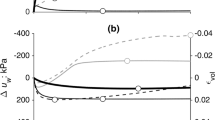
Abstract
Bridge failure due to local scour has stimulated the enthusiasm of many researchers to study the causes of scouring and to predict the ultimate scour depth at bridge foundation. A brief review of the state of artwork of investigation conducted on local scour at bridge pier in cohesive bed material is presented. Scour process and mechanism at bridge pier in cohesive and noncohesive soil are presented. The effects of parameters influencing local scour around bridge pier is discussed. Empirical equations for predicting ultimate scour depth at bridge pier embedded in cohesive soil are outlined. Comparisons of the equations are made considering two examples: one under laboratory condition and another under field condition.













Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- b :
-
pier width or pier diameter
- B :
-
diameter of scour hole
- b ′ :
-
projected width of pier perpendicular to the flow
- b * :
-
foundation diameter of circular non-dimensional pier
- C :
-
clay content
- CEC :
-
cation-exchange capacity
- Comp.:
-
degree of compaction of clayey soil
- C u :
-
cohesion
- d a :
-
arithmetic mean size of the sediment mixture
- d 50 :
-
mean particle size
- d 84 :
-
sediment size for which 84% of bed material is finer
- d 16 :
-
sediment size for which 16% of bed material is finer
- \( \hat{d} \) :
-
ratio of pier diameter to median sediment size
- E :
-
compaction energy
- F r :
-
flow Froude number
- F p :
-
pier Froude number
- g :
-
gravitational acceleration
- h :
-
flow depth
- k sh :
-
pier or abutment shape factor
- k sp :
-
correction factor for pier spacing effect
- k a :
-
correction factor for pier spacing effect
- k b :
-
correction factor for bed condition
- k w :
-
shallow water effect factor
- l :
-
length of pier
- PI :
-
plasticity index
- R p :
-
pier Reynolds number
- t :
-
time of scour
- t * :
-
dimensionless time
- UCS * :
-
dimensionless unconfined compressive strength of cohesive sediment bed
- UCS :
-
unconfined compressive strength of cohesive sediment bed
- V :
-
approaching flow velocity
- V a :
-
armour velocity
- V s :
-
scour volume
- V cs :
-
critical threshold velocity for sand used in clay–sand mixture
- V c :
-
critical mean velocity at the threshold condition
- V * :
-
shear velocity
- V *c :
-
critical shear velocity
- \( \hat{V} \) :
-
non-dimensional approach velocity
- W * :
-
antecedent moisture content required to saturate the soil sample
- W c :
-
initial moisture content (%)
- W copt :
-
proctor optimum water content
- \( \hat{W} \) :
-
non-dimensional water content
- X max :
-
maximum equilibrium scour hole diameter
- \( \hat{X}_{\hbox{max} } \) :
-
non-dimensional maximum equilibrium scour hole diameter
- Y :
-
depth from bed level to the top of the foundation
- y smax :
-
maximum scour depth
- y sms :
-
maximum scour depth below the bed level in cohesionless sediment
- y scw :
-
depth of scour in wake zone of pier in cohesive soil
- y ss :
-
depth of scour in wake zone of pier in non-cohesive soil
- y st :
-
scour depth as a function of time
- y smx :
-
extrapolated ultimate depth of scour at \( t \to \alpha \)
- \( \hat{y}_{s\hbox{max} } \) :
-
non-dimensional maximum equilibrium scour depth
- Z :
-
side slope of scour hole
- α :
-
flow attack angle
- Δγ s :
-
difference in specific weight of sediment and fluid
- γ s :
-
specific weight of sediment
- γ w :
-
specific weight of water
- ρ :
-
density of water
- ϕ c :
-
angle of repose of cohesive sediments
- θ :
-
kinematic viscosity of water
- ϕ s :
-
angle of repose of sand
- σ g :
-
sediment gradation
- τ s :
-
vane shear strength of bed
- τ c :
-
critical shear stress of bed sediment at threshold condition
- τ cs :
-
shield’s critical shear stress for cohesionless sediments
- τ max :
-
maximum shear stress
- \( \hat{\tau }_{s} \) :
-
non-dimensional bed shears strength
References
Briaud J L, Ting F C K, Chen H C, Gudavalli R, Perugu S and Wei G 1999 SRICOS: prediction of scour rate in cohesive soils at Bridge Piers. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 125(4): 237–246
Shirole A M and Holt R C 1991 Planning for comprehensive bridge safety assurance program. Transportation Research Record No.1290, Third Bridge Engineering Conference 1: 39–50
Dey S, Bose S K and Sastry G L N 1995 Clear water scour at Circular pier: a model. J. Hydraul. Eng. 121(12): 869–876
Laursen E M and Toch A 1953 A generalized model study of scour around bridge piers and abutment. In: Proceedings of IAHR International Hydraulics Conference, Minnesota, pp. 123–131
Melville B M and Cheiw Y M 1999 Time scale for local scour at bridge piers. J. Hydraul. Eng. 125(1): 59–65
Melville B W 1997 Pier and abutment scour: integrated approach. J. Hydraul. Eng. 123(2): 125–136
Raudkivi A J and Ettema R 1983 Clear-water scour at cylindrical piers. J. Hydraul. Eng. 109(3): 338–350
Sheppard D M and Miller W 2006 Live bed local pier scour experiments. J. Hydraul. Eng. 132(7): 635–642
Kumar A and Kothyari U C 2012 Three-dimensional flow characteristics within the scour hole around circular uniform and compound piers. J. Hydraul. Eng. 138(5): 420–429
Sheppard D M, Melville B and Demir H 2013 Evaluation of existing equations for local scour at bridge pier. J. Hydraul. Eng. 140(1): 14–32
Kothyari U C 2007 Indian practice on estimation of scour around bridge piers—a comment. Sadhana 32(3): 187–197
Kothyari U C and Fish 2008 Bridge scour: status and research challenges. J. Hydraul. Eng. 14(1): 1–27
Ansari S A, Kothyari U C and Ranga Raju K G 2002 Influence of cohesion on scour around bridge piers. J. Hydraul. Res. 40(6): 717–729
Briaud J L, Chen H C, Li Y and Nurtjahyo P 2004 SRICOS-EFA method for complex pier in fine-grained soil. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 130 (11): 1180–1191
Debnath K and Chaudhuri S 2010a Bridge pier scour in clay–sand mixed sediments at near-threshold velocity for sand. J. Hydraul. Eng. 136(9): 597–609
Debnath K and Chaudhuri S 2010b Laboratory experiments on local scour around cylinder for clay and clay–sand mixed bed. Elsevier Eng. Geol. 111(12): 51–61
Debnath K and Chaudhuri S 2012 Local scour around non-circular piers in clay–sand cohesive sediment beds. Elsevier Eng. Geol. 151(10): 1–14
Kho K T, Valentine E and Glendinning S 2004 An experimental study of local scour around bridge piers in cohesive soils. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Scour & Erosion, International Society of Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering (ISSMGE), London, UK
Li Y, Briaud J L, Chen H C, Nurtjahyo P and Wang J 2002 Shallow water effect on pier scour in clay. In: First International conference on scour of foundation
Link O, Klischies K, Montalva G and Dey S 2013 Effect of bed compaction on scour at piers in sand–clay mixture. J. Hydraul. Eng. 139(9): 1013–1019
Molinas A and Hosny M M 1999 Effect of gradations and cohesion on bridge scour. vol. 4. Experimental study of scour around Circular Piers in Cohesive soils. FHWA-RD-99-186
Najafzadeh M and Barani G A 2014 Experimental study of local scour around a vertical pier in cohesive soils. Scientia Iranica 21(2): 241–250
Rambabu M, Narasimha Rao S and Sundar 2003 Current-induced scour around a vertical pile in cohesive soil. Ocean Eng. 30(4): 893–920
Salaheldin T M, Imran J, Kassem A and Chaudhry H M 2003 Scale physical modeling of local scour in cohesive soil. TRB Annual Meeting. Washington, D.C., January 12–16
Ting F C K, Briaud J L, Chen H C, Gudavalli Rao, Perugu S and Wei G 2001 Flume test for scour in clay at circular pier. J. Hydraul. Eng. 127(11): 969–978
Melville B W 1975 Local scour at bridge sites. Ph.D. Dissertation. University of Auckland, School of Engineering, New Zealand
Dargahi B 1990 Controlling mechanism of local scouring. J. Hydraul. Eng. 116(10): 1197–1214
Melville B M and Coleman S E 2000 Bridge Scour. Water Resources Publication, Littleton, pp. 550
Guo J 2012 Pier scour in clear water for sediment mixture. J. Hydraul. Res. 50(1): 18–27
Ahmad F and Rajaratnam N 1998 Flow around bridge pier. J. Hydraul. Eng. 124(3): 288–300
Ali K H M and Karim O 2000 Simulation of flow around piers. J. Hydraul. Res. 40(2): 161–174
Kothyari U C, Kumar A and Jain R K 2014 Influence of cohesion on river bed scour in wake region of piers. J. Hydraul. Eng. 14(1): 1–13
Chabert J and Engeldinger P 1956 Etude des affouillements autour des pile de pont. Series A, Laboratoire Nationald’Hydraulique. Chatou, France (in French)
Shen H W, Schneider V R and Karaki S 1969 Local scour around bridge piers. J. Hydraul. Div. ASCE 96(6): 1919–1940
Sha Y Q 1965 Basic principles of sediment transport. J. Sediment Res. Beijing, China, 1(2): 1–54
Zhang Rui-jin 1989 River and sediment mechanics. Beijing, China Water Resources and Hydropower Press, pp. 63–84 (in Chinese)
Namjoshi A G 1992 Anticipated scour depth in non-alluvial/ clayey beds. In: Proceedings of International Seminar on Bridge Structure and Foundation Bombay Document 3. Conference Document 3 vol. 2
Melville B W and Sutherland A J 1988 Design method for local scour at bridge pier. J. Hydraul. Eng. 114(10): 1210–1226
Melville B W 1984 Live bed scour at Bridge Piers. J. Hydraul. Eng. 110(9): 1234–1247
Ettema R, Kirkil G and Muste M 2006 Similitude of large-scale turbulence in experiments on local scour at cylinder. J. Hydraul. Eng. 132 (1): 33–40
Sumer B M, Fredsoe J and Christiansen N 1993 Influence of cross section on wave scour around piles. J. Waterway Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 119(5): 477–495
Tison L J 1940 Erosion autour de piles de pont en riviere. Ann. Des Travaux Publics de Belgique 41(6): 813–871
Larras J 1963 Profondcurs maximales d’crosion des fonds mobiles autour des piles en rivière. Ann. Ponts et Chaussées, Vl. 133(4): 411–424
Paintal A S and Garde R J 1965 Effect of inclination and shape of obstruction on local scour. Roorkee University Res. J. 8(1&2): 51–64
Dietz J W 1973 Kolkbildung an einem krciszylindrischen Pfeilerpaar. Die Bautechnik 50(6): 203–208
Melville B W and Raudkivi A J 1996 Effect of foundation geometry on bridge pier scour. J. Hydraul. Eng. 122(4): 203–209
Richardson E V and Davis S R 2001 Evaluating scour at bridge. 4th edn. Hydraulic Engineering Circular No. 18 (HEC-18). Publication No. FHWA NHI 01-001, Federal Highway Administration, U.S. Department of Transportation, Washington, DC
Laursen E M 1960 Scour at bridge crossings. In: Proceedings of ASCE, vol. 86, pp. 39–54
Ettema R 1980 Scour at bridge pier. No. 216, School of Engineering, University of Auckland, Aukland, New Zealand
Cheiw 1984 Local scour at bridge pier. PhD thesis, Auckland University, New Zealand
Nicollet G and Ramette M 1971 Scour at bridge cylindrical piers. In: Proceedings of the 14th IAHR Congress, Paris, vol. 3, pp. 315–322
Dietz J W 1972 Ausbildung von langen Pfeilern bei Schraganströmung am Beispiel der BAB-Mainbrücke Ed-dersheim; Mitt. blatt der Bundesanstalt für Wasserbau, Karlsruhe, No. 31, pp. 79–94
Lacey G 1930 Stable channel in alluvium. Minutes Proc. Instit. Civ. Eng. 229(1930): 259–292
Press W H, Flnnery B P, Teukolsky S A and Vetterling W T 1986 Numerical recipes—the art of scientific computing, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Briaud J L, Chen H C, Kwak, K W, Han S W and Ting F C K, 2001 Multiflood and multilayer method for scour rate prediction at bridge piers. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 127(2): 114–125
Indian Railway Standard 1985 Code of practice for the design of sub-structures and foundation of bridges. Research Designs and Standards Organisation, Lucknow
IRC 1998 Standard specifications and code of practice for road bridges. Section 1, IRC: 5-1998
IRC 2000 Standard specifications and code of practice for road bridges. Section VII, IRC: 78-2000
Arneson L A, Zevenbergen L W, Lagasse P F and Clopper P E 2012 Evaluating scour at bridge. 5th edn. Hydraul. Eng. Circular No.18 (HEC-18). Rep.No. FHWA-HIF-12-003, Federal Highway Administration, U.S. Dept. of Transportation, Washington, D.C.
Acknowledgements
Support provided by MHRD and National Institute of Technology, Silchar, India, for the research is appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sonia Devi, Y., Barbhuiya, A.K. Bridge pier scour in cohesive soil: a review. Sādhanā 42, 1803–1819 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-017-0698-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-017-0698-5