Abstract
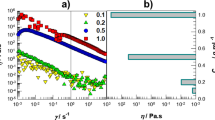
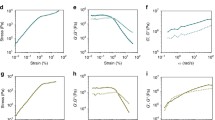
A stable gel of Au nanoparticles in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) nanocomposite is prepared by employing the curing agent of PDMS elastomer as a reducing agent for the formation of Au nanoparticles by an in-situ process. The viscoelastic nature of these gels is very sensitive to the Au nanoparticle loading and the synthetic temperature conditions. Even a very low Au content of 0.09 wt% is sufficient enough to bring in the transition from sponge state to gel state at room temperature. Higher synthetic temperature also forms sponge formation. Infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy measurements have provided insight into PDMS crosslinking and nanoparticle formation, respectively. The optimization of the gel properties can have direct influence on the processability of Au nanoparticle–PDMS nanocomposite gels, with interesting implications in electronic, optical and microfluidic devices.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takahashi H, Ishimuro Y and Watanabe H 2006 Nihon Reoroji Gakk 34 135
Mark J E 2004 Acc. Chem. Res. 37 946
Rajan G, Sur G, Mark J, Schaefer D and Beaucage G 2003 J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Phys. 41 1897
Qin D, Xia Y and Whitesides G M 2010 Nat. Protoc. 5 491
Lacour S P, Wagner S, Huang Z and Suo Z 2003 Appl. Phys. Lett. 82 2404
Adrega T and Lacour S P 2010 J. Micromech. Microeng. 20 055025
Buyl F D 2001 Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 21 411
Rosen M R 2005 Delivery system handbook for personal care and cosmetic products: technology, applications and formulations (Norwich, NY: William Andrew Publishing) ISBN: 978-0-8155-1504-3
Kumar S K and Krishnamoorti R 2010 Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 1 37
Niu X Z, Peng S L, Liu L Y, Wen W J and Sheng P 2007 Adv. Mater. 19 2682
Cong H and Pan T 2008 Adv. Funct. Mater. 18 1912
Kujawski M, Pearse J D and Smela E 2010 Carbon 48 2409
Zhang Y, Sheehan C J, Zhai J, Zou G, Luo H, Xiong J, Zhu Y T and Jia Q X 2010 Adv. Mater. 22 3027
Hong J, Lee J, Hong C K and Shim S E 2010 Curr. Appl. Phys. 10 359
Liu C H and Fan S S 2005 Appl. Phys. Lett. 86 123106
Mackay M E 2006 Science 311 1740
Kayatin M J and Davis V A 2009 Macromolecules 42 6624
Moreira L, Fulchiron R, Seytre G, Dubois P and Cassagnau P 2010 Macromolecules 43 1467
Anderson B J and Zukoski C F 2010 Langmuir 26 8709
Huang Y Y, Ahir S V and Terentjev E M 2006 Phys. Rev. B 73 125422
Bokobza L and Diop A L 2010 Express Polym. Lett. 4 355
Austin J R and Kontopoulou M 2006 Polym. Eng. Sci. 46 1491
Guimont A, Beyou E, Martin G, Sonntag P and Cassagnau P 2011 Macromolecules 44 3893
Marceau S, Dubois P, Fulchiron R and Cassagnau P 2011 Macromolecules 44 3893
Takahashi H, Ishimuro Y and Watanabe H 2007 Nihon Reoroji Gakk 35 191
Scott A, Gupta R and Kulkarni G U 2010 Macromol. Chem. Phys. 211 1640
Muñoz P, Patricia M A and Vargas M D 2001 J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 82 3460
Zhang Q, Xu J J, Liu Y and Chen H Y 2008 Lab. Chip 8 352
Zhang Q, Xu J J, Liua Y and Chen H Y 2008 Lab. Chip 8 352
Goyal A, Kumar A, Patra P K, Mahendra S, Tabatabaei S, Alvarez P. J J, John G and Ajayan P M 2009 Rapid Commun. 30 1116
Rau K R, Singh R and Goldberg E 2002 Mat. Res. Innovat. 5 162
Cai D and Neyer A 2010 Microfluid Nanofluid 9 855
Bhattacharya S, Srivastava A and Pal A 2006 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45 2934
Thomas S and Stephen R 2009 Rubber nanocomposites: preparation, properties and applications (Wiley) ISBN: 978-0-470-82345-3
Walberer J A and McHugh A J 2001 J. Rheol. 45 187
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor CNR Rao for his encouragement. Support from the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, is gratefully acknowledged. RG thanks ICMS, JNCASR for financial support. Thanks to K Veeresh and Swati (CPMU, JNCASR) for their assistance in gel preparation and B Vanitha for manuscript formatting.
ᅟ
Electronic Supplementary Material
Electronic Supplementary Material Supplementary Material pertaining to this article is available on the Bulletin of Materials Science website (www.ias.ac.in/matersci).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
GIRIDHAR U KULKARNI is on lien from JNCASR, Bangalore 560064, India
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GUPTA, R., NAGAMANASA, H.K., GANAPATHY, R. et al. Viscoelastic nature of Au nanoparticle–PDMS nanocomposite gels. Bull Mater Sci 38, 817–823 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-015-0957-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-015-0957-1