degrading Raffinose Family Oligosaccharides. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 176, 2157–2169 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1705-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-015-1705-0