Abstract
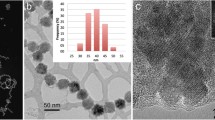
Nano magnetic oxides are promising candidates for high density magnetic storage and other applications. Nonspherical mesoscopic iron oxide particles are also candidate materials for studying the shape, size and strain induced modifications of various physical properties viz. optical, magnetic and structural. Spherical and nonspherical iron oxides having an aspect ratio, ∼2, are synthesized by employing starch and ethylene glycol and starch and water, respectively by a novel technique. Their optical, structural, thermal and magnetic properties are evaluated. A red shift of 0·24 eV is observed in the case of nonspherical particles when compared to spherical ones. The red shift is attributed to strain induced changes in internal pressure inside the elongated iron oxide particles. Pressure induced effects are due to the increased overlap of wave functions. Magnetic measurements reveal that particles are superparamagnetic. The marked increase in coercivity in the case of elongated particles is a clear evidence for shape induced anisotropy. The decreased specific saturation magnetization of the samples is explained on the basis of weight percentage of starch, a nonmagnetic component and is verified by TGA and FTIR studies. This technique can be modified for tailoring the aspect ratio and these particles are promising candidates for drug delivery and contrast enhancement agents in magnetic resonance imaging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anantharaman M R, Joseph K V and Keer H V 1997 Bull. Mater. Sci. 20 975
Arndt V, Basf A G and Ludwigshafen 1998 Magn. IEEE Trans. 24 1796
Bate G 1991 J. Magn. & Magn. Mater. 100 413
Bhattacharyya D, Chaudhuri S and Pal A K 1992 Vacuum 43 313
Chakrabarti S, Ganguli D and Chaudhuri S 2004 Physica E24 333
Chikazumi S 1964 Physics of magnetism (New York: John Wiley & Sons)
Cohen J B 1990 Ultramicroscopy 34 41
Cullity B D 1972 Introduction to magnetic materials (Philippines: Addison-Wesley Publishing Company)
Dallas Panagiotis, Moutis Nicolas, Devlin Eamonn, Niarchos Dimitrios and Pentridis Dimitros 2006 Nanotechnology 17 5019
Deng M C, Hsu S L and Chin T S 1992 IEEE Trans. Magn. 28 2385
Hyeon Taeghwan 2003 Chem. Commun. 927
Kachkachi H, Ezzir A, Nogues M and Tronc E 2000 Eur. Phys. J. B14 681
Khaleel Abbas A 2004 Chem. Eur. J. 10 925
Nair Swapna S, Mathews Mercy and Anantharaman M R 2005 Chem. Phys. Letts 406 398
Pankov J J 1971 Optical processes in semiconductors (New Jersey: Prentice-Hall)
Raksha Sharma, Subhalakshmi Lamba and Annapoorni S 2005 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 38 3354
Sabino Veintemillas-Verdaguer et al 2004 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 37 2054
Silverstein Robert M and Webster Francis X 1964 Spectroscopic identification of organic compounds (New York: John Wiley & Sons)
Vassiliou John K, Mehrotra Vivek, Russell Michal W, McMichael R D, Shull R D and Ronald F Ziolo 1993 J. Appl. Phys. 73 10
Venkatesh Rao, Shashimohan A L and Biswas A B 1974 J. Mater. Sci. 9 430
Viswanathan B 1990 Ferrite materials: Science and Technology (New Delhi: Narosa Publishing House)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narayanan, T.N., Sakthi Kumar, D., Yoshida, Y. et al. Strain induced anomalous red shift in mesoscopic iron oxide prepared by a novel technique. Bull Mater Sci 31, 759–766 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-008-0120-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-008-0120-3