Abstract
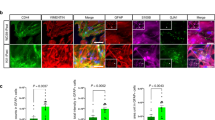
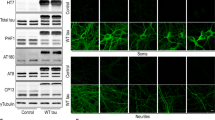
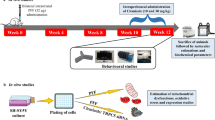
Astrocytes are the most abundant glial cell type in the brain. Impairment in astrocyte functions can critically influence neuronal survival and leads to neurodegeneration. Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by motor dysfunction that results from progressive neuronal loss. Astrocytic dysfunction was demonstrated in human samples and in experimental models of PD. Mutations in DJ-1 (PARK7) leading to loss of functional protein cause familial PD and enhance sensitivity to oxidative insults. Recently, an increase in DJ-1’s expression was found in reactive astrocytes in various neurodegenerative disorders. Here we show that lack of DJ-1 attenuates astrocytes’ ability to support neuronal cells, thereby leading to accelerated neuronal damage. DJ-1 knockout mice demonstrated increased vulnerability in vivo to 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) hemiparkinsonian PD model. Astrocytes isolated from DJ-1 knockout mice showed an inferior ability to protect human neuroblastoma cells against 6-OHDA insult both by co-culture and through their conditioned media, as compared to wild-type astrocytes. DJ-1 knockout astrocytes showed blunted ability to increase the expression of cellular protective mechanisms against oxidative stress mediated via Nrf-2 and HO-1 in response to exposure to 6-OHDA. These experiments demonstrated that lack of DJ-1 impairs astrocyte-mediated neuroprotection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Sleiman PM, Healy DG, Quinn N et al (2003) The role of pathogenic DJ-1 mutations in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 54:283–286
Akazawa YO, Saito Y, Hamakubo T et al (2010) Elevation of oxidized DJ-1 in the brain and erythrocytes of Parkinson disease model animals. Neurosci Lett 483:201–205
Aleyasin H, Rousseaux MW, Phillips M et al (2007) The Parkinson’s disease gene DJ-1 is also a key regulator of stroke-induced damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:18748–18753
Aleyasin H, Rousseaux MW, Marcogliese PC et al (2010) DJ-1 protects the nigrostriatal axis from the neurotoxin MPTP by modulation of the AKT pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:3186–3191
Ashley AK, Hanneman WH, Katoh T et al (2009) Analysis of targeted mutation in DJ-1 on cellular function in primary astrocytes. Toxicol Lett 184:186–191
Bader V, Ran Zhu X, Lübbert H et al (2005) Expression of DJ-1 in the adult mouse CNS. Brain Res 1041:102–111
Bandopadhyay R, Kingsbury AE, Cookson MR et al (2004) The expression of DJ-1 (PARK7) in normal human CNS and idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Brain 127:420–430
Baulac S, Lu H, Strahle J et al (2009) Increased DJ-1 expression under oxidative stress and in Alzheimer’s disease brains. Mol Neurodegener 4:12
Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ et al (2003) Mutations in the DJ-1 gene associated with autosomal recessive early-onset parkinsonism. Science 299:256–259
Canet-Aviles RM, Wilson MA et al (2004) The Parkinson’s disease protein DJ-1 is neuroprotective due to cysteine-sulfinic acid-driven mitochondrial localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:9103–9108
Choi J, Sullards MC, Olzmann JA et al (2006) Oxidative damage of DJ-1 is linked to sporadic Parkinson and Alzheimer diseases. J Biol Chem 281:10816–10824
Clements CM, McNally RS, Conti BJ et al (2006) DJ-1, a cancer- and Parkinson’s disease-associated protein, stabilizes the antioxidant transcriptional master regulator Nrf2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:15091–15096
Corti O, Lesage S, Brice A (2011) What genetics tells us about the causes and mechanisms of Parkinson’s disease. Physiol Rev 91:1161–1218
Devic I, Hwang H, Edgar JS et al (2011) Salivary α-synuclein and DJ-1: potential biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Brain 134:e178
Fan J, Ren H, Jia N et al (2008) DJ-1 decreases Bax expression through repressing p53 transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem 283:4022–4030
Fisher-Shoval Y, Barhum Y, Sadan O et al (2012) Transplantation of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the EAE mouse model of MS. J Mol Neurosci 48:176–184
Gan L, Johnson DA, Johnson JA (2010) Keap1-Nrf2 activation in the presence and absence of DJ-1. Eur J Neurosci 31:967–977
Gorner K, Holtorf E, Waak J et al (2007) Structural determinants of the C-terminal helix-kink-helix motif essential for protein stability and survival promoting activity of DJ-1. J Biol Chem 282:13680–13691
Halliday GM, Stevens CH (2011) Glia: initiators and progressors of pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 26:6–17
Hauser DN, Cookson MR (2011) Astrocytes in Parkinson’s disease and DJ-1. J Neurochem 117:357–358
Hong Z, Shi M, Chung KA et al (2010) DJ-1 and alpha-synuclein in human cerebrospinal fluid as biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 133:713–726
Im JY, Lee KW, Woo JM et al (2012) DJ-1 induces thioredoxin 1 expression through the Nrf2 pathway. Hum Mol Genet 21:3013–3024
Inden M, Taira T, Kitamura Y et al (2006) PARK7 DJ-1 protects against degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease rat model. Neurobiol Dis 24:144–158
Junn E, Taniguchi H, Jeong BS et al (2005) Interaction of DJ-1 with Daxx inhibits apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 activity and cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:9691–9696
Kotaria N, Hinz U, Zechel S et al (2005) Localization of DJ-1 protein in the murine brain. Cell Tissue Res 322:503–507
Larsen NJ, Ambrosi G, Mullett SJ et al (2011) DJ-1 knock-down impairs astrocyte mitochondrial function. Neuroscience 196:251–264
Lev N, Ickowicz D, Melamed E et al (2008) Oxidative insults induce DJ-1 upregulation and redistribution: implications for neuroprotection. Neurotoxicology 29:397–405
Lev N, Ickowicz D, Barhum Y et al (2009) DJ-1 protects against dopamine toxicity. J Neural Transm 116:151–160
Lev N, Barhum Y, Pilosof NS, et al (2012) DJ-1 Protects Against Dopamine Toxicity: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease and Aging. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci [Epub ahead of print]
Malhotra D, Thimmulappa R, Navas-Acien A et al (2008) Decline in NRF2-regulated antioxidants in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease lungs due to loss of its positive regulator, DJ-1. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178:592–604
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (2008) Glial reactions in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 23:474–483
Meulener MC, Xu K, Thomson L et al (2006) Mutational analysis of DJ-1 in Drosophila implicates functional inactivation by oxidative damage and aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:12517–12522
Mullett SJ, Hinkle DA (2009) DJ-1 knock-down in astrocytes impairs astrocyte-mediated neuroprotection against rotenone. Neurobiol Dis 33:28–36
Mullett SJ, Hinkle DA (2011) DJ-1 deficiency in astrocytes selectively enhances mitochondrial Complex I inhibitor-induced neurotoxicity. J Neurochem 117:375–387
Mullett SJ, Hamilton RL, Hinkle DA (2009) DJ-1 immunoreactivity in human brain astrocytes is dependent on infarct presence and infarct age. Neuropathology 29:125–131
Mythri RB, Venkateshappa C, Harish G et al (2011) Evaluation of markers of oxidative stress, antioxidant function and astrocytic proliferation in the striatum and frontal cortex of Parkinson’s disease brains. Neurochem Res 36:1452–1463
Przedborski S (2001) The role of glial cells in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Opin Neurol 14:483–489
Rizzu P, Hinkle DA, Zhukareva V et al (2004) DJ-1 colocalizes with tau inclusions: a link between parkinsonism and dementia. Ann Neurol 55:113–118
Schmidt S, Linnartz B, Mendritzki S et al (2011) Genetic mouse models for Parkinson’s disease display severe pathology in glial cell mitochondria. Hum Mol Genet 20:1197–1211
Shi M, Bradner J, Hancock AM et al (2011) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Parkinson disease diagnosis and progression. Ann Neurol 69:570–580
Shin JH, Kim SW, Jin Y et al (2012) Ethyl pyruvate-mediated Nrf2 activation and hemeoxygenase 1 induction in astrocytes confer protective effects via autocrine and paracrine mechanisms. Neurochem Int 61:89–99
Takuma K, Baba A, Matsuda T (2004) Astrocyte apoptosis: implications for neuroprotection. Prog Neurobiol 72:111–127
Vila M, Jackson-Lewis V, Guegan C et al (2001) The role of glial cells in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Opin Neurol 14:483–489
Waak J, Weber SS, Waldenmaier A et al (2009) Regulation of astrocyte inflammatory responses by the Parkinson’s disease-associated gene DJ-1. FASEB J 23:2478–2489
Waragai M, Wei J, Fujita M et al (2006) Increased level of DJ-1 in the cerebrospinal fluids of sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 345:967–972
Waragai M, Nakai M, Wei J et al (2007) Plasma levels of DJ-1 as a possible marker for progression of sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 425:18–22
Xie Z, Zhuang X, Chen L (2009) DJ-1 mRNA anatomical localization and cell type identification in the mouse brain. Neurosci Lett 465:214–219
Yanagida T, Tsushima J, Kitamura Y et al (2009) Oxidative stress induction of DJ-1 protein in reactive astrocytes scavenges free radicals and reduces cell injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2:36–42
Yokoyama H, Uchida H, Kuroiwa H et al (2011) Role of glial cells in neurotoxin-induced animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Neurol Sci 32:1–7
Yust-Katz S, Fisher-Shoval Y, Barhum Y et al (2012) Placental mesenchymal stromal cells induced into neurotrophic factor-producing cells protect neuronal cells from hypoxia and oxidative stress. Cytotherapy 14:45–55
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by funding from the Israel Science Foundation (ISF grant no. 1690/09) and UGH Pharma, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lev, N., Barhum, Y., Ben-Zur, T. et al. Knocking Out DJ-1 Attenuates Astrocytes Neuroprotection Against 6-Hydroxydopamine Toxicity. J Mol Neurosci 50, 542–550 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-9984-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-9984-9