Abstract
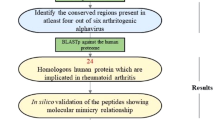
Etiology, pathogenesis, and immunology of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) form a complex, still undeciphered picture that recently has been further made complicated by a new factor of morbidity: human papillomaviruses (HPVs). Indeed, a prevalence of HPV infections has been reported among SLE patients. Searching for molecular mechanisms that might underlie and explain the relationship between HPV infection and SLE, we explored the hypothesis that immune responses following HPV infection may crossreact with proteins that, when altered, associate with SLE. Analyzing HPV L1 proteins and using Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and human retrovirus (HERV) as controls, we found a vast peptide overlap with human proteins comprehending lupus Ku autoantigen proteins p86 and p70, lupus brain antigen 1 homolog, lupus antigen expressed in neurons and muscles, natural killer cell IgG-like receptors, complement proteins C4-A and C4-B, complement receptor CD19, and others. The multitude and heterogeneity of peptide overlaps not only further support the hypothesis that crossreactivity can represent a primum movens in SLE onset, but also provide a molecular framework to the concept of SLE as “an autoimmune mosaic syndrome.” Finally, once more, it emerges the need of using the principle of peptide uniqueness as a new paradigm for safe and efficacious vaccinology.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wallace DJ, Hahn BH, (Eds). Dubois’ lupus erythematosus. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA: 2007.
Tsokos GC, Gordon C, Smolen JS, (Eds). Systemic lupus erythematosus: a companion to rheumatology. Mosby Elsevier; Philadelphia: 2007.
Zhu H, Luo H, Yan M, Zuo X, Li QZ. Autoantigen microarray for high-throughput autoantibody profiling in systemic lupus erythematosus. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2015;13:210–8.
Dema B, Charles N. Autoantibodies in SLE: specificities, isotypes and receptors. Antibodies. 2016;5:2.
Hagberg N, Theorell J, Eloranta ML, Pascal V, Bryceson YT, Rönnblom L. Anti-NKG2A autoantibodies in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013;52:1818–23.
Nelson P, Rylance P, Roden D, Trela M, Tugnet N. Viruses as potential pathogenic agents in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2014;23:596–605.
Haaheim LR, Halse AK, Kvakestad R, Stern B, Normann O, Jonsson R. Serum antibodies from patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus recognize multiple epitopes on the La(SS-B) autoantigen resembling viral protein sequences. Scand J Immunol. 1996;43:115–21.
Esposito S, Bosis S, Semino M, Rigante D. Infections and systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014;33:1467–75.
Rigante D, Mazzoni MB, Esposito S. The cryptic interplay between systemic lupus erythematosus and infections. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:96–102.
Rigante D, Esposito S. Infections and systemic lupus erythematosus: binding or sparring partners? Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16:17331–43.
Barzilai O, Ram M, Shoenfeld Y. Viral infection can induce the production of autoantibodies. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007;19:636–43.
McClain MT, Heinlen LD, Dennis GJ, Roebuck J, Harley JB, James JA. Early events in lupus humoral autoimmunity suggest initiation through molecular mimicry. Nat Med. 2005;11:85–9.
Ramos-Casals M. Viruses and lupus: the viral hypothesis. Lupus. 2008;17:163–5.
Harley JB, Harley IT, Guthridge JM, James JA. The curiously suspicious: a role for Epstein-Barr virus in lupus. Lupus. 2006;15:768–77.
Incaprera M, Rindi L, Bazzichi A, Garzelli C. Potential role of the Epstein-Barr virus in systemic lupus erythematosus autoimmunity. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1998;16:289–94.
Poole BD, Scofield RH, Harley JB, James JA. Epstein-Barr virus and molecular mimicry in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmunity. 2006;39:63–70.
James JA, Harley JB, Scofield RH. Epstein-Barr virus and systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2006;18:462–7.
James JA, Neas BR, Moser KL, Hall T, Bruner GR, Sestak AL, Harley JB. Systemic lupus erythematosus in adults is associated with previous Epstein-Barr virus exposure. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44:1122–6.
Harley JB, James JA. Epstein-Barr virus infection induces lupus autoimmunity. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2006;64:45–50.
Ascherio A, Munger KL. EBV and autoimmunity. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;390:365–85.
Kasapcopur O, Ergul Y, Kutlug S, Candan C, Camcioglu Y, Arisoy N. Systemic lupus erythematosus due to Epstein-Barr virus or Epstein-Barr virus infection provocating acute exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus? Rheumatol Int. 2006;26:765–7.
Toussirot E, Roudier J. Epstein-Barr virus in autoimmune diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2008;22:883–96.
Posnett DN. Herpesviruses and autoimmunity. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2008;9:505–14.
Blank M, Shoenfeld Y, Perl A. Cross-talk of the environment with the host genome and the immune system through endogenous retroviruses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2009;18:1136–43.
Perl A, Nagy G, Koncz A, Gergely P, Fernandez D, Doherty E, Telarico T, Bonilla E, Phillips PE. Molecular mimicry and immunomodulation by the HRES-1 endogenous retrovirus in SLE. Autoimmunity. 2008;41:287–97.
Adelman MK, Marchalonis JJ. Endogenous retroviruses in systemic lupus erythematosus: candidate lupus viruses. Clin Immunol. 2002;102:107–16.
Naito T, Ogasawara H, Kaneko H, Hishikawa T, Sekigawa I, Hashimoto H, Maruyama N. Immune abnormalities induced by human endogenous retroviral peptides: with reference to the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Immunol. 2003;23:371–6.
Sukapan P, Promnarate P, Avihingsanon Y, Mutirangura A, Hirankarn N. Types of DNA methylation status of the interspersed repetitive sequences for LINE-1, Alu, HERV-E and HERV-K in the neutrophils from systemic lupus erythematosus patients and healthy controls. J Hum Genet. 2014;59:178–88.
Christensen T. Association of human endogenous retroviruses with multiple sclerosis and possible interactions with herpes viruses. Rev Med Virol. 2005;15:179–211.
Piotrowski PC, Duriagin S, Jagodzinski PP. Expression of human endogenous retrovirus clone 4–1 may correlate with blood plasma concentration of anti-U1 RNP and anti-Sm nuclear antibodies. Clin Rheumatol. 2005;24:620–4.
Gergely Jr P, Pullmann R, Stancato C, et al. Increased prevalence of transfusion-transmitted virus and cross-reactivity with immunodominant epitopes of the HRES-1/p28 endogenous retroviral autoantigen in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. 2005;116:124–34.
Lyrio LD, Grassi MFR, Santana IU, et al. Prevalence of cervical human papillomavirus infection in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. 2013;33:335–40.
Klumb EM, Pinto AC, Jesus GR, Araujo M, Jascone L, Gayer CR, et al. Are women with lupus at higher risk of HPV infection? Lupus. 2010;19:1485–91.
Bae SC, Kim YJ, Suh CH, Kim HA, Hur NW, Lee J. Prevalence of human papilloma virus infections and cervical cytological abnormalities among Korean women with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Korean Med Sci. 2010;25:1431–7.
Nath R, Mant C, Luxton J, et al. High risk of human papillomavirus type 16 infections and of development of cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;57:619–25.
Soldevilla HF, Briones SF, Navarra SV. Systemic lupus erythematosus following HPV immunization or infection? Lupus. 2012;21:158–61.
Ito H, Noda K, Hirai K, Ukichi T, Furuya K, Kurosaka D. A case of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) following human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2016;39:145–9.
Geier DA, Geier MR. Quadrivalent human papillomavirus vaccine and autoimmune adverse events: a case–control assessment of the vaccine adverse event reporting system (VAERS) database. Immunol Res. 2016 Jul;13
Natale C, Giannini T, Lucchese A, Kanduc D. Computer-assisted analysis of molecular mimicry between human papillomavirus 16 E7 oncoprotein and human protein sequences. Immunol Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;78(6):580–5.
Kanduc D, Stufano A, Lucchese G, Kusalik A. Massive peptide sharing between viral and human proteomes. Peptides. 2008 Oct;29(10):1755–66.
Kanduc D. Penta-and hexapeptide sharing between HPV16 and Homo sapiens proteomes. Int J Med Med Sci. 2009 Oct 1;1:383–7.
Kanduc D. Quantifying the possible cross-reactivity risk of an HPV16 vaccine. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2009;8(1):65–76.
Kanduc D. Potential cross-reactivity between HPV16 L1 protein and sudden death-associated antigens. J Exp Ther Oncol. 2011;9:159–65.
Kanduc D, Shoenfeld Y. From HBV to HPV: designing vaccines for extensive and intensive vaccination campaigns worldwide. Autoimmun Rev. 2016 Aug 1
Magrane M; UniProt Consortium. UniProt Knowledgebase: a hub of integrated protein data. Database (Oxford). 2011; 2011: bar009.
Hom G, Graham RR, Modrek B, et al. Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:900–9.
Hatta Y, Tsuchiya N, Matsushita M, Shiota M, Hagiwara K, Tokunaga K. Identification of the gene variations in human CD22. Immunogenetics. 1999;49:280–6.
Lokki ML, Circolo A, Ahokas P, Rupert KL, Yu CY, Colten HR. Deficiency of human complement protein C4 due to identical frameshift mutations in the C4A and C4B genes. J Immunol. 1999;162:3687–93.
Wetsel RA, Kulics J, Lokki ML, et al. Type II human complement C2 deficiency. Allele-specific amino acid substitutions (Ser189->Phe; Gly444->Arg) cause impaired C2 secretion. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:5824–31.
Singer L, Whitehead WT, Akama H, Katz Y, Fishelson Z, Wetsel RA. Inherited human complement C3 deficiency. An amino acid substitution in the beta-chain (ASP549 to ASN) impairs C3 secretion. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:28494–9.
Petry F, Hauptmann G, Goetz J, Grosshans E, Loos M. Molecular basis of a new type of C1q-deficiency associated with a non-functional low molecular weight (LMW) C1q: parallels and differences to other known genetic C1q-defects. Immunopharmacology. 1997;38:189–201.
Dragon-Durey MA, Quartier P, Frémeaux-Bacchi V, et al. Molecular basis of a selective C1s deficiency associated with early onset multiple autoimmune diseases. J Immunol. 2001;166:7612–6.
Wu H, Boackle SA, Hanvivadhanakul P, et al. Association of a common complement receptor 2 haplotype with increased risk of systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:3961–6.
Yasutomo K, Horiuchi T, Kagami S, et al. Mutation of DNASE1 in people with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. 2001;28:313–4.
Stenmark H, Aasland R, Toh BH, D’Arrigo A. Endosomal localization of the autoantigen EEA1 is mediated by a zinc-binding FYVE finger. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:24048–54.
Yasuda S, Stevens RL, Terada T, et al. Defective expression of Ras guanyl nucleotide-releasing protein 1 in a subset of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2007;179:4890–900.
Nath SK, Han S, Kim-Howard X, et al. A nonsynonymous functional variant in integrin-alpha(M) (encoded by ITGAM) is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. 2008;40:152–4.
Lee YH, Bae SC. Association between the functional ITGAM rs1143679 G/A polymorphism and systemic lupus erythematosus/lupus nephritis or rheumatoid arthritis: an update meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int. 2015;35:815–23.
Belot A, Kasher PR, Trotter EW, et al. Protein kinase cδ deficiency causes mendelian systemic lupus erythematosus with B cell-defective apoptosis and hyperproliferation. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:2161–71.
Hou YF, Zhang YC, Jiao YL, et al. Disparate distribution of activating and inhibitory killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor genes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2010 Jan;19(1):20–6.
Pellett F, Siannis F, Vukin I, Lee P, Urowitz MB, Gladman DD. KIRs and autoimmune disease: studies in systemic lupus erythematosus and scleroderma. Tissue Antigens. 2007 Apr;69(Suppl 1):106–8.
Toloza S, Pellett F, Chandran V, Ibanez D, Urowitz M, Gladman D. Association of killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor genotypes with vascular arterial events and anticardiolipin antibodies in patients with lupus. Lupus. 2008 Sep;17(9):793–8.
Bai Y, Zhang Y, Yang Q, et al. The aberrant expression of stimulatory and inhibitory killer immunoglobulin-like receptors in NK- and NKT-cells contributes to lupus. Clin Lab. 2014;60:717–27.
Glenn HL, Wang Z, Schwartz LM. Acheron, a lupus antigen family member, regulates integrin expression, adhesion, and motility in differentiating myoblasts. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010;298:C46–55.
McCurdy DK, Tai LQ, Nguyen J, et al. MAGE Xp-2: a member of the MAGE gene family isolated from an expression library using systemic lupus erythematosus sera. Mol Genet Metab. 1998;63:3–13.
Jin Y, Mailloux CM, Gowan K, et al. NALP1 in vitiligo-associated multiple autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1216–25.
Matsudaira R, Takeuchi K, Takasaki Y, Yano T, Matsushita M, Hashimoto H. Relationships between autoantibody responses to deletion mutants of Ki antigen and clinical manifestations of lupus. J Rheumatol. 2003;30:1208–14.
Kyogoku C, Langefeld CD, Ortmann WA, et al. Genetic association of the R620W polymorphism of protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22 with human SLE. Am J Hum Genet. 2004;75:504–7.
Bottini N, Musumeci L, Alonso A, et al. A functional variant of lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is associated with type I diabetes. Nat Genet. 2004;36:337–8.
Ravenscroft JC, Suri M, Rice GI, Szynkiewicz M, Crow YJ. Autosomal dominant inheritance of a heterozygous mutation in SAMHD1 causing familial chilblain lupus. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155A:235–7.
Surolia I, Pirnie SP, Chellappa V, et al. Functionally defective germline variants of sialic acid acetylesterase in autoimmunity. Nature. 2010;466:243–7.
Cai LQ, Wang ZX, Lu WS, et al. A single-nucleotide polymorphism of the TNFAIP3 gene is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese Han population. Mol Biol Rep. 2010;37:389–94.
Gateva V, Sandling JK, Hom G, et al. A large-scale replication study identifies TNIP1, PRDM1, JAZF1, UHRF1BP1 and IL10 as risk loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. 2009;41:1228–33.
Goes FS, Hamshere ML, Seifuddin F, et al. Genome-wide association of mood-incongruent psychotic bipolar disorder. Transl Psychiatry. 2012;2:e180.
Jahantigh D, Salimi S, Mousavi M, et al. Association between functional polymorphisms of DNA double-strand breaks in repair genes XRCC5, XRCC6 and XRCC7 with the risk of systemic lupus erythematosus in south east Iran. DNA Cell Biol. 2015;34:360–6.
Kelavkar U, Wang S, Badr K. KU 70/80 lupus autoantigen is the transcription factor induced by interleukins (IL)-13 and -4 leading to induction of 15-lipoxygenase (15-LO) in human cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;507:469–81.
Kanduc D. Pentapeptides as minimal functional units in cell biology and immunology. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2013;14:111–20.
Lucchese A, Mittelman A, Tessitore L, Serpico R, Sinha AA, Kanduc D. Proteomic definition of a desmoglein linear determinant common to Pemphigus vulgaris and Pemphigus foliaceous. J Transl Med. 2006;4:37.
Kanduc D, Serpico R, Lucchese A, Shoenfeld Y. Correlating low-similarity peptide sequences and HIV B-cell epitopes. Autoimmun Rev. 2008;7:291–6.
Lucchese A, Serpico R, Crincoli V, Shoenfeld Y, Kanduc D. Sequence uniqueness as a molecular signature of HIV-1-derived B-cell epitopes. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2009;22:639–46.
Vita R, Zarebski L, Greenbaum JA, et al. The immune epitope database 2.0. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38:D854–62.
Capone G, Fasano C, Lucchese G, Calabrò M, Kanduc D. EBV-associated cancer and autoimmunity: searching for therapies. Vaccines (Basel). 2015 Feb 5;3(1):74–89.
Capone G, Calabrò M, Lucchese G, Fasano C, Girardi B, Polimeno L, Kanduc D. Peptide matching between Epstein-Barr virus and human proteins. Pathog Dis. 2013;69(3):205–12.
Tsokos GC (Ed) Complement in autoimmunity. Curr Dir Autoimmun. vol 7, Basel, Karger, 2004.
Kanduc D, Lucchese A, Mittelman A. Non-redundant peptidomes from DAPs: towards “the vaccine”? Autoimmun Rev. 2007;6:290–4.
Kanduc D. Epitopic peptides with low similarity to the host proteome: towards biological therapies without side effects. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2009;9:45–53.
Kanduc D. Peptides for anti-ebolavirus vaccines. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2016 Sep;2
Lucchese G, Kanduc D. Zika virus and autoimmunity: from microcephaly to Guillain-Barré syndrome, and beyond. Autoimmun Rev. 2016;15:801–8.
Lucchese G, Kanduc D. Potential crossreactivity of human immune responses against HCMV glycoprotein B. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2016;13:16–24.
Kanduc D. Immunogenicity, immunopathogenicity, and immunotolerance in one graph. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem. 2015;15:1264–8.
Shoenfeld Y, Isenberg DA. The mosaic of autoimmunity. Immunol Today. 1989;10(4):123–6.
Agmon-Levin N, Lian Z, Shoenfeld Y. Explosion of autoimmune diseases and the mosaic of old and novel factors. Cell Mol Immunol. 2011;8:189–92.
Perricone C, Agmon-Levin N, Shoenfeld Y. Novel pebbles in the mosaic of autoimmunity. BMC Med. 2013;11:101.
Kivity S, Agmon-Levin N, Zandman-Goddard G, Chapman J, Shoenfeld Y. Neuropsychiatric lupus: a mosaic of clinical presentations. BMC Med. 2015;4:13–43.
Acknowledgements
We apologize to the many authors whose works we have used but not discussed and cited because of space limitations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yehuda Shoenfeld appears as a medical consultant in vaccine compensation court, USA.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 117 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Segal, Y., Dahan, S., Calabrò, M. et al. HPV and systemic lupus erythematosus: a mosaic of potential crossreactions. Immunol Res 65, 564–571 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-016-8890-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-016-8890-y