Abstract
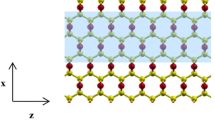
Structures and electronic properties of zigzag graphene nanoribbon (ZGNR) with pyridine (3NV-ZGNR) functionalized by Scandium (Sc) at the edge were studied through quantum chemical calculations in the formalism of density-functional theory (DFT). Pyridine-like nitrogen defects is very crucial for enhancing the Sc atom binding to the defects and is thermodynamically favoured. During Sc decoration of ZGNR there is a shift from 0.35 eV small gap semiconductor regime to that of a metal which can be used for band gap tuning by controlled saturation of Sc. ZGNR decorated with Sc can attract H2. Upon saturation of multiple H2 in quasi-molecular fashion, the metallic character is converted to semiconductors of small gap of 0.10 eV, which are predicted to be interesting materials not only for hydrogen storage but also for their band gap engineered properties.

Scandium decoration of zigzag graphene nanoribbon with pyridine can attract H2 and upon saturation of multiple H2 in quasi-molecular fashion the metallic character is converted to small gap semiconductor of 0.10 eV, predicted to be interesting materials not only for hydrogen storage but also for their band engineering properties.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Novoselov K S, Geim A K, Morozov S V, Jiang D, Katsnelson I V, Grigorieva I V, Dubonos S V and Firsov A A 2005 Nature 438 197
Katsnelson M L, Novoselov K S and Geim A K 2006 Nature Phys. 2 620
Castro Neto A H, Guinea F and Peres N M R 2006 Phys. World 19 33
Zhou S Y, Gwenon G H, Graf J, Ferdorov A V, Spataru C D, Diehl R D, Kopelevich Y, Lee D H, Louie S G and Lanzara A 2006 Nature Phys. 2 595
Geim A K and Novoselov K S 2007 Nature Mat. 6(3) 183
Novoselov K S, Jiang Z, Zhang Y, Morozov S V, Stormer H L, Zeitler U, Maan J C, Boebinger G S, Kim P and Geim A K 2007 Science 315 1379
Zheng Y and Ando T 2002 Phys. Rev. B 65 ID 245420
Novoselov K S, Geim A K, Morozov S V, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos S V and Firsov A A 2004 Science 306 (5696) 666
Fujita M, Wakabayashi K, Nakada K and Kusakabe K J J 1996 Phys. Soc. Jap. 65 1920
Miyamoto Y, Nakada K and Fujita M 1999 Phys. Rev. B 60 16211
Nakada K, Fujita M, Dresselhaus G and Dresselhaus M S 1996 Phys. Rev. B 54 17954
Maruyama K K 2003 Mat. Phys. Rev. B 67 092406
Lee H, Son Y W, Park N Han and Yu S 2005 J. Phys. Rev. B 72 174431
Rudberg E, Salek P and Luo Y 2007 Nano Lett. 7 2211
Pisani L, Chan J A and Harrison B M 2007 Nano Mat. Phys. Rev. B 75 064418
Hod O, Barone V and Scuseria G E 2008 Phys. Rev. B 77 035411
Hod O, Peralta J E and Scuseria G E 2007 Phys. Rev. B 76 233401
Hod O, Barone V, Peralta J E and Scuseria G E 2007 Nano Lett. 7 2295
Barone V, Hod O and Scuseria G E 2006 Nano Lett. 6 2748
Son Y W, Cohen M L and Louie S G 2006 Phys. Rev. Lett. 97 216803
Groot R A, Mueller F M, Engen P G and Buschow K H J Phys. Rev. Lett. 1983 50 2024
Prinz G A 1998 Science 282 1660
Ziese M 2002 Rep. Prog. Phys. 65 143
Son Y W, Cohen M L and Louie S G 2006 Nature 444 347
Kan E J, Li Z, Yang J L and Hou J G 2007 App. Phys. Lett. 91 243116
Zhao J, Ding Y, Wang X G, Cai Q and Wang X Z 2011 Diamond Relat. Mater. 20 36
Delley B 1990 J. Chem. Phys. 92 508
Delley B 2003 J. Chem. Phys. 113 7756
Dmol 3 is a density functional theory quantum mechanical package available from Accelrys Software Inc.
Perdew J P and Ernzerhof K B 1996 Mat. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77 3865
Monkhorst H J and Pack J D 1976 Phys. Rev. B 13 5188
Jose D and Datta A 2012 J. Phys. Chem. C 116 24639
Jose D and Datta A 2011 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13 7304
Jose D, Nijamudheen A and Datta A 2013 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 15 8700
Mananghaya M 2014 Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 35 (1) 253
Adamson A W and Gast A P 1997 In Physical Chemistry of Surfaces (Michigan: Wiley)
Mananghaya M, Rodulfo E, Santos G N, Villagracia A R and Ladines A N 2012 J. Nanomater. 2012 104891
Mananghaya M, Rodulfo E, Santos G N and Villagracia A R 2012 J. Nanotechnol. 2012 780815
Mananghaya M 2012 J. Korean Chem. Soc. 56(1) 34
Dong L, Craig M M, Khang D and Chen C J 2012 J. Nanotechnol. 2012 780815
Datta A 2011 Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 13 7304
Acknowledgement
This work was supported in part by the Department of Science and Technology, Philippine Council for Industry, Energy and Emerging Technology Research and Development (PCIEERD) formerly Philippine Council for Advanced Science and Technology Research and Development (DOST, PCASTRD) and De La Salle University Manila for the acquisition of the Dmol 3 v6.0 software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MANANGHAYA, M. Understanding the structure and electronic properties of N-doped graphene nanoribbons upon hydrogen saturation. J Chem Sci 126, 1737–1742 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-014-0744-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-014-0744-3