Abstract
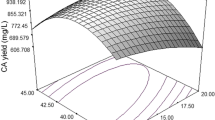
Central composite rotatable design (CCRD) of experiments was used to obtain data for Lipopeptide and Biomass concentrations from fermentation medium containing the following five components: glucose, monosodium glutamate, yeast extract, MgSO4⋅7H2O, and K2HPO4. Data was used to develop a second order regression response surface model (RSM) which was coupled with ant colony optimization (ACO) to optimize the media compositions so as to enhance the productivity of lipopeptide. The optimized media by ACO was found to yield 1.501 g/L of lipopeptide concentration which was much higher compared to 1.387 g/L predicted by Nelder–Mead optimization (NMO). The optimum from ACO was validated experimentally. RSM-based ACO is thus shown to be an effective tool for medium optimization of biosurfactant production.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Desai J D and Banat I M 1997 Microbial production of surfactants and their commercial potential. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. R. 61 (1): 47–64
Abdel-Mawgoud A M, Lépine F and Déziel E 2010 Rhamnolipids: Diversity of structures, microbial origins, and roles. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 86 (1): 323–1336
Morikawa M, Hirata Y and Imanaka T 2000 A study on the structure–function relationship of lipopeptide biosurfactants. BBA-Mol. Cell Biol. L. 1488 (3): 211–218
Peypoux F, Bonmatin J M and Wallach J 1999 Recent trends in the biochemistry of surfactin. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 51 (5): 553–563
Haddad N I, Liu X, Yang S and Mu B 2008 Surfactin isoforms from bacillus subtilus HSO121: Separation and characterization. Protein. Peptide Lett. 15 (3): 265–269
Tang J, Gao H, Hong K, Yu Y, Jiang M and Lin H 2007 Complete assignments of 1H and 13C NMR spectral data of nine surfactin isomers. Magn. Reson. Chem. 45 (9): 792–796
Cameotra S S and Makkar R S 2004 Recent applications of biosurfactants as biological and immunological molecules. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 7 (3): 262–66
Abalos A, Maximo F, Manresa M A and Bastida J 2002 Utilization of response surface methodology to optimize the culture media for the production of rhamnolipids by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa AT10. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 77: 777–784
Al-Araji L I Y, Abd-Rahman R N Z R, Basri M and Salleh A B 2007 Optimization of rhamnolipids produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa 181 using response surface modeling. Ann. Microbiol. 57 (4): 571–575
Rispoli F J, Badia D and Shah V 2010 Optimization of the fermentation media for sophorolipid production from Candida bombicola ATCC 22214 using a simplex centroid design. Biotechnol. Progr. 26 (4): 938–944
Rikalović M G, Gojgić-cvijović G, Vrvić M M and Karadzic I 2012 Production and characterization of rhamnolipids from Pseudomonas Aeruginosa-AI. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 77: 27–42
Suwansukho P, Rukachisirikul V, Kawai F and H-Kittikun A 2008 Production and applications of biosurfactant from Bacillus subtilis MUV4, Songklanakarin. J. Sci. Technol. 30 (Suppl 1): 87–93
Gu X, Zheng Z, Yu H, Wang J, Liang F and Liu R 2005 Optimization of medium constituents for a novel lipopeptide production by Bacillus Subtilis MO-01 by a response surface method. Process Biochem. 40 (10): 3196–3201
Abdel-Mawgoud M, Aboulwafa M M and Hassouna N A 2008 Optimization of surfactin production by bacillus subtilis isolate BS5. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 150: 305–325
Liu X, Ren B, Gao H, Liu M, Dai H, Song F, Yu Z, Wang S, Hu J, Kokare C R and Zhang L 2012 Optimization for the production of surfactin with a new synergistic antifungal activity. PLoS ONE 7 (5): e34430
Mutalik S R, Vaidya B K, Joshi R M, Desai K M and Nene S N 2008 Use of response surface optimization for the production of biosurfactant from Rhodococcus spp. MTCC 2574. Bioresource Technol. 99 (10): 7875–7880
Seghal Kiran S, Anto-Thomas T, Joseph S, Sabarathnam B and Lipton A P 2010 Optimization and characterization of a new biosurfactant produced by marine Brevibacterium aureum MSA 13 in solid state culture. Bioresource Technol. 101: 2389–2396
De Lima C J, Ribeiro E J, Servulo E F, Resende M M and Cardoso V L 2009 Biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa grown on residual soybean oil. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 152 (1): 156–168
Pal M P, Vaidya B K, Desai K M, Joshi R M, Nene S N and Kulkarni B D 2009 Media optimization for biosurfactant production by Rhodococcuserythropolis MTCC 2794: Artificial intelligence versus a statistical approach. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biot. 36: 747–756
Satya Eswari J, Anand M and Venkateswarlu C 2013 Optimum culture medium composition for Rhamnolipid production by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa AT10 using a novel multi-objective optimization method. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 88 (2): 271–279
Chen L Z, Nguang S K, Chen X D and Li X M 2004 Modeling and optimization of fed-batch fermentation processes using dynamical neural networks and genetic algorithms. Biochem. Eng. J. 22 (1): 51–61
Deb K 2001 Multi-objective optimization using evolutionary algorithms. New York: John Wiley & Sons
Shopova E G and Vaklieva-Bancheva N G 2006 BASIC-A genetic algorithm for engineering problem solution. Comput. Chem. Eng. 30 (8): 1293–1309
Faber R, Jockenhovel T and Tsatsaronis G 2005 Dynamic optimization with simulated annealing. Comput. Chem. Eng. 29: 273–290
Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt Jr. C D and Vecchi M P 1983 Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 220 (4598): 671–680
Blum C 2005 Beam-ACO- hybridizing ant colony optimization with beam search: An application to open shop scheduling. Comput. Oper. Res. 32 (6): 1565–1591
Dorigo M, Birattari M and Stutzle T 2006 Ant colony optimization. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 1 (4): 28–39
Socha K, Sampels M and Manfrin M 2003 Ant algorithms for the university course timetabling problem with regard to the state-of-the-art. Proceedings of the Third European Workshop on Evolutionary Computation in Combinatorial Optimization, Essex: UK, pp. 334–345
Parsopoulos K E and Vrahatis 2002 Recent approaches to global optimization problems through particle swarm optimization. Nat. Comput. 1 (2–3): 235–306
Anand P, Bhagvanth Rao M and Venkateswarlu C 2013 Multi-stage dynamic optimization of a copolymerization reactor using differential evolution. Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 8 (5): 687–698
Satya Eswari J and Venkateswarlu C 2012 Optimization of culture conditions for Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells production using differential evolution. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 4 (1): 465–470
Dorigo M, Maniezzo V and Colorni A 1996 Ant system: Optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE. Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B: Cybern. 26 (1): 29–41
Dorigo M and DiCaro G 1999 The ant colony meta-heuristic in “New Ideas in Optimization”. New York: McGraw-Hill
Dorigo M, Bonabeau E and Theraulaz G 2000 Ant algorithms and stigmergy. Future Gener. Comp. Syst. 16 (8): 851–871
Guerra-Santos L, Kappeli O and Fiechter A 1984 Pseudomonas aeruginosa biosurfactant production in continuous culture with glucose as carbon source. Appl. Environ. Microb. 48 (2): 301–305
Wei Q F, Mather R R and Fotheringham A F 2005 Oil removal from used sorbents using a biosurfactant. Bioresource Technol. 96 (3): 331–334
Cameotra S S and Makkar R S 1998 Synthesis of biosurfactants in extreme conditions. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 50: 520–529
Kuester J L and Mize J H 1973 Optimization techniques with Fortran. New York: McGraw-Hill
Satya Eswari J and Venkateswarlu C 2013 Evaluation of anaerobic biofilm reactor kinetic parameters using ant colony optimization. Environ. Eng. Sci 30 (9): 527–535
Venkateswarlu C and Gangiah K 1992 Dynamic modeling and optimal state estimation using extended Kalman filter for a kraft pulping digester. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 31 (3): 848–855
Acknowledgements
Financial assistance from DST through the grant SR/WOSA/ET-20/2009 is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ESWARI, J.S., ANAND, M. & VENKATESWARLU, C. Optimum culture medium composition for lipopeptide production by Bacillus subtilis using response surface model-based ant colony optimization. Sadhana 41, 55–65 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-015-0451-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-015-0451-x