Abstract
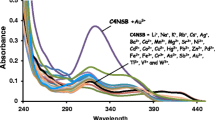
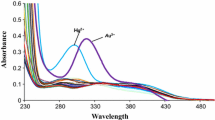
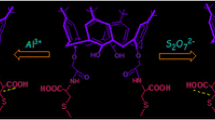
This article presents a brief account on designing of calixarene-based molecular sensor for recognition of various metal ions and anions and also different analytical techniques to monitor the recognition event. This review focuses only on calix[4]arene derivatives, in which mainly the lower rim is modified incorporating either crown moiety to make calix–crown hybrid ionophore to encapsulate metal ions or some fluoregenic inorganic and organic moieties to use it as signalling unit. In order to investigate effect of conformation of the calixarene unit and steric crowding on ion selectivity, designing of these molecules have been made using both the cone and 1,3-alternate conformations of the calixarene unit and also incorporating bulky ter-butyl group in few cases to impose controlled steric crowding. Among various ions, here focuses are mainly on biologically and commercially important alkali metal ion such as K + , toxic metal ions such as Hg2 + , Pb2 + , Cd2 + , important transition metal ion such as Cu2 + and toxic anion like F − . The techniques used to monitor the recognition event and also to determine binding constants with strongly interacting ions are fluorescence, UV-vis and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Most of the ionophores reported in this review have been characterized crystallographically, however no structural information (except one case) are incorporated in this article, as it will occupy space without significant enhancement of chemistry part. Different factors such as size of the ionophore cavity, size of metal ion, coordination sites/donor atoms, steric crowding and solvents, which determine selectivity have been discussed. Response of ion recognition process to different analytical techniques is another interesting factor discussed in this article.

Ion-recognition property of a large variety of calix[4]arenes incorporating crown moiety to make hybrid ionophore, substituents to impose steric crowding and fluoregenic moieties as signalling unit has been reported. This report demonstrates how factors such as sizes of the ionophore and metal ions, donor atoms, steric crowding and solvents, influence ion-selectivity.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
(a) de Silva A P, Gunaratne H Q N, Gunnlaugsson T, Huxley J M, Mchoy C P, Rademacher J T and Rice T E 1997 Chem. Rev. 97 1515; (b) Beer P D and Gale P A 2001 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40 486; (c) Beer P D and Hayes E 2003 J. Coord. Chem. Rev. 240 167; (d) Yoon J, Kim S K, Sing N J and Kim K S 2006 Chem. Soc. Rev. 35 355; (e) Kim J S and Quang D T 2007 Chem. Rev. 107 3780; (f) Liu Y, Li Z and Guo D S 2009 Supramolecular Chem. 21 465
(a) Gutsche C D 1989 Calixarenes (Cambridge, UK: The Royal Society of Chemistry); (b) Gutsche C D 1991 Calixarenes, A versatile class of macrocyclic compounds (eds) J Vicens and V BÖhmer) (Dordrecht, Netherlands: Kluwer); (c) BÖhmer V 1995 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34 713; (d) Gutsche C D 1998 Calixarene revisited (Cambridge, UK: The Royal Society of Chemistry); (e) Gutsche C D 2000 Calixarenes in action (eds) L Mandolini and R Ungaro (London: Imperial College Press); (f) Casnati A, Sansone F and Ungaro R 2003 Calixarene receptors in ion recognition and sensing: Advances in supramolecular chemistry (ed.) G W Gokel (Miami, FL, USA: Cerberus Press Inc.) vol. 9, p. 165; (g) Gutsche C D 2008 Calixarenes: An introduction, 2nd edition (UK: The Royal Society of Chemistry Cambridge)
(a) Kim S K, Lee S H, Lee J Y, Lee J Y, Bartsch R A and Kim J S 2004 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126 16499; (b) Lo P K and Wong M S 2008 Sensors 8 5313; (c) Yuan M, Zhou W, Liu X, Zhu M, Li J, Yin X, Zheng H, Zuo Z, Ouyang C, Liu H, Li Y and Zhu D 2008 J. Org. Chem. 73 5008; (d) Creaven B S and Mcginley D D F 2009 J. Coord. Chem. Rev. 253 893
(a) Mokhtari Bahram, Pouabdollah Kobra and Dalali Naser 2011 J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl Chem. 69 1; (b) Kim Hyun Jung, Lee Min Hee, Mutihac Lucia, Vicens Jacques and Jong Seung Kim 2012 Chem. Soc. Rev. 41 1173; (c) Joseph Roymon and Rao Chebrolu Pulla 2011 Chem. Rev. 111 3433
Agnihotri P, Suresh E, Paul P and Ghosh P K 2006 Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 3369
Patra S and Paul P 2009 Dalton Trans. 8683
Patra S, Suresh E and Paul P 2007 Polyhedron 26 4971
Patra S, Maity D, Sen A, Suresh E, Ganguly B and Paul P 2010 New J. Chem. 34 2796
Maity Debdeep, Chakraborty Ashish, Gunupuru Ravi and Paul P 2011 Inorg. Chim. Acta 372 126
Patra S, Gunupuru R, Lo R, Suresh E, Ganguly B and Paul P 2012 New J. Chem. 36 988
(a) Ikeda A, Tsudera T and Shinkai S 1997 J. Org. Chem. 62 3568; (b) Takahashi K, Gunji A, Guillaumont D, Pichierri F and Nakamura S 2000 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39 2925; (c) Kim J S, Shon O J, Ko J W, Cho M H, Yu I Y and Vicens J 2000 J. Org. Chem. 65 2386; (d) Luo J, Zheng Q-Y, Chen C-F and Huang Z-T 2005 Chem. Eur. J. 11 5917; (e) Lee Y J, Kwon J, Park C S, Lee J-E, Sim W, Kim J S, Seo J, Yoon ll, Jung J H and Lee S S 2007 Org. Lett. 9 493
(a) Casnati A, Pochini A, Ungaro R, Ugozzoli F, Arnaud F, Fanni S, Schwing M-J, Egberink R J M, de Jong F and Reinhoudt D N 1995 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117 2767; (b) Casnati A, Pochini A, Ungaro R, Bocchi C, Ugozzoli F, Egberink R J M, Struijk H, Lugtenberg R, Jong F D and Reinhoudt D N 1996 Chem. Eur. J. 2 436
Hirose K 2001 J. Incl. Phenom. 39 193
(a) Diamond D and Nolan K 2001 Anal. Chem. 73 22A; (b) Matthews S E, Schmitt P, Felix V, Drew M G B and Beer P D 2002 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 124 1341; (c) Li G-K, Xu Z-X, Chen C-F and Huang Z-T 2008 Chem. Commun.1774; (d) Dhir A, Bhalla V and Kumar M 2008 Org. Lett. 10 4891
(a) Muegge B D and Richter M M 2002 Anal. Chem. 74 547; (b) Schmittel M, Lin H-W, Thiel E, Meixner A J and Ammon H 2006 Dalton Trans.4020; (c) Schmittel M and Lin H-W 2007 Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 119 911; (d) Li M-J, Chen Z, Zhu N, Yam V W-W and Zu Y 2008 Inorg. Chem. 47 1218
(a) Jin T, Ichikawa K and Koyama T 1992 J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 499; (b) Ludwig R and Dzung N T K 2002 Sensors 2 397
(a) Lee S H, Kim S H, Kim S K, Jung J H and Kim J S 2005 J. Org. Chem. 70 9288; (b) Kim S K, Kim S H, Kim H J, Lee S H, Lee S W, Ko J, Bartsch R A and Kim J S 2005 Inorg. Chem. 44 7866; (c) Choi J K, Kim S H, Yoon J, Lee K-H, Bartsch R A and Kim J S 2006 J. Org. Chem. 71 8011; (d) Kim H J, Quang D T, Hong J, Kang G, Ham S and Kim J S 2007 Tetrahedron 63 10788
Kumar M, Kumar R and Bhalla V 2009 Tetrahedron 65 4340
(a) Ghosh K and Adhikari S 2006 Tetrahedron Lett. 47 3577; (b) Pramanik A and Das G 2009 Tetrahedron 65 2196
(a) Lin Z, Zhao Y, Duan C, Zhang B and Bai Z 2006 Chem. Commun. 3678; (b) Lin T, Chen C, Wen Y and Sun S 2007 Inorg. Chem. 46 6427; (c) Shang X, Li J, Lin H, Jiang P, Cai Z and Lin H 2009 Dalton Trans. 2096
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi, Government of India, for financial support. They thank the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi for generous support towards infrastructures and core competency development. SP and DM gratefully acknowledge the CSIR for awarding Senior Research Fellowship (SRF). Thanks are also due to Dr. E Suresh and Dr. B Ganguly for their contributions in crystallography and computational studies, respectively. Authors thank Mr. A K Das, Dr. V P Boricha and Mr. V Agrawal for recording mass, NMR and IR spectra, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendix: Drawings of the chemical structures of the receptors and complexes (1–15).
Appendix: Drawings of the chemical structures of the receptors and complexes (1–15).









Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PATRA, S., MAITY, D., GUNUPURU, R. et al. Calixarenes: Versatile molecules as molecular sensors for ion recognition study. J Chem Sci 124, 1287–1299 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-012-0329-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-012-0329-y