Abstract
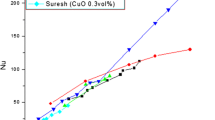
Nanofluids are a new class of heat transfer fluids developed by suspending nanosized solid particles in liquids. Larger thermal conductivity of solid particles compared to the base fluid such as water, ethylene glycol, engine oil etc. significantly enhances their thermal properties. Several phenomenological models have been proposed to explain the anomalous heat transfer enhancement in nanofluids. This paper presents a systematic literature survey to exploit the characteristics of nanofluids, viz., thermal conductivity, specific heat and other thermal properties. An empirical correlation for the thermal conductivity of Al2O3 + water and Cu + water nanofluids, considering the effects of temperature, volume fraction and size of the nanoparticle is developed and presented. A correlation for the evaluation of Nusselt number is also developed and presented and compared in graphical form. This enhanced thermophysical and heat transfer characteristics make fluids embedded with nanomaterials as excellent candidates for future applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S U S Choi, Development and applications of non-Newtonian flows edited by D A Singer and H P Wang (ASME, New York, 1995) vol. FED 231, pp. 99–105
J Buongiorno, ASME J. Heat Transfer 128, 240 (2006)
A S Ahuja, J. Appl. Phys. 46(8), 855 (1975)
H Masuda, A Ebata, K Teramae and N Hishinuma, Netsu Bussei (Japan) 4, 227 (1993)
X Wang, X Xu and S U S Choi, J. Thermophys. Heat Transfer 13(4), 474 (1999)
S K Das, N Putra, P Thiesen and W Roetzel, ASME J. Heat Transfer 125, 567 (2003)
J A Eastman, S U S Choi, S Li and L J Thompson, Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 718 (2001)
P Keblinski, S R Phillpot, S U S Choi and J A Eastman, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 45, 855 (2002)
S K Das, N Putra and W Roetzel, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 46, 851 (2003)
N Putra, W Roetzel and S K Das, ASME J. Heat Mass Transfer 39, 775 (2003)
Y Xuan and Q Li, ASME J. Heat Transfer 125, 151 (2003)
B C Pak and Y I Cho, Expt. Heat Transfer 11, 151 (1998)
H C Brinkman, J. Chem. Phys. 20, 571 (1952)
J C Maxwell, A treatise on electricity and magnetism, 2nd Ed. (Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK, 1881) vol. 1, p. 440
R L Hamilton and O K Crosser, Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals 1(3), 187 (1962)
S P Jang and S U S Choi, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84(21), 4316 (2004)
D A G Bruggeman, Ann. Phys. Leipzig 430, 285 (1935)
J E Spanier and I P Herman, Phys. Rev. B61(15), 10437 (2000)
D J Jeffery, Proc. R. Soc. London A335, 355 (1973)
R H Davis, Int. J. Thermophys. 7, 6761 (1986)
P Ravi, P Bhattacharya and P E Phelan, Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 25901 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasu, V., Rama Krishna, K. & Kumar, A.C.S. Analytical prediction of forced convective heat transfer of fluids embedded with nanostructured materials (nanofluids). Pramana - J Phys 69, 411–421 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-007-0142-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-007-0142-1