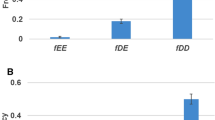
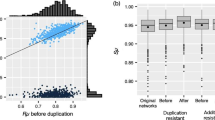
Abstract
Gene duplicates have the inherent property of initially being functionally redundant. This means that they can compensate for the effect of deleterious variation occurring at one or more sister sites. Here, I present data bearing on evolutionary theory that illustrates the manner in which any functional adaptation in duplicate genes is markedly constrained because of the compensatory utility provided by a sustained genetic redundancy. Specifically, a two-locus epistatic model of paralogous genes was simulated to investigate the degree of purifying selection imposed, and whether this would serve to impede any possible biochemical innovation. Three population sizes were considered to see if, as expected, there was a significant difference in any selection for robustness. Interestingly, physical linkage between tandem duplicates was actually found to increase the probability of any neofunctionalization and the efficacy of selection, contrary to what is expected in the case of singleton genes. The results indicate that an evolutionary trade-off often exists between any functional change under either positive or relaxed selection and the need to compensate for failures due to degenerative mutations, thereby guaranteeing the reliability of protein production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basu M. K., Carmel L., Rogozin I. B. and Koonin E. 2008 Evolution of protein domain promiscuity in eukaryotes. Genome Res. 18, 449–461.
Bozorgmehr J. E. H. 2011 An ancient frame-shifting event in the highly conserved KPNA gene family has undergone extensive compensation by natural selection in vertebrates. Biosystems 105, 210–215.
Brookfield J. F. 2003 Gene duplications: the gradual evolution of functional divergence. Curr. Biol. 13, 229–230.
Caterina J. J., Ciavatta D. J., Donze D., Behringer R. R. and Townes T. M. 1994 Multiple elements in human beta-globin locus control region 50 HS 2 are involved in enhancer activity and position-independent, transgene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 1006–1011.
Clark A. G. 1994 Invasion and maintenance of a gene duplication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 2950–2954.
Comeron J. M., Williford A. and Kliman R. M. 2008 The Hill-Robertson effect: evolutionary consequences of weak selection and linkage in finite populations. Heredity 100, 19–31.
Conant G. C. and Wagner A. 2004 Duplicate genes and robustness to transient gene knock-downs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Biol. Sci. 271, 89–96.
Dean E. J., Davis J. C., Davis R. W. and Petrov D. A. 2008 Pervasive and persistent redundancy among duplicated genes in yeast. PLoS Genet. 4, e1000113.
Ding W., Lin L., Chen B. and Dai J. 2006 L1 elements, processed pseudogenes and retrogenes in mammalian genomes. IUBMB Life 58, 677–685.
Edger P. P. and Pires J. C. 2009 Gene and genome duplications: the impact of dosage-sensitivity on the fate of nuclear genes. Chromosome Res. 17, 699–717.
Evans B. J., Chain F. J. and Ilieva D. 2008 Duplicate gene evolution and expression in the wake of vertebrate allopolyploidization. BMC Evol. Biol. 8, 43.
Goodstadt L. and Ponting C. P. 2006 Phylogenetic reconstruction of orthology, paralogy, and conserved synteny for dog and human. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2, e133.
Greer J. M., Puetz J., Thomas K. R. and Capecchi M. R. 2000 Maintenance of functional equivalence during paralogous Hox gene evolution. Nature 403, 661–665.
Gu Z., Steinmetz L. M., Gu X., Scharfe C., Davis R. W. and Li W. H. 2003 Role of duplicate genes in genetic robustness against null mutations. Nature 421, 63–66.
Guan Y., Dunham M. J. and Troyanskaya O. G. 2007 Functional analysis of gene duplications in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 175, 933–943.
Hanada K., Kuromori T., Myouga F., Toyoda T., Li W. H. and Shinozaki K. 2009 Evolutionary persistence of functional compensation by duplicate genes in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol. Evol. 1, 409–414.
Hannay K., Marcotte E. M. and Vogel C. 2008 Buffering by gene duplicates: an analysis of molecular correlates and evolutionary conservation. BMC Genomics 9, 609.
He X. and Zhang J. 2006 Transcriptional reprogramming and backup between duplicate genes: is it a genomewide phenomenon? Genetics 172, 1363–1367.
Hsiao T. L. and Vitkup D. 2008 Role of duplicate genes in robustness against deleterious human mutations. PLoS Genet. 4, e1000014.
Hughes T., Ekman D., Ardawatia H., Elofsson A. and Liberles D. A. 2007 Evaluating dosage compensation as a cause of duplicate gene retention in Paramecium tetraurelia. Genome Biol. 8, 213.
Jordan I., Wolf Y. and Koonin E. 2004 Duplicated genes evolve slower than singletons despite the initial rate increase. BMC Evol. Biol. 4, 22.
Kafri R., Levy M. and Pilpel Y. 2006 The regulatory utilization of genetic redundancy through responsive backup circuits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 11653–11658.
Kimura M. 1962 On the probability of fixation of mutant genes in a population. Genetics 47, 713–719.
Lenski R. E., Barrick J. E. and Ofria C. 2006 Balancing robustness and evolvability. PLoS Biol. 4, e428.
Li J., Yuan Z. and Zhang Z. 2010 The cellular robustness by genetic redundancy in budding yeast. PLoS Genet. 6, e1001187.
Liang H. and Li W. H. 2009 Functional compensation by duplicated genes in mouse. Trends Genet. 25, 441–442.
Long M., Zhang J., Yang H., Li L. and Dean A. M. 2010 Evolution of enzymatic activities of testis-specific short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase in Drosophila. J. Mol. Evol. 71, 241–249.
Lynch M. and Conery J. 2000 The evolutionary fate and consequences of duplicate genes. Science 290, 1151–1155.
Lynch M., O’Hely M., Walsh B. and Force A. 2001 The probability of preservation of a newly arisen gene duplicate. Genetics 159, 1789–1804.
Maltsev N., Glass E. M., Ovchinnikova G. and Gu Z. 2005 Molecular mechanisms involved in robustness of yeast central metabolism against null mutations. J. Biochem. 137, 177–187.
Negoro S., Ohki T., Shibata N., Mizuno N., Wakitani Y., Tsurukame J. et al. 2005 X-ray crystallographic analysis of 6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase: molecular basis for the birth of a nylon oligomer-degrading enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 39644–39652.
Ohta T. 2000 Evolution of gene families. Gene 259, 45–52.
Patwa Z. and Wahl L. M. 2008 The fixation probability of beneficial mutations. J. R. Soc. Interface 5, 1279–1289.
Roth C., Rastogi S., Arvestad L., Dittmar K., Light S., Ekman D. and Liberles D. A. 2006 Evolution after gene duplication: models, mechanisms, sequences, systems, and organisms. J. Exp. Zool. B. Mol. Dev. Evol. 308, 58–73.
Saitou N., Ezawa K. and Oota S. 2006 Genome-wide search of gene conversions in duplicated genes of mouse and rat. Mol. Biol. Evol. 23, 927–940.
Shastry B. S. 1995 Overexpression of genes in health and sickness. A bird’s eye view. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 112, 1–13.
Skipper M. 2003 Compensation or innovation? Nat. Rev. Genet. 4, 80.
Storz J. F. 2009 Gene duplication and the resolution of adaptive conflict. Heredity 102, 99–100.
Taverna D. M. and Goldstein R. M. 2000 The evolution of duplicated genes considering protein stability constraints. Pac. Sym. Comput. Biol. 69–80.
Tawfik D. S., Aharoni A., Gaidukov L., Khersonsky O., McQ Gould S. and Roodveldt C. 2005 The ‘evolvability’ of promiscuous protein functions. Nat. Genet. 37, 73–76.
Teichmann S. A. and Babu M. M. 2004 Gene regulatory network growth by duplication. Nat. Genet. 36, 492–496.
Vavouri T., Semple J. I. and Lehner B. 2008 Widespread conservation of genetic redundancy during a billion years of eukaryotic evolution. Trends Genet. 24, 485–488.
Wagner A. 1999 Redundant gene functions and natural selection. J. Evol. Biol. 12, 1–16.
Wagner A. 2001 Birth and death of duplicated genes in completely sequenced eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 17, 237–239.
Wagner A. 2002 Selection and gene duplication: a view from the genome. Genome Biol. 3, 1012.1–1012.3
Wagner A. 2005 Energy constraints on the evolution of gene expression. Mol. Biol. Evol. 22, 1365–1374.
Zhang J. 2003 Evolution by gene duplication: an update. Trends Ecol. Evol. 18, 292–298.
Ziha K. 2000 Redundancy and robustness of systems of events. Probabilistic engineering mechanics 15, 347–357.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Bozorgmehr J. E. H. 2012 The effect of functional compensation among duplicate genes can constrain their evolutionary divergence. J. Genet. 91, xx–xx]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BOZORGMEHR, J.E.H. The effect of functional compensation among duplicate genes can constrain their evolutionary divergence. J Genet 91, 1–8 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-012-0125-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-012-0125-y