Abstract
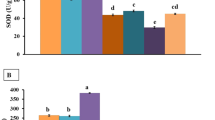
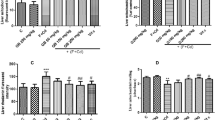
The aim of the study was to investigate the ameliorative properties of ascorbic acid against the subchronic effect of co-exposure of fluoride (F) and chlorpyrifos (CPF) on oxidative damage markers such as lipid peroxidation (MDA) and antioxidant defense system in the liver of adult Wistar rats. The animal groups were provided with either vehicle or ascorbic acid (60 mg/kg, b.w.) or NOAEL dose of fluoride (1 ppm) or CPF (1 mg/kg, b.w.) or ten times of such doses orally alone and in combination or pre-treated with ascorbic acid along with co-exposure of F and CPF every consecutive day for 28 days. Hepatic damage marker analysis in blood revealed that aspartate and alanine aminotransferases, alkaline phosphatase, and lactate dehydrogenase were significantly (P < 0.05) increased with single or combined exposure of F or CPF at either dose levels. Significant increased oxidative damage of hepatocytes as indicated by increased MDA levels with decrease in tissue ascorbate and free radical scavenging enzymes like catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase was observed in groups treated with either F or CPF as well as in combinedly treated animals as compared to control animals. Supplementation of ascorbic acid restored the hepatic specific marker enzymes in blood following co-exposure of F and CPF at lower doses which were otherwise increased in the F and CPF co-exposed rats. The results show that ascorbic acid supplementation with F and CPF prevents or diminishes the hepatic damage in rats co-exposed to toxicants and may act as a putative protective agent against toxicant-induced liver tissue injury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aspelin A (1994) US Environmental Protection Agency, Report no733-k-94-001
Gultekin F, Delibas N, Yasar S, Kilinc I (2001) In vivo changes in antioxidant systems and protective role of melatonin and a combination of vitamin C and vitamin E on oxidative damage in erythrocytes induced by chlorpyrifos-ethyl in rats. Arch Toxicol 75:88–96
Baba NA, Raina R, Verma PK, Sultana M (2014) Alterations in plasma and tissue acetylcholinesterase activity following repeated oral exposure of chlorpyrifos alone and in conjunction with fluoride in Wistar rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci 4:969–972
Canadas F, Cardona D, Davila E, Sanchez-Santed F (2005) Long-term neurotoxicity of chlorpyrifos: spatial learning impairment on repeated acquisition in a water maze. Toxicol Sci 85:944–951
Rehman MF, Mahboob M, Danadevi K, Saleha BB, Grover P (2002) Assessment of genotoxic effects of chlorpyriphos and acephate by the comet assay in mice leucocytes. Mutat Res 516:139–147
Harfod AJO, Halloran K, Wright PF (2005) The effects of in vitro pesticide exposures on the phagocytic function of four native Australian freshwater fish. Aquat Toxicol 75:330–342
Verma RS, Mehta A, Srivastava N (2007) In vivo chlorpyrifos induced oxidative stress: attenuation by antioxidant vitamins. Pestic Biochem Physiol 88:191–196
Ahmed NS, Mohamed AS, Abdel-Wahhab MA (2010) Chlorpyrifos-induced oxidative stress and histological changes in retinas and kidney in rats: protective role of ascorbic acid and alpha tocopherol. Pestic Biochem Physiol 98:33–38
Ambali S, Akanbi O, Igbokwe N, Shittu M, Kawu AJ (2007) Evaluation of sub-chronic chlorpyrifos poisoning on haematological and serum biochemical changes in mice and protective effect of vitamin C. J Toxicol Sci 32:111–120
Mansour SA, Mossa AH (2009) Lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress in rat erythrocytes induced by chlorpyrifos and protective role of zinc. Pestic Biochem Physiol 93:34–39
Zhavoronkov AA, Strochkova LS (1981) Fluorosis geographical pathology and some experimental findings. Fluoride 14:183–191
Tao X, Xu ZR, Wang YZ (2006) Effects of dietary fluoride on growth serum indexes and antioxidant systems in growing pigs. Turk J Vet Anim Sci 30:65–70
Nelson SD (1990) Molecular mechanisms of the hepatotoxicity caused by acetaminophen. Semin Liver Dis 10:267–278
Kant V, Srivastava AK, Verma PK, Raina R, Pankaj NK (2009) Negligible ameliorative effect of aluminum sulphate on oxidative stress induced in goats during subacute fluoride intoxication. Fluoride 42:120–123
Possamai FP, Fortunato JJ, Feier G, Agostinho FR, Quevedo J, Wilhelm Filho D, Dal-Pizzol F (2007) Oxidative stress after acute and sub-chronic malathion intoxication in Wistar rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 23:198–204
Baba NA, Raina R, Verma PK, Sultana M, Prawez S, Nisar NA (2013) Toxic effects of fluoride and chlorpyrifos on antioxidant parameters in rats: protective effects of vitamins C and E. Fluoride 46:73–79
Ola AK, Sandhu HS, Ranjan B, Dumka VK (2013) Fipronil-induced biochemical alterations during oral subacute toxicity in buffalo calves. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci. doi:101007/s40011-013-0167-9
Akhtar N, Srivastava MK, Raizada RB (2009) Assessment of chlorpyrifos toxicity on certain organs in rat. J Environ Biol 30:6
El-Hossary GG, Mansour SM, Mohamed AS (2009) Neurotoxic effects of chlorpyrifos and possible protective role of antioxidant supplements. J Appl Sci Res 5:1218–1222
Raina R, Verma PK, Pankaj NK, Kant V, Prawez S (2010) Protective effect of ascorbic acid on oxidative stress induced by repeated dermal application of cypermethrin. Toxicol Environ Chem 92:947–953
Goel A, Danni V, Dhawan DK (2005) Protective effects of zinc on lipid peroxidation, antioxidant enzymes and hepatic histoarchitecture in chlorpyrifos induced toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 156:131–134
Marklund S, Marklund G (1974) Involvement of superoxide anion radical in autoxidation of pyrogallol and a convenient assay for superoxide dismutase. Eur J Biochem 47:469–474
Aebi HE (1983) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of Enzymatic Analysis. Academic, New York, pp 276–286
Hafeman DG, Sunde RA, Hoekstra WG (1974) Effect of dietary selenium on erythrocyte and liver glutathione peroxidase in the rat. J Nutr 104:580–587
ur Rehman S (1984) Lead induced regional lipid peroxidation in brain. Toxicol Lett 21:333–337
Omaye ST, Turnbull JD, Sauberlich HE (1979) Selected methods for the determination of ascorbic acid in animal cells, tissues and fluids methods. Enzymology 62:1–7
Poppy JA, Cattley RC (1991) Hepatobillary system. In: Haschek WM, Rousseaux CG (eds) Handbook of toxicological pathology. Academic, Inc San Diego, pp 279–315
Tang J, Cao Y, Rose RL, Brimfield AA, Dai D, Goldstein JA, Hodgson E (2001) Metabolism of chlorpyrifos by human cytochrome PCYP isoforms and human, mouse, and rat liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos 29:1201–1204
Khan IA, Reddy BV, Mahboob M, Rahman MF, Jamil K (2001) Effect of phosphorothionate on the reproductive system of male rats. J Environ Sci Health 36:445–456
Singh JL, Swarup D (1999) Biochemical changes in serum and urine in bovine fluorosis. Ind J Anim Sci 69:776–778
Gomes J, Dawodu AH, Lloyd O, Revitt DM, Anilal SV (1999) Hepatic injury and disturbed amino acid metabolism in mice following prolonged exposure to organophosphorous pesticides. Hum Exp Toxicol 18:33–37
Sayeed I, Parvez S, Pandey S, Bin-Hafeez B, Haque R, Raisuddin (2003) Oxidative stress biomarkers of exposure to deltamethrin in fresh water fish Channa punctatus. Bloch Exotoxicol Environ Safety 56:295–301
Inkielewicz I, Krechniak J, Gdansk (2006) Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activity in rats exposed to fluoride and ethanol. Fluoride 39:53–59
Oncu M, Gultekin F, Karaoz E, Altuntas I, Delibas N (2002) Nephrotoxicity in rats induced by chlorpyrifos-ethyl and ameliorating effects of antioxidants. Hum Exp Toxicol 21:223–230
Verma RS, Srivastava N (2003) Effect of chlorpyrifos on thiobarbituric acid reactive substances scavenging enzymes and glutathione in rat tissues. Ind J Biochem Biophy 40:423–428
Halliwell B, Gutterridge JMC (1989) Free radicals in biology and medicine. Clarendon, Oxford, pp 188–276
Cross CE (1987) The spectrum of diseases In: Cross CE ed. Moderator oxygen radicals and human disease. Annual Int Med 107:526-545
Maxwell SR (1995) Prospects for the use of antioxidant therapies. Drugs 49:345–361
Kushnareva Y, Murphy AN, Andreyev A (2002) Complex mediated reactive oxygen species generation: modulation by cytochrome C and NAD(P)+ oxidation-reduction state. Biochem J 368:545–553
Hussein MS, Abdou KA, Mahmoud AS, Abd-El-Rahaman W (2008) Toxic interaction of pyrethroid (Katron) and sodium fluoride on reproductive performance of male albino rats. Vet Med J 54:119
McCord JM, Fridovich I (1969) Superoxide dismutase: an enzymatic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprien). J Biol Chem 244:6049–6055
Hertwig B, Steb P, Feierabend J (1992) Light dependence of catalase synthesis and degradation in leaves and the influence of interfering stress conditions. Plant Physiol 100:1547–1553
Padayatty SA, Katz Y, Wang P, Eck O, Kwon J, Lee S, Chen et al (2003) Vitamin C as an antioxidant: evaluation of its role in disease prevention. J Am College Nutri 22:18–35
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raina, R., Baba, N.A., Verma, P.K. et al. Hepatotoxicity Induced by Subchronic Exposure of Fluoride and Chlorpyrifos in Wistar Rats: Mitigating Effect of Ascorbic Acid. Biol Trace Elem Res 166, 157–162 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0263-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0263-1