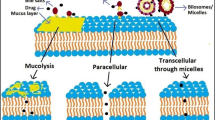
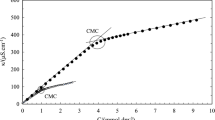
Abstract
In this review, bile salt, bile salt–surfactant, and bile salt–drug interactions and their solubilization studies are mainly focused. Usefulness of bile salts in digestion, absorption, and excretion of various compounds and their rare properties in ordering the shape and size of the micelles owing to the presence of hydrophobic and hydrophilic faces are taken into consideration while compiling this review. Bile salts as potential bio-surfactants to solubilize drugs of interest are also highlighted. This review will give an insight into the selection of drugs in different applications as their properties get modified by interaction with bile salts, thus influencing their solution behavior which, in turn, modifies the phase-forming behavior, microemulsion, and clouding phenomenon, besides solubilization. Finally, their future perspectives are taken into consideration to assess their possible uses as bio-surfactants without side effects to human beings.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hofmann, A. F., & Mekhjian, H. S. (1971). In P. P. Nair & D. Kritchevsky (Eds.), The bile acids, chemistry, physiology and metabolism (Vol. 2). New York: Plenum Press.
Chu, B. S., Rich, G. T., Ridout, M. J., Faulks, R. M., Wickham, M. S. J., & Wilde, P. J. (2009). Modulating pancreatic lipase activity with galactolipids: effects of emulsion interfacial composition. Langmuir, 25, 9352–9360.
Maldonado-Valderrama, J., Wilde, P., Macierzanka, A., & Mackie, A. (2011). The role of bile salts in digestion. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 165, 36–46.
Holm, R., Mullertz, A., & Mu, H. (2013). Bile salts and their importance for drug absorption. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 453, 44–55.
Madenci, D., & Egelhaaf, S. U. (2010). Self-assembly in aqueous bile salt solutions. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 15, 109–115.
Small, D. M., Penkett, S., & Chapman, D. (1969). Studies on simple and mixed bile salt micelles by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 21, 178–89.
Small, D. M. (1968). A classification of biologic lipids based upon their interaction in aqeous systems. Journal of American Oil Chemical Society, 45, 108–119.
Carey, M. C., Small, D. M., & Bliss, C. M. (1983). Lipid digestion and absorption. Annual Review Physiology, 45, 651–677.
Coreta-Gomes, F. M. I., Vaz, W. L., Wasielewski, E., Geraldes, C. F., & Moreno, M. J. (2012). Quantification of cholesterol solubilized in bile salt micellar aqueous solutions using (13)C nuclear magnetic resonance. Analytical Biochemistry, 427, 41–8.
Enhsen, A., Kramer, W., & Wess, G. (1998). Bile acids in drug discovery. Drug Discovery Today, 3, 409–418.
Davis, A. P. (2007). Bile acid scaffolds in supramolecular chemistry: the interplay of design and synthesis. Molecules, 12, 2106–2122.
Milhaj, P., Popovic, K., Cirin, D., & Farkas, Z. (2015). Binary mixed micelles of polysorbates (Tween 20 and Tween 60) and bile salts (Na-hyodeoxycholate and Na-cholate): regular solution theory and change of pKa values of micellar bile acid – a novel approach to estimate of the stability of the mixed micelles. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 396, 1–8.
Barry, B. W., & Gray, G. M. T. (1975). Mixed micelle formation in aqueous solutions of alkyltrimethylammonium cholates. Journal of Colloid Interface Science., 52, 314–325.
Barry, B. W., & Gray, G. M. T. (1975). Micelle formation and coacervation in mixtures of alkyltrimethylammonium bromides with di and trihydroxy bile salts. Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 52, 327–339.
George, A., Vora, S., Desai, H., & Bahadur, P. (1998). Mixed micelles of cationic surfactants and bile acid salts in aqueous media. Journal of Surfactants and Detergents, 1, 507–514.
Vethamuthu, M. S., Almgren, M., Brown, W., & Mukhtar, E. (1995). Aggregate structure, gelling, and coacervation within the L1 phase of the quasi-ternary system alkyltrimethylammonium bromide-sodium desoxycholate-water. Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 174, 461–479.
Small, D. M. (1971). In P. P. Nair & D. Kritchevsky (Eds.), bile acids. New York: Plenum Press.
Vethamuthu, M. S., Almgren, M., Karlsson, G., & Bahadur, P. (1996). Effect of sodium chloride and varied alkyl chain length on aqueous cationic surfactant−bile salt systems. cryo-TEM and fluorescence quenching studies. Langmuir, 12, 2173–2185.
Small, D. M., & Bourges, M. (1966). Lyotropic paracrystalline phases obtained with ternary and quaternary systems of amphiphilic substances in water: studies on aqueous systems of lecithin, bile salt, and cholesterol. Molecular Crystals, 1, 541–561.
Fontell, K. (1965). The micellar structure of bile salt solutions. In P. Ekwall, K. Groth, & V. Runnstro¨m-Reio (Eds.), surface chemistry (pp. 252–267). Copenhagen: Munksgaard.
Malik, N. A., & Anwar, A. (2016). Krafft temperature and thermodynamic study of interaction of glycine, diglycine, and triglycine with hexadecylpyridinium chloride and hexadecylpyridinium bromide: a conductometric approach. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 213, 213–220.
Reis, S., Moutinho, C. G., Matosa, C., de Castroc, B., Paula Gameiroc, P., & Lima, J. L. F. C. (2004). Noninvasive methods to determine the critical micelle concentration of some bile acid salts. Analytical Biochemistry, 334, 117–126.
Sridevi, N., & Prabhune, A. A. (2009). Brevibacillus sp: a novel thermophilic source for the production of bile salt hydrolase. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 157, 257–262.
Li, G., & McGown, L. B. (1994). Model for bile salt micellization and solubilization from studies of a “polydisperse” array of fluorescent probes and molecular modeling. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 98, 13711–13719.
Pavlovic, N., Stankov, K., & Mikov, M. (2012). Probiotics-interactions with bile acids and impact on cholesterol metabolism. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 168, 1880–1895.
Zana, R. (1978). The role of hydrogen bonding in the formation of bile salt micelles. Comments. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 82, 2440–2443.
Oakenfull, D. G., & Fisher, L. R. (1978). The role of hydrogen bonding in the formation of bile salt micelles. Reply to comments. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 82, 2443–2445.
Fisher, L. R., & Oakenfull, D. G. (1980). The role of hydrogen bonding in the formation of bile salt micelles. 2. A demonstration of geometric effects on the stabilizing role of hydrogen bonding. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 84, 936–937.
Ventaketusan, P., Cheng, Y., & Kahne, D. (1994). Hydrogen Bonding in Micelle Formation. Journal of American Chemical Society, 116, 6955–6956.
Carey, M. C., & Small, D. M. (1969). Micellar properties of dihydroxy and trihydroxy bile salts: effects of counterion and temperature. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 31, 382–396.
Seret, A., & Bahri, A. (2009). The CMC-like behaviour of bile salts as probed by photoexcited Rose Bengal. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 339, 153–158.
Hinze, W. L., Hu, W., Quina, F. H., & Mohammadzai, I. U. (2000). Bile acid/salt surfactant systems: general properties and survey of analytical applications. In W. L. Hinze (Ed.), Organized Assemblies in Chemical Analysis (pp. 1–70). Stamford, CT: JAI Press.
Matsuoka, K., Maeda, M., & Moroi, Y. (2003). Micelle formation of sodium glyco- and taurocholates and sodium glyco- and taurodeoxycholates and solubilization of cholesterol into their micelles. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 32, 87–95.
Sugioka, H., & Moroi, Y. (1998). Micelle formation of sodium cholate and solubilization into the micelle. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Lipids and Lipid Metabolism, 1394, 99–110.
Megyesi, M., & Biczók, L. (2007). Berberine alkaloid as a sensitive fluorescent probe for bile salt aggregates. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 111, 5635–5639.
Philp, D., & Stoddart, J. F. (1996). Self-assembly in natural and unnatural systems. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 35, 1154–1196.
Paul, S., & Patey, G. N. (2007). The influence of urea and trimethylamine-N-oxide on hydrophobic interactions. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 111, 7932–7933.
Tanford, C. (1980). The hydrophobic effect. New York: Wiley.
Israelachvili, J. N. (1992). Intermolecular and surface forces. London: Academic.
Hofmann, A. F., & Small, D. M. (1967). Detergent properties of bile salts: correlation with physiological function. Annual Review of Medicine, 18, 333–376.
Carey, M. C., & Small, D. M. (1970). The characteristics of mixed micellar solutions with particular reference to bile. The American Journal of Medicine, 49, 590–608.
Carey, M. C., & Small, D. M. (1972). Micelle formation by bile salts. Physical-chemical and thermodynamic considerations. Archives of Internal Medicine, 130, 506–527.
Oakenfull, D. G., & Fisher, L. R. (1977). The role of hydrogen bonding in the formation of bilesalt. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 81, 1838–1841.
Kawamura, H., Murata, Y., Yamaguchi, T., Igimi, H., Tanaka, M., Sugihara, G., & Kratovihil, J. P. (1989). Spin label studies of bile salt micelles. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 93, 3321–3326.
Warren, D. B., Chalmers, D. K., Hutchinson, K., Dang, W., & Poton, C. W. (2006). Molecular dynamics simulation of spontaneous bile salt aggregation. Colloids and Surfaces A, 280, 182–93.
Hofmann, A. F. (1999). Bile acids: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Physiology, 14, 24–29.
Ulmius, J., Lindblom, G., Wennerstrom, H., Johansson, L. B., Fontell, K., Soderman, O., & Arvidson, G. (1982). Molecular organization in the liquid-crystalline phases of lecithin--sodium cholate-water systems studied by nuclear magnetic resonance. Biochemistry, 21, 1553–1560.
Hjelm, R. P., Jr., Thiyagarajan, P., & Alkan-Onyuksel, H. (1992). Organization of phosphatidylcholine and bile salt in rodlike mixed micelles. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 96, 8653–8661.
Long, A. M., Kaler, E. W., Lee, S. P., & Wignall, G. D. (1994). Characterization of lecithin-taurodeoxycholate mixed micelles using small-angle neutron scattering and static and dynamic light scattering. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 98, 4402–4410.
Schubert, R., Beyer, K., Wolburg, H., & Schmidt, K. H. (1986). Structural changes in membranes of large unilamellar vesicles after binding of sodium cholate. Biochemistry, 25, 5263–5269.
Lichtenberg, D., Zilberman, Y., Greenzaid, P., & Zamir, S. (1979). Structural and kinetic studies on the solubilization of lecithin by sodium deoxycholate. Biochemistry, 18, 3517–3525.
Almog, S., Kushnir, T., Nir, S., & Lichtenberg, D. (1986). Kinetic and structural aspects of reconstitution of phosphatidylcholine vesicles by dilution of phosphatidylcholine-sodium cholate mixed micelles. Biochemistry, 25, 2597–2605.
Small, D. M. (1971). In P. P. Nair & D. Kritchevsky (Eds.), The bile acids: chemistry, physiology and metabolism (Vol. 1). New York: Plenum.
Ju, C., & Bohn, C. (1996). Dynamics of probe complexation to bile salt aggregates. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 100, 3847–3854.
Mukherjee, B., Dar, A. A., Bhat, P. A., Moulik, S. P., & Das, A. R. (2015). Micellization and adsorption behavior of bile salt systems. RSC Advances. doi:10.1039/c5ra20909a.
Fontell, K. (1971). Micellar behaviour in solutions of bile-acid salts. Kolloid-Zeitschrift und Zeitschrift für Polymere, 246, 710–718.
Camile, W. (2003). The practice of medicinal chemistry. Oxford: Academic.
De Castro, B., Gameiro, P., Guimaraes, C., Lima, J. L. F. C., & Reis, S. (2001). Study of partition of nitrazepam in bile salt micelles and the role of lecithin. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 24, 595–602.
Bowe, C., Mokhtarzadeh, L., Venkatesen, P., Babu, S., Axelrod, H., Sofia, M. J., Kakarla, R., Chan, T. Y., Kim, J. S., Lee, H. J., Amidon, G. L., Choe, S. Y., Walker, S., & Kahne, D. (1997). Design of compounds that increase the absorption of polar molecules. In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 94 (pp. 12218–12223).
Gordon, G. S., Moses, A. C., Silver, R. D., Flier, J. R., & Carey, M. C. (1985). Nasal absorption of insulin: enhancement by hydrophobic bile salts. In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 82 (pp. 7419–7423).
Roda, A., Hofmann, A. F., & Mysels, K. J. (1983). The influence of bile salt structure on self-association in aqueous solutions. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 258, 6362–6370.
Zana, R., & Guveli, D. (1985). Fluorescence probing study of the association of bile salts in aqueous solutions. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 89, 1687–1690.
Small, D. M. (1968). Size and structure of bile salt micelles influence of structure, concentration, counterion concentration, pH, and temperature. Advances in Chemistry, 84, 31–52.
Small, D. M. (1971). In P. P. Nair & D. KritMukuchevsky (Eds.), The bile acids (Vol. 1, p. 249). New York: Plenum Press.
Kratohvil, J. (1984). Size of bile salt micelles: techniques, problems and results. Hepatology, 4, 85S–95S.
Roy, A., Kundu, N., Banik, D., Kuchlyan, J., & Sarkar, N. (2015). How does bile salt penetration affect the self-assembled architecture of pluronic P123 micelles? – light scattering and spectroscopic investigations. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 17, 19977–19990.
Malik, N. A. (2015). Surfactant–amino acid and surfactant–surfactant interactions in aqueous medium: a review. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 176, 2077–2106.
Pártay, L. B., & Jedlovszky, P. (2007). Molecular Aggregates in Aqueous Solutions of Bile Acid Salts. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 111, 9886–9896.
Matsuoka, K., & Moroi, Y. (2002). Micelle formation of sodium deoxycholate and sodium ursodeoxycholate (Part 1). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1580, 189–199.
Heinze, W. L. (1996). Organized assemblies in chemical analysis (Vol. 2). JAI: Press.
Furusawa, T., & Matuura, R. (1967). Surface chemistry of gallstone formation. Hyomen (Surface), 5, 749–764.
Cabral, D. J., & Small, D. M. (1989). In S. G. Schultz, J. G. Forte, & B. B. Rauner (Eds.), Handbook of physiology (Vol. 3, pp. 621–662). New York: Waverly Press.
Erlinger, S. (1987). Physiology of bile secretion and enterohepatic circulation in physiology of the gastrointestinal tract. New York: Raven.
Coello, A., Meijide, F., Nunez, E. R., & Tato, J. V. (1993). Aggregation behavior of sodium cholate in aqueous solution. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 97, 10186–10191.
Coello, A., Meijide, F., Nunez, E. R., & Tato, J. V. (1996). Aggregation behavior of bile salts in aqueous solution. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 85, 9–15.
Lefebvre, P., Cariou, B., Lien, F., Kuipers, F., & Staels, B. (2009). Role of bile acids and bile acid receptors in metabolic regulation. Physiological Reviews, 89, 147–191.
Funasaki, N., Fukuba, T., Kitagawa, M., Nomura, M., Ishikawa, S., Hirota, S., & Neya, S. (2004). Two-dimensional NMR study on the structures of micelles of sodium taurocholate. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 108, 438–443.
Pártay, L. B., Sega, M., & Jedlovszky, P. (2007). Morphology of bile salt micelles as studied by computer simulation methods. Langmuir, 23, 12322–12328.
Small, D. M., Penkett, S. A., & Chapman, D. (1969). Studies on simple and mixed bile salt micelles by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Lipids and Lipid Metabolism, 176, 178–189.
Esposito, G., Giglio, E., Pavel, N. V., & Zanobi, A. (1987). Size and shape of sodium deoxycholate micellar aggregates. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 91, 356–362.
Lopez, F., Samseth, J., Mortensen, K., Rosenqvist, E., & Rouch, J. (1996). Micro- and macrostructural studies of sodium deoxycholate micellar complexes in aqueous solutions. Langmuir, 12, 6188–6196.
Mysels, K. J. (1984). Surface tension studies of bile salt association. Hepatology, 4, 80S–84S.
Spivak, W., Morrison, C., Devinuto, D., & Yuey, W. (1988). Spectrophotometric determination of the critical micellar concentration of bile salts using bilirubin monoglucuronide as a micellar probe. Utility of derivative spectroscopy. Biochemical Journal, 252, 275–281.
Hofmann, A. F., & Rods, A. (1984). Physicochemical properties of bile acids and their relationship to biological properties: an overview of the problem. Journal of Lipid Research, 25, 1477–1489.
Schurtenberger, P., Mazer, N., & Kaenzig, W. (1985). Micelle to vesicle transition in aqueous solutions of bile salt and lecithin. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 89, 1042–1049.
Simonovi, B. R., & Momirovi, M. (1997). Determination of critical micelle concentration of bile acid salts by micro-calorimetric titration. Mikrochimica Acta, 127, 101–104.
Subuddhi, U., & Mishra, A. K. (2007). Micellization of bile salts in aqueous medium: a fluorescence study. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 57, 102–107.
Wu, N., Barker, G. E., & Huie, C. W. (1994). Separation of porphyrins and porphyrin isomers in capillary electrophoresis using mixed ionic surfactant-bovine serum albumin buffer systems. Journal of Chromatography A, 659, 435–442.
Kratohvil, J. P. (1986). Size of bile salt micelles: techniques, problems and results. Advanced Colloid and Interface Science, 26, 131–154.
Schurtenberger, P., Mazer, N., & Kaenzig, W. (1983). Static and dynamic light scattering studies of micellar growth and interactions in bile salt solutions. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 87, 308–315.
Warren, D. B., Chalmers, D. K., Hutchison, K., Dang, W., & Pouton, C. W. (2006). Molecular dynamics simulations of spontaneous bile salt aggregation. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 280, 182–193.
Mohapatra, M., & Mishra, A. K. (2010). 1-Naphthol as a sensitive fluorescent molecular probe for monitoring the interaction of submicellar concentration of bile salt with a bilayer membrane of DPPC, a lung surfactant. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 114, 14934–14940.
Maestre, A., Guardado, P., & Moyá, M. L. (2014). Thermodynamic study of bile salts micellization. Journal of Chemical Engineering Data, 59, 433–438.
Danielson, H. (1999). In P. P. Nair & D. Kritchvsky (Eds.), The bile acids: chemistry, physiology and metabolism (Vol. 1–3, p. 73). New York: Plenum.
Hofmann, A. F. (1999). In T. Northfield, P. L. Zentler-Munro, & R. P. Jazrawi (Eds.), Bile acids and hepatobiliary diseases (pp. 303–332). Boston: Kluwer.
Carey, M. C. (1983). In P. Avogadro (Ed.), Phospholipids and atherosclerosis (pp. 33–63). New York: Raven.
Hofmann, A. F. (1994). In I. M. Arias et al. (Eds.), The liver: biology and pathology (Thirdth ed., p. 667). New York: Raven.
Nair, P. P., & Kritchevsky, D. (1971). In P. P. Nair & D. Kritchvsky (Eds.), The bile acids: chemistry, physiology and metabolism (Vol. 1, pp. 1–9). New York: Plenum.
Borne, J., Nylander, T., & Khan, A. (2003). Vesicle formation and other structures in aqueous dispersions of monoolein and sodium oleate. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 257, 310–320.
Hammad, M. A., & Muller, B. W. (1998). Solubility and stability of tetrazepam in mixed micelles. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 7, 49–55.
Lee, S. S., Kiserow, D. J., & McGown, L. B. (1997). Enzyme solubilization in a reversed micellar microreactor with a bile salt cosurfactant. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 193, 32–40.
Keno, M., Kimoto, Y., Ikeda, Y., Momose, H., & Zana, R. (1987). Study on the aggregation number of mixed micelles in aqueous binary mixtures of the bile salts and nonionic surfactant. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 117, 179–186.
Jana, P. K., & Moulik, S. P. (1991). Interaction of bile salts with hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide and sodium dodecyl sulfate. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 95, 9525–9532.
Fernández-Leyes, M. D., Messina, P. V., & Schulz, P. C. (2007). Aqueous sodium dehydrocholate-sodium deoxycholate mixtures at low concentration. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 314, 659–664.
Clint, J. H. (1975). Micellization of mixed nonionic surface active agents. Journal of the Chemical Society, Faraday Transactions 1: Physical Chemistry in Condensed Phases, 71, 1327–1334.
Rubingh, D. N. (1979). In K. L. Mittal (Ed.), Solution Chemistry of Surfactants (pp. 337–354). New York: Plenum Press.
Holland, P. M., & Rubingh, D. N. (1983). Nonideal multicomponent mixed micelle model. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 87, 1984–1990.
Hidalgo-Rodríguez, M., Fuguet, E., Ràfols, C., & Rosés, M. (2010). Solute–solvent interactions in micellar electrokinetic chromatography: VII. Characterization of sodium cholate–sodium deoxycholate mixed-micellar systems. Journal of Chromatography A, 1217, 1701–1708.
Santhanalakshmi, J., Lakashmi, G. S., Aswal, V. K., & Goyal, P. S. (2001). Small-angle neutron scattering study of sodium cholate and sodium deoxycholate interacting micelles in aqueous medium. In Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section A: Chemical Sciences (Vol. 113, pp. 55–62).
Wu, Q., Cheng, Y., Hu, J., Zhao, L., & Xu, T. (2009). Insights into the interactions between dendrimers and bioactive surfactants: 3. size-dependent and hydrophobic property-dependent encapsulation of bile salts. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 113, 12934–12943.
Lee, Y. K., Nam, J. H., Shin, H. C., & Byun, Y. (2001). Conjugation of low-molecular-weight heparin and deoxycholic acid for the development of a new oral anticoagulant agent. Circulation, 104, 3116–3120.
Poša, M., & Farkaš, Z. (2010). Cholesterol solubilization by oxo derivatives of selected bile acids and their membranotoxicity. Collection of Czechoslovak Chemical Communications, 75, 767–787.
Mikov, M., & Fawcett, J. P. (2007). Bile acids. Geneva: Medishet Publisher.
Posa, M., & Ćirin, D. (2012). Mixed micelles of sodium salts of bile acids and tween 40: effect of the steroid skeleton on the coefficient of interaction in mixed micelles. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 51, 14722–14728.
Hildebrand, A., Neubert, R., Garidel, P., & Blume, A. (2002). Bile salt induced solubilization of synthetic phosphatidylcholine vesicles studied by isothermal titration calorimetry. Langmuir, 18, 2836–2847.
Hildebrand, A., Beyer, K., Neubert, R., Garidel, P., & Blume, A. (2003). Temperature dependence of the interaction of cholate and deoxycholate with fluid model membranes and their solubilization into mixed micelles. Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 32, 335–351.
Lichtenberg, D., Opatowski, E., & Kozlov, M. M. (2000). Phase boundaries in mixtures of membrane-forming amphiphiles and micelle-forming amphiphiles. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes, 1508, 1–19.
Mannaa, K., Changb, C. H., & Pandaa, A. K. (2012). A potentiometric titration study on the dissociation of bile acids related to the mode of interaction between different head groups of nonionic surfactants with free bile salts upon mixed micelle formation in water. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 415, 10–21.
Nydh, M., Sodeman, O., Wiedmer, S. K., & Riekkola, M. L. (2000). Mixed micelles of SDS and sodium cholate. A nuclear magnetic resonance diffusion and relaxation study. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 21, 209–227.
Tanaka, T., Nakashima, T., Lee, S., Nagadome, S., Sasaki, Y., Ueno, M., & Sugihara, G. (1995). A potentiometric titration study on the dissociation of bile acids related to the mode of interaction between different head groups of nonionic surfactants with free bile salts upon mixed micelle formation in water. Colloid and Polymer Science, 273, 392–398.
Motomura, K., & Aratono, M. (1993). In K. Ogino & M. Abe (Eds.), Mixed Surfactant Systems (pp. 99–144). New York: Marcel Dekker.
Ćirin, D. M., Poša, M. M., & Krstonošić, V. S. (2012). Interactions between sodium cholate or sodium deoxycholate and nonionic surfactant (Tween 20 or Tween 60) in aqueous solution. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 51, 3670–3676.
Cirin, D. M., Posa, M. M., & Krstonosic, V. S. (2011). Interactions between selected bile salts and Triton X-100 or sodium lauryl ether sulfate. Chemistry Central Journal, 5, 89–97.
Haque, M. E., Das, A. R., & Moulik, S. P. (1995). Behaviors of sodium deoxycholate (NaDC) and polyoxyethylene tert-octylphenyl ether (Triton X-100) at the air/water interface and in the bulk. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 99, 14032–14038.
Jendric, M., Filipović-Vincekovic, N., Vincekovic, M., Bujan, M., & Primožic, I. (2005). Phase behavior of bis(quaternary ammonium bromide)/sodium cholate/H2O system. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 26, 39–51.
Jiang, L., Wang, K., Deng, M., Wang, Y., & Huang, J. (2008). Bile salt-induced vesicle-to-micelle transition in catanionic surfactant systems: steric and electrostatic interactions. Langmuir, 2008(24), 4600–4606.
Zimmerman, H. J. (1999). Drug-induced liver disease. In H. J. Zimmerman (Ed.), Hepatotoxicity: the adverse effects of drugs and other chemicals on the liver (2nd ed., pp. 427–456). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Bates, T. R., Gibaldi, M., & Kanig, J. L. (1966). Solubilizing properties of bile salt solutions II. Effect of inorganic electrolyte, lipids, and a mixed bile salt system on solubilization of glutethimide, griseofulvin, and hexestrol. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 55, 901–906.
Amundson, L. L., Li, R., & Bohne, C. (2008). Effect of the guest size and shape on its binding dynamics with sodium cholate aggregates. Langmuir, 24, 8491–8500.
Mandal, S., Ghosh, S., Banik, D., Banerjee, C., Kuchlyan, J., & Sarkar, N. (2013). An investigation into the effect of the structure of bile salt aggregates on the binding interactions and ESIHT dynamics of curcumin: a photophysical approach to probe bile salt aggregates as a potential drug carrier. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 117, 13795–13807.
Pedersen, J. M., Matsson, P., Bergström, C. A. S., Hoogstraate, J., Norén, A., LeCluyse, E. L., & Artursson, P. (2013). Early identification of clinically relevant drug interactions with the human bile salt export pump (BSEP/ABCB11). Toxicological Sciences, 136, 328–343.
Hermida, L. G., Sabes-Xamani, M., & Barnadas-Rodríguez, R. (2014). Characteristics and behaviour of liposomes when incubated with natural bile salt extract: implications for their use as oral drug delivery systems. Soft Matter, 10, 6677–6685.
Rosoff, M., & Serajuddin, A. T. M. (1980). Solubilization of diazepam in bile salts and in sodium cholate-lecithin-water phases. International Journal of Pharmacy, 6, 137–146.
Wiedmann, T. S., Liang, W., & Kamel, L. (2002). Solubilization of drugs by physiological mixtures of bile salts. Pharmaceutical Research, 19, 1203–1208.
Gomez-Mendoza, M., Nuin, E., Andreu, I., Marin, M. L., & Miranda, M. A. (2012). Photophysical probes to assess the potential of cholic acid aggregates as drug carriers. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 116, 10213–10218.
Miyazaki, H., Inoue, S., Yamahira, T., & Nadai, T. (1979). Interaction of drugs with bile components. I. Effects of bile salts on the dissolution behavior of indomethacin and phenylbutazone. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin Tokyo, 27, 2468–2472.
Miyazaki, S., Inoue, H., Yamahira, T., & Nadai, T. (1980). Interaction of drugs with bile components. II. Effect of bile on the absorption of indomethacin and phenylbutazone in rats. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 28, 323–326.
Mahajan, S., & Mahajan, R. K. (2012). Interactions of phenothiazine drugs with bile salts: micellization and binding studies. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 387, 194–204.
Laniado-Laborin, R., & Cabrales-Vargas, M. N. (2009). Amphotericin B: side effects and toxicity. Revista Iberoamericana de Micología, 26, 223–227.
Chen, S. C., Playford, E. G., & Sorrell, T. C. (2010). Antifungal therapy in invasive fungal infections. Current Opinion in Pharmacology, 10, 522–530.
Pagano, L., Caira, M., Valentini, C. G., Posteraro, B., & Fianchi, L. (2010). Antifungal therapy in invasive fungal infections. Blood Reviews, 24, 51–61.
Klaassen, C. D., & Aleksunes, L. M. (2010). Xenobiotic, bile acid, and cholesterol transporters: function and regulation. Pharmacological Reviews, 62, 1–96.
Rub, M. A., Sheikh, M. S., Khan, F., Khan, S. B., & Asiri, A. M. (2014). Bile salts aggregation behavior at various temperatures under the influence of amphiphilic drug imipramine hydrochloride in aqueous medium. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 228, 747–767.
Rub, M. A., Sheikh, M. S., Asiri, A. M., Azum, N., Khan, A., Khan, A. A. P., Khan, S. B., & Kabir-ud-Din. (2013). Aggregation behaviour of amphiphilic drug and bile salt mixtures at different compositions and temperatures. Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 64, 28–39.
Kumar, D., & Rub, M. A. (2015). Effect of sodium taurocholate on aggregation behavior of amphiphilic drug solution. Tenside, Surfactants, Detergents, 52, 464–472.
Al-Muhanna, M. K., Rub, M. A., Azum, N., Khan, S. B., & Asiri, A. M. (2016). Self-aggregation phenomenon of promazine hydrochloride under the influence of sodium cholate/sodium deoxycholate in aqueous medium. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology, 37, 450–463.
Lipinski, C. (2002). Poor aqueous solubility – an industry wide problem in drug discovery. American Pharmaceutical Review, 5, 82–85.
Wenlock, M. C., Austin, R. P., Barton, P., Davis, A. M., & Leeson, P. D. (2003). A comparison of physiochemical property profiles of development and marketed oral drugs. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 46, 1250–1256.
Vogtherr, M., Marx, A., Mieden, A. C., & Saal, C. (2015). Investigation of solubilising effects of bile salts on an active pharmaceutical ingredient with unusual pH dependent solubility by NMR spectroscopy. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, 92, 32–41.
Mithani, S. D., Bakatselou, V., TenHoor, C. N., & Dressman, J. B. (1996). Estimation of the increase in solubility of drugs as a function of bile salt concentration. Pharmaceutical Research, 13, 163–167.
Gil, H. N., & Lee, B. H. (2008). Study on the micellization of DPC/Brij 35 mixed surfactant systems by the conductivity method. Journal of Korean Chemical Society, 52, 461–467.
Mukerjee, P. (1967). The nature of the association equilibria and hydrophobic bonding in aqueous solutions of association colloids. Advances in Colloid Interface Science, 1, 242–275.
Zhou, Q., & Rosen, M. J. (2003). Molecular interactions of surfactants in mixed monolayers at the air/aqueous solution interface and in mixed micelles in aqueous media: the regular solution approach. Langmuir, 19, 4555–4562.
Rosen, M. J., & Hua, X. Y. J. (1982). Surface concentrations and molecular interactions in binary mixtures of surfactants. Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 86, 164–172.
Haque, M. E., Das, A. R., & Moulik, S. P. (1999). Mixed micelles of sodium deoxycholate and polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate (Tween 80). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 217, 1–7.
Acknowledgments
Nisar Ahmad Malik would like to thank Head Department of Chemistry, University of Kashmir for providing the necessary facilities and to Dr. Aijaz Ahmad Dar for his valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malik, N.A. Solubilization and Interaction Studies of Bile Salts with Surfactants and Drugs: a Review. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 179, 179–201 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-1987-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-1987-x