Abstract
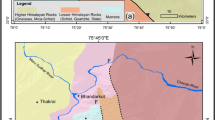
Detailed geological studies were carried out on the basaltic sequences along the Jabalpur–Niwas, Jabalpur–Chutka and Jabalpur–Mandla traverses covering an area of about \(12\hbox { km} \times 15\hbox { km}\) to characterise various basaltic lava flows and their behaviour on seismotectonics and geodynamic setting of their formation in the Mandla region of the Eastern Deccan Volcanic Province (EDVP). The studies involve an analysis of the satellite images for the identification of lineaments/faults and field geological studies consisting of geological controls such as ground check, thickness of fractures and orientation along the acknowledged lineaments/faults. The results of the present research comprising 65 lineaments/faults mainly belonging to two geometric groups, minor and major dominantly in the NW–SE and the NE–SW and altered strata varying lithology (weathered to compact basalts) are recognised in the study area. Based on their extent, 57 lineaments have been classified as minor (<100 km) trends in three different orientations, i.e., NNE–SSW, ESE–WNW and ENE–WSW, whereas 8 lineaments were classified as intermediate (300–100 km) trends in NNE–SSW. No major (>300 km) lineaments are noticed in the study region. The field geological investigations have facilitated the recognition of 10 flows with different characteristic features and a variety of volcanic structures such as columnar, vesicular, amygdaloidal, inflated pahoehoe lava flows and red bole interflow horizons have been documented. Basement rocks of these Deccan basalt lavas are represented by Tirodi Biotite gneisses, quartzite, quartz–mica schists and crystalline limestone in the SE part of the study area of the Mandla region. The present study will help evaluate the localised site characterisation for urban planning and setting up major civil structures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander P O 1979 Geochemistry and Geochronology of the Deccan Traps lava flows around Sagar, MP, India; Unpublished PhD Thesis, Sagar University, Sagar, India.
Alexander P O 1981 Age and duration of Deccan Volcanism: K-Ar evidence Deccan Volcanism and related basalt provinces in other parts of the world; Mem. J. Geol. Soc. India 3 244–258.
Arlegui L E and Soriano M A 1998 Characterizing lineaments from satellite images and field studies in the central Ebro basin (NE Spain); Int. J. Remote Sens. 19(16) 3169–3185.
Auden J B 1949 Geological discussion of the Satpura hypothesis; Proc. Nat. Inst. Sci. India 15 315–340.
Babar M D, Kaplay R D, Mukherjee S and Kulkarni P S 2017 Evidence of deformation of dykes from Central Deccan Volcanic Province, Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India; In: Tectonics of the Deccan large igneous province (eds) Mukherjee S, Misra A A, Calves G and Nemcok M, Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Publ. 445 337–353.
Bakliwal P C, Ramasamy S M and Ray A K 1983 Lineament tectonics of Proterozoic basins of western India; In: Abstracts, Proceedings of seminar on Proterozoic 1983, Lusaka, Zambia.
Bakliwal P C and Ramasamy S M 1983a Basement structures in parts of Thar desert, western India – A study aided by remote sensing; In: Abstracts, Joint INDO–US workshop on arid zone research, Central Arid Zone Research Institute (CAZARI), Jodhpur (December, 1983), p. 68.
Bakliwal P C and Ramasamy S M 1983b Occurrence of circular features in parts of Thar desert, Rajasthan; J. Geol. Soc. India 26 225–228.
Baumgartner A, Steger C, Mayer H, Eckstein W and Ebner H 1999 Automatic road extraction based on multi-scale grouping and context; Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 65 777–785.
Burdick R G and Speirer R A 1980 Development of a method to detect geologic faults and other linear features from LANDSAT images; US Bur. Mines Report Inv., pp. 8413–8474.
Casas A M, Cortes Angel L, Maestro A, Soriano M A, Riaguas A and Bernal J 2000 A program for lineament length and density analysis; Comput. Geosci. 26 1011–1022.
Chris D C and Colin W 1994 Spatial analysis of lineaments; Comput. Geosci. 20(7/8) 1237–1258.
Clark C D and Wilson C 1994 Spatial analysis of lineaments; Comput. Geosci. 20 1237–1258.
Cox K G 1980 A model for flood basalt volcanism; J. Petrol. 21(4) 629–650.
Cox K G and Hawkesworth C J 1984 Relative contribution of crust and mantle in flood basalt magmatism, Mahabaleshwar area, Deccan Traps; Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London 310 627–641.
Dasgupta S and Mukherjee S 2017 Brittle shear tectonics in a narrow continental rift: Asymmetric non-volcanic Barmer basin (Rajasthan, India); J. Geol. 125 561–591.
Dasgupta S and Mukherjee S 2019 Remote sensing in lineament identification: Examples from western India; In: Problems and solutions in structural geology and tectonics. Developments in structural geology and tectonics book series (eds) Fagereng A and Billi A, Elsevier, 5 205–221, ISSN: 2542–9000.
Dasgupta S, Pande P, Ganguly D and Iqbal Z 2000 Seismotectonic atlas of India and its environs; Geological Survey of India, 59p.
Ghosh P, Sayyed M R G, Islam R and Hundekari S M 2006 Geochemical and stable isotope studies of the Maastrichtian Inter basaltic clay (Bole bed) horizons from Deccan Traps of India: Implications for palaeo weathering and palaeo climates during Deccan Volcanism; Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 242 90–109.
Gupta H K 1994 A note on ‘stable continental region earthquakes’; J. Geol. Soc. India 43 619–620.
Gupta H K, Khanal K N, Upadhyay S K, Sarkar D, Rastogi B K and Duda S J 1995 Verification of magnitudes of Himalayan region earthquakes of 1903–1985 from Gottingen; Tectonophys. 244 267–284.
Haralick R M 1979 Statistical and structural approaches to texture; Proc. IEEE 67(5) 786–804.
Harinarayana T, Sarma S V S, Patro B P, Veeraswamy K, Sastry R S and Sarma M V C 2004 A magnetotelluric (MT) study across the Koyna seismic zone, western India: Evidence for block structure; Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 142 23–36.
Heman P J 1961 Lineament analysis on aerial photographs exemplified in the north surgeon lake area, Calgary, Alberta, West Canadian research; Publ. Geol. Relat. Sci. Ser. 2(1) 1–20.
Hobbs W H 1904 Lineaments of the Atlantic border region; Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 15 483–506.
Hobbs W H 1912 Earth features and their meaning: An introduction to geology for the student and general reader; Macmillan, New York, NY, 347p.
Hooper P R 1990 The timing of crustal extension and the eruption of continental flood basalts; Nature 349 246–249.
Hooper P R 1999 Winds of change. The Deccan traps: A personal perspective; In: Deccan volcanic province (ed.) Subbarao K V, Mem. Geol. Soc. India 43 153–165.
Hung L Q and Batelaan O 2003 Environmental geological remote sensing and GIS analysis of tropical karst areas in Vietnam; Proc. Int. Geosci. Remote Sens. Symp. (IGARSS) IV 2964–2966.
Hung L Q, Dinh N Q, Batelaan O, Tam V T and Lagrou D 2002 Remote sensing and GIS-based analysis of cave development in the Suoimuoi catchment (Son La-NW Vietnam); J. Cave Karst Stud. 64(1) 23–33.
Jensen J R 1986 Digital image processing, an introductory perspective; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Kaila K L 1988 Two alternative models for thickness of Deccan Traps (India) from DSS studies and inferences about their source origin; 28th Int. Geol. Cong., Washington, D.C., USA Abst 2, pp. 145–146.
Kaila K L, Reddy P R, Krishna V G, Roy Chowdhury K, Tewari H C, Murthy P R K and Tripathi K M 1979 Crustal investigations in India from deep seismic soundings; Geophys. Res. Bull. 17 273–292.
Kaila K L, Reddy P R, Dixit M M and Lazrenko M A 1981a Deep crustal structure at Koyna, Maharashtra indicated by deep seismic soundings; J. Geol. Soc. India 22 1–16.
Kaila K L, Murty P R K, Rao V K and Kharetchko G 1981b Crustal structure from deep seismic sounding along the KOYII (Kelsi-Loni) profile in the Deccan trap area, India; Tectonophys. 73 365–384.
Kaila K L, Murty P R K, Mall D M and Dixit M M 1987 Deep seismic soundings along Hirapur–Mandla profile, central India; Geophys. J. Roy. Astron. Soc. 89 399–404.
Kaplay R D, Kumar T V, Mukherjee S, Wesanekar P R, Babar Md and Chavan S 2017a E–W strike slip shearing of Kinwat Granitoid at South East Deccan Volcanic Province, Kinwat, Maharashtra, India; J. Earth Syst. Sci. 126 71.
Kaplay R D, Babar M D, Mukherjee S and Kumar T V 2017b Morphotectonic expression of geological structures in eastern part of south east Deccan volcanic province (around Nanded, Maharashtra, India); In: Tectonics of the deccan large igneous province (eds) Mukherjee S, Misra A A, Calvès G and Nemčok M, Geol. Soc. London, Spec. Publ. 445 317–335.
Karnieli A, Meisels A, Fisher L and Arkin Y 1996 Automatic extraction of geological linear features from digital remote sensing data using a Hough transform; Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 62 525–531.
Kashyap M, Shrivastava J P and Raju K 2010 Occurrence of small scale inflated pahoehoe lava flows in the Mandla lobe of the Eastern Deccan Volcanic Province; Curr. Sci. 98 72–76.
Keszthelyi L, Self S and Thordarson T 1999 Application of recent studies on the emplacement of basaltic lava flows to the Deccan Traps; In: Deccan volcanic province (ed.) Subba Rao K V, Mem. J. Geol. Soc. India 43 485–520.
Kim G B, Lee J Y and Lee K K 2004 Construction of lineament maps related to groundwater occurrence with ArcView and avenue TM scripts; Comput. Geosci. 30 1117–1126.
Koike K, Nagano S and Kawaba K 1998 Construction and analysis of interpreted fracture planes through combination of satellite-image derived lineaments and digital elevation model data; Comput. Geosci. 24(6) 573–583.
Lillesand T M, Keifer R W and Chipman J W 2004 Remote sensing and image interpretation (5th edn), Wiley, New York.
Mahadevan T M 1994 Deep continental structure of India: A review; Geol. Soc. India Memoir 28 1–562.
McElfresh S B Z, Harbert W, Ku C Y and Lin J S 2002 Stress modeling of tectonic blocks at Cape Kamchatka, Russia using principal stress proxies from high-resolution SAR: New evidence for the Komandorskiy block; Tectonophys. 354 239–256.
Mishra S, Misra S, Digant V, Dinesh N, Ashish W and Sukanta R 2017 A 1251 m thick deccan flood basalt pile recovered by scientific drilling in the Koyna region, western India; J. Geol. Soc. India 90 788–794.
Misra A A, Bhattacharya G, Mukherjee S and Bose N 2014 Near N-S paleo-extension in the western Deccan region in India: Does it link strike-slip tectonics with India-Seychelles rifting? Int. J. Earth Sci. 103 1645–1680.
Mukherjee S, Misra A A, Calves G and Memcok M 2017 Tectonics of the deccan large igneous province: An introduction; In: Tectonics of the deccan large igneous province (eds) Mukherjee S, Misra A A, Calves G and Nemcok M, Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 445 1–9.
Naqvi S M 2005 Geology and evolution of the Indian plate (from Hadean to Holocene-4Ga to 4 Ka); Capital Publishing Company, New Delhi, 448p.
O’Leary D W, Friedman J D and Pohn H A 1976 Lineament, linear, lineation: Some proposed new standards for old terms; Geol. Soc. America Bull. 87(10) 1463–1469.
Pattanayak S K and Shrivastava J P 2002 Basalts of the eastern deccan volcanic province, India; Gondwana Res. 5(3) 649–665.
Pawel H K and Wojciech O 1999 Multi-coverage geological interpretation of satellite images: A case study from selected areas of Poland; J. Appl. G. 1(2) 1–14.
Philpotts A R and Dickson L D 2002 Millimeter-scale modal layering and the nature of the upper solidification zone in thick flood basalt flows and other sheets of magma; J. Struct. Geol. 24 1171–1177.
Raja Rao C S, Sahasrabudhe Y S, Deshmukh S S and Raman R 1999 Distribution, structure and petrography of the Deccan traps, India; Mem. Geol. Soc. India 43 401–414.
Ramakrishnan M and Vaidhyanadhan R 2008 Geology of India; Geol. Soc. India 2 733–784.
Ramesh D S, Srinagesh D, Rai S S, Prakasam K S and Gaur V K 1993 High velocity under the deccan volcanic province; Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 77 285–296.
Ravi S 1988 Heat flow map of India and discussions on its geological and economic significance; Indian Miner. 42 89–110.
Ravishankar S 1991 Thermal and crustal structure of ‘SONATA’. A zone of mid-continental rifting in the Indian shield; J. Geol. Soc. India 37 211–220.
Ray A K, Bakliwal P C and Sharma S B 1980 Lineament fabric of western India and its relation with genesis and localization of mineral deposits – A study aided by remote sensing; In: Proceedings of the seminar on applications of photo interpretation and remote sensing for natural resources survey and environmental analysis, Ind. Soc. Photo interpretation and Remote Sensing, Dehradun, pp. 52–56.
Richards J P 2000 Lineaments revisited; SEG Newsl. 42 14–21.
Sabins F 1997 Principles and interpretation (2nd edn); Remote Sensing, Freeman, New York, NY.
Subbarao K V and Hooper P R 1988 Reconnaissance map of the deccan basalt group in the Western Ghats, India; In: Deccan flood basalts (ed.) Subbarao K V, Mem. Geol. Soc. India 10 393.
Suzen M L and Toprak V 1998 Filtering of satellite images in geological lineament analyses: An application to a fault zone in Central Turkey; Int. J. Remote Sens. 19 1101–1114.
Tiwari V M and Mishra D C 1999 Estimation of effective elastic thickness from gravity and topography data under the Deccan Volcanic Province, India; Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 171 289–299.
Tiwari V M, Vyaghreswara Rao M B S and Mishra D C 2001 Density in homogeneities beneath Deccan Volcanic Province, India as derived from gravity data; J. Geodyn. 31 1–17.
West W D 1962 The line of the Narmada and Son valleys; Curr. Sci. 31 143.
West W D 1981 The duration of Deccan trap volcanicity; Mem. Geol. Soc. India 3 277–278.
Wilkins A, Subbarao K V and Walsh G 1994 Weathering regimes in Deccan basalts; Volcanism 217–232.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their sincere thanks to Dr V M Tiwari, director, CSIR–NGRI, for his permission to submit this paper. The authors wish to thank Dr H V S Satyanarayana, project leader, Dr R K Tiwari, chief scientist (retd.) and Dr T Seshunarayana, chief scientist (retd.) for the encouragement and support during this research work. The authors also wish to thank the entire Engineering Geophysics group members of CSIR–NGRI for their help during field geological studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Saibal Gupta
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srinivas, K.N.S.S.S., Kishore, P.P. & Rao, D.V.S. The geological site characterisation of the Mandla region, Eastern Deccan Volcanic Province, Central India. J Earth Syst Sci 128, 139 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-019-1131-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-019-1131-8