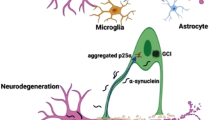
Abstract
The search for diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for neurodegenerative conditions is of high importance, since these disorders may present difficulties in differential diagnosis. Biomarkers with high sensitivity and specificity are required. Neurofilament light chain (NfL) is a unique biomarker related to axonal damage and neural cell death, which is elevated in a number of neurological disorders, and can be detected in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), as well as blood, serum, or plasma samples. Although the NfL concentration in CSF is higher than that in blood, blood measurement may be easier in practice due to its lesser invasiveness, reproducibility, and convenience. Many studies have investigated NfL in both CSF and serum/plasma as a potential biomarker of neurodegenerative disorders. Neuroimaging biomarkers can also potentially improve detection of CNS-related disorders at an early stage. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) are sensitive techniques to visualize neuroaxonal loss. Therefore, investigating the combination of NfL levels with indices extracted from MRI and DTI scans could potentially improve diagnosis of CNS-related disorders. This review summarizes the evidence for NfL being a reliable biomarker in the early detection and disease management in several CNS-related disorders. Moreover, we highlight the correlation between MRI and NfL and ask whether they can be combined.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Strimbu K, Tavel JA (2010) What are biomarkers? Curr Opin HIV AIDS 5(6):463–466. https://doi.org/10.1097/COH.0b013e32833ed177
Califf RM (2018) Biomarker definitions and their applications. Exp Biol Med (Maywood, NJ) 243(3):213–221. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370217750088
Lim J, Yue Z (2015) Neuronal aggregates: formation, clearance, and spreading. Dev Cell 32(4):491–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2015.02.002
Jeromin A, Bowser R (2017) Biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases. Adv Neurobiol 15:491–528. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-57193-5_20
Di Battista AP, Buonora JE, Rhind SG, Hutchison MG, Baker AJ, Rizoli SB, Diaz-Arrastia R, Mueller GP (2015) Blood biomarkers in moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury: potential utility of a multi-marker approach in characterizing outcome. Front Neurol 6:110. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2015.00110
Henley SM, Bates GP, Tabrizi SJ (2005) Biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Opin Neurol 18(6):698–705
Herrmann W, Obeid R (2011) Homocysteine: a biomarker in neurodegenerative diseases. Clin Chem Lab Med 49(3):435–441. https://doi.org/10.1515/CCLM.2011.084
Soylu-Kucharz R, Sandelius Å, Sjögren M, Blennow K, Wild EJ, Zetterberg H, Björkqvist M (2017) Neurofilament light protein in CSF and blood is associated with neurodegeneration and disease severity in Huntington’s disease R6/2 mice. Sci Rep 7(1):14114. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14179-1
Fuchs E, Cleveland DW (1998) A structural scaffolding of intermediate filaments in health and disease. Science 279(5350):514–519
Gaiottino J, Norgren N, Dobson R, Topping J, Nissim A, Malaspina A, Bestwick JP, Monsch AU et al (2013) Increased neurofilament light chain blood levels in neurodegenerative neurological diseases. PLoS One 8(9):e75091. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075091
Petzold A, Thompson EJ, Keir G, Quinn N, Holmberg B, Dizdar N, Wenning GK, Rascol O et al (2009) Longitudinal one-year study of levels and stoichiometry of neurofilament heavy and light chain concentrations in CSF in patients with multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Sci 279(1–2):76–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2008
Abe A, Numakura C, Saito K, Koide H, Oka N, Honma A, Kishikawa Y, Hayasaka K (2009) Neurofilament light chain polypeptide gene mutations in Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease: nonsense mutation probably causes a recessive phenotype. J Hum Genet 54(2):94–97. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2008.13
Scherling CS, Hall T, Berisha F, Klepac K, Karydas A, Coppola G, Kramer JH, Rabinovici G et al (2014) Cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament concentration reflects disease severity in frontotemporal degeneration. Ann Neurol 75(1):116–126. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24052
Poesen K, De Schaepdryver M, Stubendorff B, Gille B, Muckova P, Wendler S, Prell T, Ringer TM et al (2017) Neurofilament markers for ALS correlate with extent of upper and lower motor neuron disease. Neurology 88(24):2302–2309. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000004029
Verde F, Steinacker P, Weishaupt JH, Kassubek J, Oeckl P, Halbgebauer S, Tumani H, von Arnim CAF et al (2018) Neurofilament light chain in serum for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2018-318704
Gille B, De Schaepdryver M, Goossens J, Dedeene L, De Vocht J, Oldoni E, Goris A, Van Den Bosch L et al (2018) Serum neurofilament light chain levels as a marker of upper motor neuron degeneration in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/nan.12511
Rossi D, Volanti P, Brambilla L, Colletti T, Spataro R, La Bella V (2018) CSF neurofilament proteins as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. 265 (3):510–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-017-8730-6
Feneberg E, Oeckl P, Steinacker P, Verde F, Barro C, Van Damme P, Gray E, Grosskreutz J et al (2018) Multicenter evaluation of neurofilaments in early symptom onset amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 90(1):e22–e30. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000004761
Gaiani A, Martinelli I, Bello L, Querin G, Puthenparampil M, Ruggero S, Toffanin E, Cagnin A et al (2017) Diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: neurofilament light chain levels in definite subtypes of disease. JAMA Neurol 74(5):525–532. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.5398
Steinacker P, Huss A, Mayer B, Grehl T, Grosskreutz J, Borck G, Kuhle J, Lule D et al (2017) Diagnostic and prognostic significance of neurofilament light chain NF-L, but not progranulin and S100B, in the course of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: data from the German MND-net. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis & frontotemporal degeneration 18(1–2):112–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/21678421.2016.1241279
Oeckl P, Jardel C, Salachas F, Lamari F, Andersen PM, Bowser R, de Carvalho M, Costa J et al (2016) Multicenter validation of CSF neurofilaments as diagnostic biomarkers for ALS. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis & frontotemporal degeneration 17(5–6):404–413. https://doi.org/10.3109/21678421.2016.1167913
Weydt P, Oeckl P, Huss A, Muller K, Volk AE, Kuhle J, Knehr A, Andersen PM et al (2016) Neurofilament levels as biomarkers in asymptomatic and symptomatic familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 79(1):152–158. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24552
Menke RA, Gray E, Lu CH, Kuhle J, Talbot K, Malaspina A, Turner MR (2015) CSF neurofilament light chain reflects corticospinal tract degeneration in ALS. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2(7):748–755. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.212
Lu CH, Macdonald-Wallis C, Gray E, Pearce N, Petzold A, Norgren N, Giovannoni G, Fratta P et al (2015) Neurofilament light chain: a prognostic biomarker in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 84(22):2247–2257. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000001642
Zetterberg H, Jacobsson J, Rosengren L, Blennow K, Andersen P (2007) Cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light levels in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: impact of SOD1 genotype. Eur J Neurol 14(12):1329–1333
Sadaba MC, Tzartos J, Paino C, Garcia-Villanueva M, Alvarez-Cermeno JC, Villar LM, Esiri MM (2012) Axonal and oligodendrocyte-localized IgM and IgG deposits in MS lesions. J Neuroimmunol 247(1–2):86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2012.03.020
Huizinga R, Linington C, Amor S (2008) Resistance is futile: antineuronal autoimmunity in multiple sclerosis. Trends Immunol 29(2):54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2007.11.002
Huizinga R, Heijmans N, Schubert P, Gschmeissner S, t Hart BA, Herrmann H, Amor S (2007) Immunization with neurofilament light protein induces spastic paresis and axonal degeneration in Biozzi ABH mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66(4):295–304. https://doi.org/10.1097/nen.0b013e318040ad5c
Silber E, Semra YK, Gregson NA, Sharief MK (2002) Patients with progressive multiple sclerosis have elevated antibodies to neurofilament subunit. Neurology 58(9):1372–1381. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.58.9.1372
Soussan L, Tchernakov K, Bachar-Lavi O, Yuvan T, Wertman E, Michaelson DM (1994) Antibodies to different isoforms of the heavy neurofilament protein (NF-H) in normal aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 9(1–3):83–91. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02816107
Talja I, Reimand T, Uibo O, Reimand K, Aun S, Talvik T, Janmey PA, Uibo R (2009) Antibodies to neurofilaments. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1173(1):130–136. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04624.x
Turner MR, Kiernan MC, Leigh PN, Talbot K (2009) Biomarkers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 8(1):94–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70293-X
Tortelli R, Ruggieri M, Cortese R, D'errico E, Capozzo R, Leo A, Mastrapasqua M, Zoccolella S et al (2012) Elevated cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light levels in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a possible marker of disease severity and progression. Eur J Neurol 19(12):1561–1567. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2012.03777.x
Menke RA, Gray E, Lu CH, Kuhle J, Talbot K, Malaspina A, Turner MR (2015) CSF neurofilament light chain reflects corticospinal tract degeneration in ALS. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2(7):748–755
Lu C-H, Macdonald-Wallis C, Gray E, Pearce N, Petzold A, Norgren N, Giovannoni G, Fratta P et al (2015) Neurofilament light chain: a prognostic biomarker in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 84(22):2247–2257. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001642
Gaiani A, Martinelli I, Bello L, Querin G, Puthenparampil M, Ruggero S, Toffanin E, Cagnin A et al (2017) Diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: neurofilament light chain levels in definite subtypes of disease. JAMA Neurol 74(5):525–532. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.5398
Tortelli R, Copetti M, Ruggieri M, Cortese R, Capozzo R, Leo A, D'errico E, Mastrapasqua M et al (2015) Cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light chain levels: marker of progression to generalized amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 22(1):215–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.12421
Miller DB, O’Callaghan JP (2015) Biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease: present and future. Metabolism 64(3):S40–SS6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014
Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H et al (1997) Mutation in the α-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science 276(5321):2045–2047
Wang J, Xiao Y, Chen S, Zhong C, Luo M, Luo H (2012) Creatine for Parkinson’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2
Halliday GM, Leverenz JB, Schneider JS, Adler CH (2014) The neurobiological basis of cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 29(5):634–650. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25857
Yarnall AJ, Rochester L, Burn DJ (2013) Mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Age Ageing 42(5):567–576
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ (1992) Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 55(3):181–184
Tolosa E, Wenning G, Poewe W (2006) The diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 5(1):75–86
Sako W, Murakami N, Izumi Y, Kaji R (2015) Neurofilament light chain level in cerebrospinal fluid can differentiate Parkinson’s disease from atypical parkinsonism: evidence from a meta-analysis. J Neurol Sci 352(1–2):84–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2015.03.041
Hansson O, Janelidze S, Hall S, Magdalinou N, Lees AJ, Andreasson U, Norgren N, Linder J et al (2017) Blood-based NfL a biomarker for differential diagnosis of parkinsonian disorder. Neurology 88(10):930–937. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003680
Abdo WF, Bloem BR, Van Geel WJ, Esselink RA, Verbeek MM (2007) CSF neurofilament light chain and tau differentiate multiple system atrophy from Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 28(5):742–747
Hall S, Öhrfelt A, Constantinescu R, Andreasson U, Surova Y, Bostrom F, Nilsson C, Widner H et al (2012) Accuracy of a panel of 5 cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the differential diagnosis of patients with dementia and/or parkinsonian disorders. Arch Neurol 69(11):1445–1452
Constantinescu R, Mondello S (2013) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker candidates for parkinsonian disorders. Front Neurol 3:187. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2012.00187
Steinman L (2001) Multiple sclerosis: a two-stage disease. Nat Immunol 2(9):762
Munemoto M, Otaki Y, Kasama S, Nanami M, Tokuyama M, Yahiro M, Hasuike Y, Kuragano T et al (2011) Therapeutic efficacy of double filtration plasmapheresis in patients with anti-aquaporin-4 antibody-positive multiple sclerosis. J Clin Neurosci 18(4):478–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2010.07.141
Carson MJ (2002) Microglia as liaisons between the immune and central nervous systems: functional implications for multiple sclerosis. Glia 40(2):218–231
Kuhle J, Barro C, Disanto G, Mathias A, Soneson C, Bonnier G, Yaldizli Ö, Regeniter A et al (2016) Serum neurofilament light chain in early relapsing remitting MS is increased and correlates with CSF levels and with MRI measures of disease severity. Mult Scler J 22(12):1550–1559
Cai L, Huang J (2018) Neurofilament light chain as a biological marker for multiple sclerosis: a meta-analysis study. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 14:2241. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S173280
Khalil M, Salzer J (2016) CSF neurofilament light: a universal risk biomarker in multiple sclerosis? Neurology 87(11):1068–1069. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003107
Novakova L, Zetterberg H, Sundström P, Axelsson M, Khademi M, Gunnarsson M, Malmeström C, Svenningsson A et al (2017) Monitoring disease activity in multiple sclerosis using serum neurofilament light protein. Neurology 89(22):2230–2237. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000004683
Arrambide G, Espejo C, Eixarch H, Villar LM, Alvarez-Cermeño JC, Picón C, Kuhle J, Disanto G et al (2016) Neurofilament light chain level is a weak risk factor for the development of MS. Neurology 87(11):1076–1084. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003085
Bergman J, Dring A, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Norgren N, Gilthorpe J, Bergenheim T, Svenningsson A (2016) Neurofilament light in CSF and serum is a sensitive marker for axonal white matter injury in MS. Neurol Neurophysiol Neurosci 3(5):e271. https://doi.org/10.1212/NXI.0000000000000271
Masjuan J, Alvarez-Cermeno J, Garcia-Barragan N, Diaz-Sanchez M, Espiño M, Sadaba M, Gonzalez-Porque P, San Millán JM et al (2006) Clinically isolated syndromes a new oligoclonal band test accurately predicts conversion to MS. Neurology 66(4):576–578
Petzold A, Keir G, Green A, Giovannoni G, Thompson E (2003) A specific ELISA for measuring neurofilament heavy chain phosphoforms. J Immunol Methods 278(1–2):179–190
Williams A, Piaton G, Aigrot M-S, Belhadi A, Théaudin M, Petermann F, Thomas J-L, Zalc B et al (2007) Semaphorin 3A and 3F: key players in myelin repair in multiple sclerosis? Brain 130(10):2554–2565
Teunissen CE, Khalil M (2012) Neurofilaments as biomarkers in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler J 18(5):552–556. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458512443092
Kuhle J, Nourbakhsh B, Grant D, Morant S, Barro C, Yaldizli Ö, Pelletier D, Giovannoni G et al (2017) Serum neurofilament is associated with progression of brain atrophy and disability in early MS. Neurology 88(9):826–831. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003653
Burman J, Zetterberg H, Fransson M, Loskog AS, Raininko R, Fagius J (2014) Assessing tissue damage in multiple sclerosis: a biomarker approach. Acta Neurol Scand 130(2):81–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/ane.12239
Kuhle J, Plattner K, Bestwick JP, Lindberg RL, Ramagopalan SV, Norgren N, Nissim A, Malaspina A et al (2013) A comparative study of CSF neurofilament light and heavy chain protein in MS. Mult Scler J 19(12):1597–1603. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458513482374
Villar L, Picon C, Costa-Frossard L, Alenda R, García-Caldentey J, Espiño M, Muriel A, Álvarez-Cermeño J (2015) Cerebrospinal fluid immunological biomarkers associated with axonal damage in multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 22(8):1169–1175. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.12579
Comabella M, Fernández M, Martin R, Rivera-Vallve S, Borrás E, Chiva C, Julià E, Rovira A et al (2010) Cerebrospinal fluid chitinase 3-like 1 levels are associated with conversion to multiple sclerosis. Brain 133(4):1082–1093. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq035
Nylen K, Csajbok L, Öst M, Rashid A, Karlsson J-E, Blennow K, Nellgård B, Rosengren L (2006) CSF–neurofilament correlates with outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosci Lett 404(1–2):132–136
Burns A, Perry E, Holmes C, Francis P, Morris J, Howes M-JR, Chazot P, Lees G et al (2011) A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial of Melissa officinalis oil and donepezil for the treatment of agitation in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 31(2):158–164. https://doi.org/10.1159/000324438
Hyman BT, Phelps CH, Beach TG, Bigio EH, Cairns NJ, Carrillo MC, Dickson DW, Duyckaerts C et al (2012) National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association guidelines for the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 8(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2011.10.007
Zetterberg H, Skillbäck T, Mattsson N, Trojanowski JQ, Portelius E, Shaw LM, Weiner MW, Blennow K (2016) Association of cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light concentration with Alzheimer disease progression. JAMA Neurol 73(1):60–67. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.3037
Lewczuk P, Ermann N, Andreasson U, Schultheis C, Podhorna J, Spitzer P, Maler JM, Kornhuber J et al (2018) Plasma neurofilament light as a potential biomarker of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 10(1):71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-018-0404-9
Weston PS, Poole T, Ryan NS, Nair A, Liang Y, Macpherson K, Druyeh R, Malone IB et al (2017) Serum neurofilament light in familial Alzheimer disease: a marker of early neurodegeneration. Neurology 89(21):2167–2175. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000004667
Hoy AR, Ly M, Carlsson CM, Okonkwo OC, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Sager MA, Asthana S et al (2017) Microstructural white matter alterations in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease detected using free water elimination diffusion tensor imaging. PLoS One 12(3):e0173982. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173982
Lista S, Toschi N, Baldacci F, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Kilimann I, Teipel SJ, Cavedo E et al (2017) Diagnostic accuracy of CSF neurofilament light chain protein in the biomarker-guided classification system for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 108:355–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2017.05.010
Pijnenburg YA, Verwey NA, van der Flier WM, Scheltens P, Teunissen CE (2015) Discriminative and prognostic potential of cerebrospinal fluid phosphoTau/tau ratio and neurofilaments for frontotemporal dementia subtypes. Alzheimers Dement (Amst) 4:505–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dadm.2015.11.001
Waldö ML, Santillo AF, Passant U, Zetterberg H, Rosengren L, Nilsson C, Englund E (2013) Cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light chain protein levels in subtypes of frontotemporal dementia. BMC Neurol 13(1):54. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-13-54
Meeter LH, Dopper EG, Jiskoot LC, Sanchez-Valle R, Graff C, Benussi L, Ghidoni R, Pijnenburg YA et al (2016) Neurofilament light chain: a biomarker for genetic frontotemporal dementia. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 3(8):623–636. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.325
Rascovsky K, Hodges JR, Knopman D, Mendez MF, Kramer JH, Neuhaus J, Van Swieten JC, Seelaar H et al (2011) Sensitivity of revised diagnostic criteria for the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia. Brain 134(9):2456–2477. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr179
Neary D, Snowden JS, Gustafson L, Passant U, Stuss D, Black S, Freedman M, Kertesz A et al (1998) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology 51(6):1546–1554
Skillbäck T, Farahmand B, Bartlett JW, Rosén C, Mattsson N, Nägga K, Kilander L, Religa D et al (2014) CSF neurofilament light differs in neurodegenerative diseases and predicts severity and survival. Neurology 83(21):1945–1953. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000001015
Rosengren L, Karlsson J-E, Sjögren M, Blennow K, Wallin A (1999) Neurofilament protein levels in CSF are increased in dementia. Neurology 52(5):1090–1093
Sjögren M, Rosengren L, Minthon L, Davidsson P, Blennow K, Wallin A (2000) Cytoskeleton proteins in CSF distinguish frontotemporal dementia from AD. Neurology 54(10):1960–1964
De Jong D, Jansen RW, Pijnenburg YA, van Geel WJ, Borm GF, Kremer BP, Verbeek MM (2007) CSF neurofilament proteins in the differential diagnosis of dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78(9):936–938
Steinacker P, Feneberg E, Weishaupt J, Brettschneider J, Tumani H, Andersen PM, von Arnim CA, Böhm S et al (2016) Neurofilaments in the diagnosis of motoneuron diseases: a prospective study on 455 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 87(1):12–20
Kuhle J, Disanto G, Lorscheider J, Stites T, Chen Y, Dahlke F, Francis G, Shrinivasan A et al (2015) Fingolimod and CSF neurofilament light chain levels in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Neurology. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL 0000000000001491
Weydt P, Oeckl P, Huss A, Müller K, Volk AE, Kuhle J, Knehr A, Andersen PM et al (2016) Neurofilament levels as biomarkers in asymptomatic and symptomatic familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 79(1):152–158. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24552
Rohrer JD, Woollacott IO, Dick KM, Brotherhood E, Gordon E, Fellows A, Toombs J, Druyeh R et al (2016) Serum neurofilament light chain protein is a measure of disease intensity in frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 87(13):1329–1336. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003154
Lewis SB, Wolper RA, Miralia L, Yang C, Shaw G (2008) Detection of phosphorylated NF-H in the cerebrospinal fluid and blood of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28(6):1261–1271. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2008.12
Zanier ER, Refai D, Zipfel GJ, Zoerle T, Longhi L, Esparza TJ, Spinner ML, Bateman RJ et al (2011) Neurofilament light chain levels in ventricular cerebrospinal fluid after acute aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 82(2):157–119. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2009.177667
Traenka C, Disanto G, Seiffge DJ, Gensicke H, Hert L, Grond-Ginsbach C, Peters N, Regeniter A et al (2015) Serum neurofilament light chain levels are associated with clinical characteristics and outcome in patients with cervical artery dissection. Cerebrovasc Dis 40(5–6):222–227. https://doi.org/10.1159/000440774
Gattringer T, Pinter D, Enzinger C, Seifert-Held T, Kneihsl M, Fandler S, Pichler A, Barro C et al (2017) Serum neurofilament light is sensitive to active cerebral small vessel disease. Neurology 89(20):2108–2114. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000004645
Kuhle J, Gaiottino J, Leppert D, Petzold A, Bestwick JP, Malaspina A, Lu C-H, Dobson R et al (2015) Serum neurofilament light chain is a biomarker of human spinal cord injury severity and outcome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 86(3):273–279. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2013-307454
Nguyen HP, Kobbe P, Rahne H, Worpel T, Jager B, Stephan M, Pabst R, Holzmann C et al (2006) Behavioral abnormalities precede neuropathological markers in rats transgenic for Huntington’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 15(21):3177–3194. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddl394
Vonsattel JP (2008) Huntington disease models and human neuropathology: similarities and differences. Acta Neuropathol 115(1):55–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-007-0306-6
Sharp AH, Ross CA (1996) Neurobiology of Huntington’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 3(1):3–15. https://doi.org/10.1006/nbdi.1996.0002
Reiner A, Dragatsis I, Dietrich P (2011) Genetics and neuropathology of Huntington’s disease. Int Rev Neurobiol 98:325–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-381328-2.00014-6
Glass M, Dragunow M, Faull RL (2000) The pattern of neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease: a comparative study of cannabinoid, dopamine, adenosine and GABA(A) receptor alterations in the human basal ganglia in Huntington’s disease. Neuroscience 97(3):505–519
Byrne LM, Rodrigues FB, Blennow K, Durr A, Leavitt BR, Roos RA, Scahill RI, Tabrizi SJ et al (2017) Neurofilament light protein in blood as a potential biomarker of neurodegeneration in Huntington's disease: a retrospective cohort analysis. Lancet Neurol 16(8):601–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30124-2
Wild EJ, Petzold A, Keir G, Tabrizi SJ (2007) Plasma neurofilament heavy chain levels in Huntington’s disease. Neurosci Lett 417(3):231–233
Constantinescu R, Romer M, Oakes D, Rosengren L, Kieburtz K (2009) Levels of the light subunit of neurofilament triplet protein in cerebrospinal fluid in Huntington’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 15(3):245–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.05.012
Niemelä V, Landtblom A-M, Blennow K, Sundblom J (2017) Tau or neurofilament light—which is the more suitable biomarker for Huntington’s disease? PLoS One 12(2):e0172762. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0172762
Jakobsson J, Bjerke M, Ekman CJ, Sellgren C, Johansson AG, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Landén M (2014) Elevated concentrations of neurofilament light chain in the cerebrospinal fluid of bipolar disorder patients. Neuropsychopharmacology 39(10):2349–2356. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.81
Cousins DA, Grunze H (2012) Interpreting magnetic resonance imaging findings in bipolar disorder. CNS Neurosci Ther 18(3):201–207
Isgren A, Sellgren C, Ekman CJ, Holmen-Larsson J, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Jakobsson J, Landen M (2017) Markers of neuroinflammation and neuronal injury in bipolar disorder: relation to prospective clinical outcomes. Brain Behav Immun 65:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.05.002
Khalil M, Teunissen CE, Otto M, Piehl F, Sormani MP, Gattringer T, Barro C, Kappos L et al (2018) Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders. Nat Rev Neurol 14(10):577–589. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41582-018-0058-z
Pouw M, Hosman A, Van Middendorp J, Verbeek M, Vos P, van de Meent H (2009) Biomarkers in spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 47(7):519–525. https://doi.org/10.1038/sc.2008.176
Timmerman V, Strickland AV, Zuchner S (2014) Genetics of Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease within the frame of the human genome project success. Genes 5(1):13–32. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes5010013
Saporta MA, Shy ME (2013) Inherited peripheral neuropathies. Neurol Clin 31(2):597–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2013.01.009
Timmerman V, Clowes VE, Reid E (2013) Overlapping molecular pathological themes link Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathies and hereditary spastic paraplegias. Exp Neurol 246:14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.01.010
Jordanova A, De Jonghe P, Boerkoel C, Takashima H, De Vriendt E, Ceuterick C, Martin JJ, Butler I et al (2003) Mutations in the neurofilament light chain gene (NEFL) cause early onset severe Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease. Brain 126(3):590–597
Sandelius A, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Adiutori R, Malaspina A, Laura M, Reilly MM, Rossor AM (2018) Plasma neurofilament light chain concentration in the inherited peripheral neuropathies. Neurology 90(6):e518–e524. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000004932
Petzold A (2005) Neurofilament phosphoforms: surrogate markers for axonal injury, degeneration and loss. J Neurol Sci 233(1–2):183–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2005.03.015
Rosengren LE, Karlsson JE, Karlsson JO, Persson LI, Wikkelso C (1996) Patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other neurodegenerative diseases have increased levels of neurofilament protein in CSF. J Neurochem 67(5):2013–2018
Zucchi E, Lu CH, Cho Y, Chang R, Adiutori R, Zubiri I, Ceroni M, Cereda C, Pansarasa O, Greensmith L, Malaspina A, Petzold A (2018) A motor neuron strategy to save time and energy in neurodegeneration: adaptive protein stoichiometry. 146 (5):631-641. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14542
Petzold A, Tisdall MM, Girbes AR, Martinian L, Thom M, Kitchen N, Smith M (2011) In vivo monitoring of neuronal loss in traumatic brain injury: a microdialysis study. Brain 134(Pt 2):464–483. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq360
Petzold A, Keir G, Warren J, Fox N, Rossor MN (2007) A systematic review and meta-analysis of CSF neurofilament protein levels as biomarkers in dementia. Neurodegener Dis 4(2–3):185–194. https://doi.org/10.1159/000101843
Kuhle J, Barro C, Andreasson U, Derfuss T, Lindberg R, Sandelius A, Liman V, Norgren N et al (2016) Comparison of three analytical platforms for quantification of the neurofilament light chain in blood samples: ELISA, electrochemiluminescence immunoassay and Simoa. Clin Chem Lab Med 54(10):1655–1661. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2015-1195
Rissin DM, Kan CW, Campbell TG, Howes SC, Fournier DR, Song L, Piech T, Patel PP et al (2010) Single-molecule enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay detects serum proteins at subfemtomolar concentrations. Nat Biotechnol 28(6):595–599. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1641
Norgren N, Karlsson JE, Rosengren L, Stigbrand T (2002) Monoclonal antibodies selective for low molecular weight neurofilaments. Hybrid Hybridomics 21(1):53–59. https://doi.org/10.1089/15368590252917647
Gisslen M, Price RW, Andreasson U, Norgren N, Nilsson S, Hagberg L, Fuchs D, Spudich S et al (2016) Plasma concentration of the neurofilament light protein (NFL) is a biomarker of CNS injury in HIV infection: a cross-sectional study. EBioMedicine 3:135–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2015.11.036
Martinez-Morillo E, Childs C, Garcia BP, Alvarez Menendez FV, Romaschin AD, Cervellin G, Lippi G (2015) Neurofilament medium polypeptide (NFM) protein concentration is increased in CSF and serum samples from patients with brain injury 53 (10):1575–1584. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2014-0908
Koikkalainen J, Rhodius-Meester H, Tolonen A, Barkhof F, Tijms B, Lemstra AW, Tong T, Guerrero R et al (2016) Differential diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases using structural MRI data. NeuroImage Clin 11:435–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2016.02.019
Stoessl AJ (2012) Neuroimaging in the early diagnosis of neurodegenerative disease. Trans Neurodegeneration 1(1):5. https://doi.org/10.1186/2047-9158-1-5
Stieltjes B, Brunner RM, Fritzsche K, Laun F (2013) Diffusion tensor imaging: Introduction and atlas. Springer Science & Business Media
Kantarci K, Murray ME, Schwarz CG, Reid RI, Przybelski SA, Lesnick T, Zuk SM, Raman MR et al (2017) White-matter integrity on DTI and the pathologic staging of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 56:172–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.04.024
Fornari E, Maeder P, Meuli R, Ghika J, Knyazeva MG (2012) Demyelination of superficial white matter in early Alzheimer’s disease: a magnetization transfer imaging study. Neurobiol Aging 33(2):428.e7–428.19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.11.014
Sykova E (2004) Extrasynaptic volume transmission and diffusion parameters of the extracellular space. Neuroscience 129(4):861–876
Baldaranov D, Khomenko A, Kobor I, Bogdahn U, Gorges M, Kassubek J, Müller H-P (2017) Longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging-based assessment of tract alterations: an application to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front Hum Neurosci 11:567. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2017.00567
Foerster BR, Dwamena BA, Petrou M, Carlos RC, Callaghan BC, Churchill CL, Mohamed MA, Bartels C et al (2013) Diagnostic accuracy of diffusion tensor imaging in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a systematic review and individual patient data meta-analysis. Acad Radiol 20(9):1099–1106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2013.03.017
Schreiber S, Spotorno N, Schreiber F, Acosta-Cabronero J, Kaufmann J, Machts J, Debska-Vielhaber G, Garz C et al (2018) Significance of CSF NfL and tau in ALS. J Neurol 265(11):2633–2645. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-018-9043-0
Acosta-Cabronero J, Nestor PJ (2014) Diffusion tensor imaging in Alzheimer’s disease: insights into the limbic-diencephalic network and methodological considerations. Front Aging Neurosci 6:266. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2014.00266
Winklewski PJ, Sabisz A, Naumczyk P, Jodzio K, Szurowska E, Szarmach A (2018) Understanding the physiopathology behind axial and radial diffusivity changes-what do we know? Front Neurol 9:92. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00092
Steinacker P, Feneberg E, Weishaupt J, Brettschneider J, Tumani H, Andersen PM, von Arnim CA, Bohm S et al (2016) Neurofilaments in the diagnosis of motoneuron diseases: a prospective study on 455 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 87(1):12–20. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2015-311387
Grossman M, Elman L, McCluskey L, McMillan CT, Boller A, Powers J, Rascovsky K, Hu W et al (2014) Phosphorylated tau as a candidate biomarker for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. JAMA Neurol 71(4):442–448. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.6064
Verde F, Steinacker P, Weishaupt JH, Kassubek J, Oeckl P, Halbgebauer S, Tumani H, von Arnim CAF et al (2019) Neurofilament light chain in serum for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 90(2):157–164. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2018-318704
Chitnis T, Gonzalez C, Healy BC, Saxena S, Rosso M, Barro C, Michalak Z, Paul A, Kivisakk P, Diaz-Cruz C, Sattarnezhad N, Pierre IV, Glanz BI, Tomic D, Kropshofer H, Haring D, Leppert D, Kappos L, Bakshi R (2018) Neurofilament light chain serum levels correlate with 10-year MRI outcomes in multiple sclerosis 5 (12):1478–1491. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.638
Barro C, Benkert P, Disanto G, Tsagkas C, Amann M, Naegelin Y, Leppert D, Gobbi C et al (2018) Serum neurofilament as a predictor of disease worsening and brain and spinal cord atrophy in multiple sclerosis. Brain. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awy154
Weston PSJ, Poole T, Ryan NS, Nair A, Liang Y, Macpherson K, Druyeh R, Malone IB et al (2017) Serum neurofilament light in familial Alzheimer disease: a marker of early neurodegeneration. Neurology 89(21):2167–2175. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000004667
Niikado M, Chrem-Mendez P, Barbieri-Kennedy M, Calandri I, Martinetto H, Serra M, Calvar J, Campos J et al (2018) Evaluation of CSF neurofilament light chain levels as a routine biomarker in a memory clinic. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gly179
Rohrer JD, Woollacott IO, Dick KM, Brotherhood E, Gordon E, Fellows A, Toombs J, Druyeh R et al (2016) Serum neurofilament light chain protein is a measure of disease intensity in frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 87(13):1329–1336. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000003154
Zhang Y, Schuff N, Du A-T, Rosen HJ, Kramer JH, Gorno-Tempini ML, Miller BL, Weiner MW (2009) White matter damage in frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease measured by diffusion MRI. Brain 132(9):2579–2592. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awp071
Agosta F, Scola E, Canu E, Marcone A, Magnani G, Sarro L, Copetti M, Caso F et al (2012) White matter damage in frontotemporal lobar degeneration spectrum. Cereb Cortex 22(12):2705–2714. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhr288
Lillo P, Mioshi E, Burrell JR, Kiernan MC, Hodges JR, Hornberger M (2012) Grey and white matter changes across the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-frontotemporal dementia continuum. PLoS One 7(8):e43993. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0043993
Mahoney CJ, Simpson IJ, Nicholas JM, Fletcher PD, Downey LE, Golden HL, Clark CN, Schmitz N et al (2015) Longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging in frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 77(1):33–46. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24296
Panman JL, van der Ende EL, Meeter LH, Bouts MJ, Dopper EG, Jiskoot LC, Kaat LD, van Minkelen R et al (2017) Are neurofilament light chain and white matter integrity related biomarkers for familial frontotemporal dementia? Alzheimers Dement 13(7):751–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2017.06.992
Duering M, Konieczny MJ, Tiedt S, Baykara E, Tuladhar AM, Leijsen EV, Lyrer P, Engelter ST et al (2018) Serum neurofilament light chain levels are related to small vessel disease burden. J Stroke 20(2):228–238. https://doi.org/10.5853/jos.2017.02565
Tiedt S, Duering M, Barro C, Kaya AG, Boeck J, Bode FJ, Klein M, Dorn F et al (2018) Serum neurofilament light: a biomarker of neuroaxonal injury after ischemic stroke. Neurology 91(14):e1338–e1347. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000006282
Byrne LM, Rodrigues FB (2018) Evaluation of mutant huntingtin and neurofilament proteins as potential markers in Huntington’s disease. 10 (458). https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aat7108
Ljungqvist J, Zetterberg H, Mitsis M, Blennow K, Skoglund T (2017) Serum neurofilament light protein as a marker for diffuse axonal injury: results from a case series study. J Neurotrauma 34(5):1124–1127. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2016.4496
Tortelli R, Copetti M, Ruggieri M, Cortese R, Capozzo R, Leo A, D'Errico E, Mastrapasqua M et al (2015) Cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light chain levels: marker of progression to generalized amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 22(1):215–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.12421
Tortelli R, Ruggieri M, Cortese R, D'Errico E, Capozzo R, Leo A, Mastrapasqua M, Zoccolella S et al (2012) Elevated cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light levels in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a possible marker of disease severity and progression. Eur J Neurol 19(12):1561–1567. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2012.03777.x
Siller N, Kuhle J, Muthuraman M, Barro C, Uphaus T, Groppa S, Kappos L, Zipp F et al (2018) Serum neurofilament light chain is a biomarker of acute and chronic neuronal damage in early multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England) 1352458518765666. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458518765666
Novakova L, Zetterberg H, Sundstrom P, Axelsson M, Khademi M, Gunnarsson M, Malmestrom C, Svenningsson A et al (2017) Monitoring disease activity in multiple sclerosis using serum neurofilament light protein. Neurology 89(22):2230–2237. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000004683
Novakova L, Axelsson M, Khademi M, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Malmestrom C, Piehl F, Olsson T et al (2017) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers as a measure of disease activity and treatment efficacy in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurochem 141(2):296–304. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13881
Novakova L, Axelsson M, Khademi M, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Malmestrom C, Piehl F, Olsson T et al (2017) Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of inflammation and degeneration as measures of fingolimod efficacy in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England) 23(1):62–71. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458516639384
Hakansson I, Tisell A, Cassel P, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Lundberg P, Dahle C, Vrethem M et al (2017) Neurofilament light chain in cerebrospinal fluid and prediction of disease activity in clinically isolated syndrome and relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 24(5):703–712. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13274
Disanto G, Barro C, Benkert P, Naegelin Y, Schadelin S, Giardiello A, Zecca C, Blennow K et al (2017) Serum neurofilament light: a biomarker of neuronal damage in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 81(6):857–870. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24954
Kuhle J, Barro C, Disanto G, Mathias A, Soneson C, Bonnier G, Yaldizli O, Regeniter A et al (2016) Serum neurofilament light chain in early relapsing remitting MS is increased and correlates with CSF levels and with MRI measures of disease severity. Mult Scler (Houndmills, Basingstoke, England) 22(12):1550–1559. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458515623365
Disanto G, Adiutori R, Dobson R, Martinelli V, Dalla Costa G, Runia T, Evdoshenko E, Thouvenot E et al (2016) Serum neurofilament light chain levels are increased in patients with a clinically isolated syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 87(2):126–129. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2014-309690
Zhang Y, Li X, Qiao J (2007) Neurofilament protein light in multiple sclerosis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 87(39):2745–2749
Haghighi S, Andersen O, Oden A, Rosengren L (2004) Cerebrospinal fluid markers in MS patients and their healthy siblings. Acta Neurol Scand 109(2):97–99
Norgren N, Rosengren L, Stigbrand T (2003) Elevated neurofilament levels in neurological diseases. Brain Res 987(1):25–31
Lycke J, Karlsson J, Andersen O, Rosengren L (1998) Neurofilament protein in cerebrospinal fluid: a potential marker of activity in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64(3):402–404
Malmeström C, Haghighi S, Rosengren L, Andersen O, Lycke J (2003) Neurofilament light protein and glial fibrillary acidic protein as biological markers in MS. Neurology 61(12):1720–1725
Gunnarsson M, Malmeström C, Axelsson M, Sundström P, Dahle C, Vrethem M, Olsson T, Piehl F et al (2011) Axonal damage in relapsing multiple sclerosis is markedly reduced by natalizumab. Ann Neurol 69(1):83–89. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22247
Piehl F, Kockum I, Khademi M, Blennow K, Lycke J, Zetterberg H, Olsson T (2018) Plasma neurofilament light chain levels in patients with MS switching from injectable therapies to fingolimod. Mult Scler J 24(8):1046–1054. https://doi.org/10.1177/1352458517715132
Zhou W, Zhang J, Ye F, Xu G, Su H, Su Y, Zhang X (2017) Plasma neurofilament light chain levels in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 650:60–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.04.027
Clement A, Mitchelmore C, Andersson DR, Asuni AA (2017) Cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light chain as a biomarker of neurodegeneration in the Tg4510 and MitoPark mouse models. Neuroscience 354:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.04.030
Hu YY, He SS, Wang XC, Duan QH, Khatoon S, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Wang JZ (2002) Elevated levels of phosphorylated neurofilament proteins in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer disease patients. Neurosci Lett 320(3):156–160
Mattsson N, Insel PS, Palmqvist S, Portelius E, Zetterberg H, Weiner M, Blennow K, Hansson O (2016) Cerebrospinal fluid tau, neurogranin, and neurofilament light in Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol Med 8(10):1184–1196. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201606540
Lin YS, Lee WJ, Wang SJ, Fuh JL (2018) Levels of plasma neurofilament light chain and cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer or Parkinson disease. Sci Rep 8(1):17368. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35766-w
Wilke C, Preische O, Deuschle C, Roeben B, Apel A, Barro C, Maia L, Maetzler W et al (2016) Neurofilament light chain in FTD is elevated not only in cerebrospinal fluid, but also in serum. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 87(11):1270–1272. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2015-312972
Scherling CS, Hall T, Berisha F, Klepac K, Karydas A, Coppola G, Kramer JH, Rabinovici G et al (2014) Cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament concentration reflects disease severity in frontotemporal degeneration. Ann Neurol 75(1):116–126. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24052
Landqvist Waldo M, Frizell Santillo A, Passant U, Zetterberg H, Rosengren L, Nilsson C, Englund E (2013) Cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light chain protein levels in subtypes of frontotemporal dementia. BMC Neurol 13:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2377-13-54
Hall S, Ohrfelt A, Constantinescu R, Andreasson U, Surova Y, Bostrom F, Nilsson C, Hakan W et al (2012) Accuracy of a panel of 5 cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the differential diagnosis of patients with dementia and/or parkinsonian disorders. Arch Neurol 69(11):1445–1452. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneurol.2012.1654
Mattsson N, Ruetschi U, Pijnenburg YA, Blankenstein MA, Podust VN, Li S, Fagerberg I, Rosengren L et al (2008) Novel cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of axonal degeneration in frontotemporal dementia. Mol Med Rep 1(5):757–761. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr_00000025
Mellgren A, Price RW, Hagberg L, Rosengren L, Brew BJ, Gisslen M (2007) Antiretroviral treatment reduces increased CSF neurofilament protein (NFL) in HIV-1 infection. Neurology 69(15):1536–1541. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000277635.05973.55
de Jong D, Jansen RW, Pijnenburg YA, van Geel WJ, Borm GF, Kremer HP, Verbeek MM (2007) CSF neurofilament proteins in the differential diagnosis of dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78(9):936–938. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2006.107326
Pijnenburg YA, Janssen JC, Schoonenboom NS, Petzold A, Mulder C, Stigbrand T, Norgren N, Heijst H et al (2007) CSF neurofilaments in frontotemporal dementia compared with early onset Alzheimer’s disease and controls. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 23(4):225–230. https://doi.org/10.1159/000099473
Steinacker P, Blennow K, Halbgebauer S, Shi S, Ruf V, Oeckl P, Giese A, Kuhle J et al (2016) Neurofilaments in blood and CSF for diagnosis and prediction of onset in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Sci Rep 6:38737. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38737
Meeter LH, Dopper EG, Jiskoot LC, Sanchez-Valle R, Graff C, Benussi L, Ghidoni R, Pijnenburg YA et al (2016) Neurofilament light chain: a biomarker for genetic frontotemporal dementia. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 3(8):623–636. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.325
Steinacker P, Anderl-Straub S, Diehl-Schmid J, Semler E, Uttner I, von Arnim CAF, Barthel H, Danek A et al (2018) Serum neurofilament light chain in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 91(15):e1390–e1401. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000006318
Meeter LHH, Vijverberg EG, Del Campo M, Rozemuller AJM, Donker Kaat L, de Jong FJ, van der Flier WM, Teunissen CE et al (2018) Clinical value of neurofilament and phospho-tau/tau ratio in the frontotemporal dementia spectrum. Neurology 90(14):e1231–e1239. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000005261
Thompson AGB, Luk C, Heslegrave AJ, Zetterberg H, Mead SH, Collinge J, Jackson GS (2018) Neurofilament light chain and tau concentrations are markedly increased in the serum of patients with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, and tau correlates with rate of disease progression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 89(9):955–961. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2017-317793
Abu-Rumeileh S, Capellari S, Stanzani-Maserati M, Polischi B, Martinelli P, Caroppo P, Ladogana A, Parchi P (2018) The CSF neurofilament light signature in rapidly progressive neurodegenerative dementias 10 (1):3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-017-0331-1
Rostgaard N, Roos P, Portelius E, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Simonsen AH, Nielsen JE (2018) CSF neurofilament light concentration is increased in presymptomatic CHMP2B mutation carriers. Neurology 90(2):e157–e163. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000004799
Lin YS, Lee WJ, Wang SJ, Fuh JL (2018) Levels of plasma neurofilament light chain and cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer or Parkinson disease 8 (1):17368. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35766-w
Magdalinou NK, Noyce AJ, Pinto R, Lindstrom E, Holmen-Larsson J, Holtta M, Blennow K, Morris HR et al (2017) Identification of candidate cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in parkinsonism using quantitative proteomics. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 37:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.01.016
Hansson O, Janelidze S, Hall S, Magdalinou N, Lees AJ, Andreasson U, Norgren N, Linder J et al (2017) Blood-based NfL: a biomarker for differential diagnosis of parkinsonian disorder. Neurology 88(10):930–937. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000003680
Herbert MK, Aerts MB, Beenes M, Norgren N, Esselink RA, Bloem BR, Kuiperij HB, Verbeek MM (2015) CSF neurofilament light chain but not FLT3 ligand discriminates parkinsonian disorders. Front Neurol 6:91. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2015.00091
Abdo WF, Bloem BR, Van Geel WJ, Esselink RA, Verbeek MM (2007) CSF neurofilament light chain and tau differentiate multiple system atrophy from Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 28(5):742–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.03.010
De Marchis GM, Katan M, Barro C, Fladt J, Traenka C, Seiffge DJ, Hert L, Gensicke H et al (2018) Serum neurofilament light chain in patients with acute cerebrovascular events. Eur J Neurol 25(3):562–568. https://doi.org/10.1111/ene.13554
Gattringer T, Pinter D, Enzinger C, Seifert-Held T, Kneihsl M, Fandler S, Pichler A, Barro C et al (2017) Serum neurofilament light is sensitive to active cerebral small vessel disease. Neurology 89(20):2108–2114. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000004645
Traenka C, Disanto G, Seiffge DJ, Gensicke H, Hert L, Grond-Ginsbach C, Peters N, Regeniter A et al (2015) Serum Neurofilament light chain levels are associated with clinical characteristics and outcome in patients with cervical artery dissection. Cerebrovasc Dis (Basel, Switzerland) 40(5–6):222–227. https://doi.org/10.1159/000440774
Soylu-Kucharz R, Sandelius A, Sjogren M, Blennow K, Wild EJ (2017) Neurofilament light protein in CSF and blood is associated with neurodegeneration and disease severity in Huntington’s disease R6/2 mice. 7 (1):14114. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14179-1
Kuhle J, Gaiottino J, Leppert D, Petzold A, Bestwick JP, Malaspina A, Lu CH, Dobson R et al (2015) Serum neurofilament light chain is a biomarker of human spinal cord injury severity and outcome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 86(3):273–279. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2013-307454
Shahim P, Gren M, Liman V, Andreasson U, Norgren N, Tegner Y, Mattsson N, Andreasen N et al (2016) Serum neurofilament light protein predicts clinical outcome in traumatic brain injury. Sci Rep 6:36791. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36791
Al Nimer F, Thelin E, Nyström H, Dring AM, Svenningsson A, Piehl F, Nelson DW, Bellander B-M (2015) Comparative assessment of the prognostic value of biomarkers in traumatic brain injury reveals an independent role for serum levels of neurofilament light. PLoS One 10(7):e0132177. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132177
Shahim P, Zetterberg H, Tegner Y, Blennow K (2017) Serum neurofilament light as a biomarker for mild traumatic brain injury in contact sports. Neurology. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL 0000000000003912
Goryunov D, Nightingale A, Bornfleth L, Leung C, Liem RK (2008) Multiple disease-linked myotubularin mutations cause NFL assembly defects in cultured cells and disrupt myotubularin dimerization. J Neurochem 104(6):1536–1552. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05103.x
Zhai J, Lin H, Julien JP, Schlaepfer WW (2007) Disruption of neurofilament network with aggregation of light neurofilament protein: a common pathway leading to motor neuron degeneration due to Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease-linked mutations in NFL and HSPB1. Hum Mol Genet 16(24):3103–3116. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddm272
Perez-Olle R, Jones ST, Liem RK (2004) Phenotypic analysis of neurofilament light gene mutations linked to Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in cell culture models. Hum Mol Genet 13(19):2207–2220. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddh236
Perez-Olle R, Leung CL, Liem RK (2002) Effects of Charcot-Marie-Tooth-linked mutations of the neurofilament light subunit on intermediate filament formation. J Cell Sci 115(Pt 24):4937–4946
Jakobsson J, Bjerke M, Ekman CJ, Sellgren C, Johansson AG, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Landen M (2014) Elevated concentrations of neurofilament light chain in the cerebrospinal fluid of bipolar disorder patients. Neuropsychopharmacology 39(10):2349–2356. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.81
Rolstad S, Jakobsson J, Sellgren C, Ekman CJ, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Palsson E, Landen M (2015) Cognitive performance and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of neurodegeneration: a study of patients with bipolar disorder and healthy controls. PLoS One 10(5):e0127100. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127100
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alirezaei, Z., Pourhanifeh, M.H., Borran, S. et al. Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker, and Correlation with Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Diagnosis of CNS-Related Disorders. Mol Neurobiol 57, 469–491 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01698-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01698-3