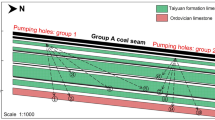
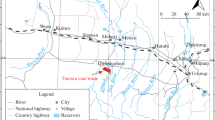
Abstract
Rapid identification of inrush water sources is vital for the safe operation of a coal mine. Hydrogeochemical (fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method and cluster analysis method) and isotope analyses are applied to identify the inrush water sources of the Mindong No. 1 mine, which is located in north-east Inner Mongolia, China. The clustering analysis and isotope analysis results show that the inrush water sources are from aquifer 1 (A1), aquifer 2 (A2) and Yimin river. However, fuzzy comprehensive evaluation shows that the inrush water sources are from A2, aquifer 3 (A3) and Yimin river. Considering the hydrogeological conditions of the study area, it is concluded that the inrush water sources are A1, A2 and Yimin river, with mixing ratios of 30.8%, 60.6% and 8.6%, respectively. The application of multiple methods makes the conclusion more reliable. Additionally, this study improves the speed and effectiveness of the identification of inrush water sources in coal mines and provides a practical reference for research related to mine water inrush to ensure the safe operation of coal mines.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belkhiri L, Boudoukha A, Mouni L and Baouz T 2010 Application of multivariate statistical methods and inverse geochemical modeling for characterization of groundwater – A case study: Ain Azel plain (Algeria); Geoderma 159(3–4) 390–398, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.08.016.
Chafouq D, El Mandour A, Elgettafi M, Himi M, Chouikri I and Casas A 2018 Hydrochemical and isotopic characterization of groundwater in the Ghis–Nekor plain (northern Morocco); J. Afr. Earth Sci. 139 1–13, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.11.007.
Chen H, Li X, Liu A and Peng S 2009 Identifying of mine water inrush sources by Fisher discriminant analysis method; J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 40(04) 1114–1120.
Chen T, Chen H, Han L, Xing X and Fu Y 2015 Stable isotopes characters of soil water movement in Shijiazhuang city; Env. Sci. 36(10) 3641–3648 (in Chinese).
Craig H 1961 Isotopic variations in meteoric waters; Science 133 1702–1703.
Dou H, Ma Z, Cao H, Liu F, Hu W and Li T 2011 Application of isotopic and hydro-geochemical methods in identifying sources of mine inrushing water; Min. Sci. Technol. (China) 21(3) 319–323, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mstc.2011.05.021.
Fallick A E, Melezhik V A, Brasier A T and Prave A R 2016 Unusual, basin-scale, fluid-rock interaction in the Palaeoproterozoic Onega basin from Fennoscandia: Preservation in calcite δ 18O of an ancient high geothermal gradient; Precamb. Res. 281 224–235, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2016.06.001.
Güler C, Thyne G D, McCray J E and Turner K A 2002 Evaluation of graphical and multivariate statistical methods for classification of water chemistry data; Hydrogeol. J. 10(4) 455–474, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-002-0196-6.
Guo X, Feng Q, Liu W, Li Z, Wen X, Si J, Xi H, Guo R and Jia B 2015 Stable isotopic and geochemical identification of groundwater evolution and recharge sources in the arid Shule River Basin of Northwestern China; Hydrol. Processes 29(22) 4703–4718, https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.10495.
Hanhu L and Yunquan C 2011 Technologies of preventing coal mine water hazards for sustainable development in North China; Geotech. Geol. Eng. 29(1) 1–5, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-010-9361-1.
Idrysy H E and Connelly R 2012 Water – The other resource a mine needs to estimate; Procedia. Eng. 46 206–212, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2012.09.466.
Jiao Y, Wang G, Fan Y, Sun T, Zhao X, Shi Z, Ma L, Lu Z, Cui L and Lv L 2014 Distinguishing water sources of the abandoned mine in Fengfeng mining area by using hydrochemistry and hydrogen, oxygen isotopes; Quat. Sci. 34(05) 1054–1061 (in Chinese).
Joshi S K, Rai S P, Sinha R, Gupta S, Densmore A L, Rawat Y S and Shekhar S 2018 Tracing groundwater recharge sources in the northwestern Indian alluvial aquifer using water isotopes (δ 18O, δ 2H and 3H); J. Hydrol. 559 835–847, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.02.056.
Jun Z, Duoxi Y and Yue S 2018 Multivariate matrix model for source identification of inrush water: A case study from Renlou and Tongting coal mine in northern Anhui province, China; In: IOP conference series: Earth and environmental science, Vol. 113, 012212, https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/113/1/012212.
Kaijun W, Baijie W and Liuqing P 2009 CVAP: Validation For cluster analyses; Data Sci. J. 8 88–93, https://doi.org/10.2481/dsj.007-020.
Li P, Wu J and Qian H 2014a Hydrogeochemistry and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in the southern part of the Yellow River alluvial plain (Zhongwei section), Northwest China; Earth Sci. Res. J. 18(1) 27–38, https://doi.org/10.15446/esrj.v18n1.34048.
Li S J, Wu Q, Cui F P, Zeng Y F and Wang G R 2014b Major characteristics of China’s coal mine water disaster occurred in recent years; Appl. Mech. Mater. 501–504 336–340, https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.501-504.336.
Liang L, Li C, Shi X, Sun B, Wang J and Zhou J 2017 Characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes of surface and groundwater and the analysis of source of lakewater in Hulun lake basin, inner Mongolia; Wetland Sci. 15(03) 385–390 (in Chinese).
Lu J, Li X, Gong F, Wang X and Liu J 2012 Recognizing of mine water inrush sources based on principal components analysis and fisher discrimination analysis method; China Saf. Sci. J. (CSSJ) 22(07) 109–115 (in Chinese).
Liu J, Wang J, Liu Y, Wu H and Zhou B 2015 Hydrochemistry analysis based on the source determination of coal mine water-bursts; J. Saf. Env. 15(01) 31–35 (in Chinese).
Ma X, Song Y, Liu S, Jiang L and Hong F 2013 Origin, age, and evolution of water in coal reservoirs: Evidence of halogen ions, stable isotopes, and 129I (in Chinese); Sci. Sin. (Terrae) 43(10) 1699–1707.
Maruyama S and Kato H 2017 Identification of waters incorporated in Laguna lake, Republic of the Philippines, based on oxygen and hydrogen isotopic ratios; Water-Sui. 9(5) 328, https://doi.org/10.3390/w9050328.
Omo-Irabor O O, Olobaniyi S B, Oduyemi K and Akunna J 2008 Surface and groundwater water quality assessment using multivariate analytical methods: A case study of the Western Niger Delta, Nigeria; Phys. Chem. Earth A/B/C 33(8–13) 666–673, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2008.06.019.
Piper A M 1944 A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis; Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 25(1) 27–39
Rozanski K, Araguás-Araguás L and Gonfiantini R 1993 Isotopic patterns in modern global precipitation; In: Climate change in continental isotopic records (eds) Swart P K, Lohmann K C, Mckenzie J and Savin S, American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, USA, pp. 1–36.
Seaman S R, Pavlou M and Copas A J 2014 Methods for observed-cluster inference when cluster size is informative: A review and clarifications; Biometrics 70(2) 449–456, https://doi.org/10.1111/biom.12151.
Shi T, Cheng J, Xie X and Zhang X 2012 Isotopic characteristics of formation waters in the North of Songliao basin and its geological significances (in Chinese); Acta Sedim. Sin. 30(02) 399–404.
Sun W, Wu Q, Dong D and Jiao J 2012 Avoiding coal-water conflicts during the development of China’s large coal-producing regions; Mine Water Environ. 31(1) 74–78, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-012-0173-9.
Wang S 2014 Identification of water bursting source based on hydrogeochemical characteristic in mixture effect of different aquifer; Min. Res. Dev. 34(03) 58–60 (in Chinese).
Wang X, Xu T and Huang D 2011 Application of distance discriminance in identifying water inrush resource in similar coalmine; J. China Coal Soc. 36(08) 1354–1358 (in Chinese).
Wu Q, Cui F, Zhao S, Liu S, Zeng Y and Gu Y 2013a Type classification and main characteristics of mine water disasters; J. China Coal Soc. 38(04) 561–565.
Wu Q, Fan S, Zhou W and Liu S 2013b Application of the analytic hierarchy process to assessment of water inrush: A case study for the No. 17 coal seam in the Sanhejian Coal Mine, China; Mine Water Environ. 32(3) 229–238, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-013-0228-6.
Xu Y, Gao Y, Li W, Wei W and Liang L 2014 Prediction of mine water inrush sources based on fuzzy evaluation of hydrochemical features; Coal Technol. 33(05) 17–20 (in Chinese).
Xu N, Gong J and Yang G 2018 Using environmental isotopes along with major hydro-geochemical compositions to assess deep groundwater formation and evolution in eastern coastal China; J. Contam. Hydrol. 208 1–9, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2017.11.003.
Yang Y, Li J, Yue J and Zhao L 2016 Study on PCA-LDA for fast identifying the type of coal mine water with LIF technology; Chem. Eng. Trans. 51 1135–1140, https://doi.org/10.3303/cet1651190.
Yi P, Yang J, Wang Y, Mugwanezal V D P, Chen L and Aldahan A 2018 Detecting the leakage source of a reservoir using isotopes; J. Environ. Radioact. 187 106–114, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2018.01.023.
Yu K, Yang Y and Zhang C 2007 Application of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method in identifying watersource of water-rush in underground shaft; Metal Mine 42(03) 47–50 (in Chinese).
Yurtsever Y 1975 Worldwide survey of stable isotopes in precipitation; Rep. Sect. Isotope Hydrol. 1–40.
Zhang G, Deng W, He Y and Ramsis S 2006 Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution laws of groundwater in Songnen Plain, Northeast China; Adv. Water Sci. 17(01) 20–28 (in Chinese).
Zhang J, Li Y, Lin M, Sun L, Du Z and Li J 2014 Hydrogeochemistry characteristics and source identification: A case study in the Zhangji coal mine in Huainan; Hydrogeol. Eng. Geol. 41(06) 32–37 +50 (in Chinese).
Zhou J, Shi X and Wang H 2010 Water-bursting source determination of mine based on distance discriminant analysis model; J. China Coal Soc. 35(02) 278–282 (in Chinese).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by ‘111’ Intellect Importation Project (B08039), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (310829161003 and 310829161010), the Special Fund for Basic Scientific Research of Central Colleges (310829163405), Xi’an Construction Science and Technology Planning Project (SJW2017-11), the open fund of Key Laboratory of Subsurface Hydrology and Ecological Effect in Arid Region of Ministry of Education (No. 300102298502) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41761144059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Abhijit Mukherjee
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, Z., Jia, Z., Zhao, Z. et al. Identification of inrush water recharge sources using hydrochemistry and stable isotopes: A case study of Mindong No. 1 coal mine in north-east Inner Mongolia, China. J Earth Syst Sci 128, 200 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-019-1232-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-019-1232-4