Abstract
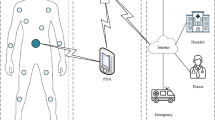
Wireless Body Area Networks (WBANs) is a revolutionary achievement in the field of health services. The field is envisioned to play an important role in medical, psychological, and even in non-medical applications. Different routing protocols are being designed in WBAN to enhance its performance, focusing on delay, energy efficiency, throughput, and network lifetime. Line-of-sight (LoS) and Non-Line-of-Sight (NLoS) communications and clustering are the least focused areas in the literature. This paper presents a routing protocol called Dual Sink approach using Clustering in Body Area Network (DSCB) which is more reliable in terms of network stability, and energy efficient in comparison to its counterparts. This protocol enhances network life-time by introducing the concept of clustering while using two sink nodes. The proposed scheme is compared with existing protocols named as SIMPLE and DARE. The cost function is established for selection of forwarder node, based on nodal distance from the sink, residual energy, and transmission power. Simulation results depict that the proposed protocol achieves significant performance improvement in network throughput by attaining 55% and 22% more efficient results compared to SIMPLE and DARE respectively. Furthermore, the results show improved performance of DSCB protocol, in terms of network stability and end-to-end delay performance metrics.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ullah S, Khan P, Ullah N, Saleem S, Higgins H, Kwak KS (2010) A review of wireless body area networks for medical applications. arXiv preprint arXiv:1001.0831
Patel M, Wang J (2010) Applications, challenges, and prospective in emerging body area networking technologies. IEEE Wirel Commun Mag 17:80–88
Cavallari R, Martelli F, Rosini R, Buratti C, Verdone R (2014) A survey on wireless body area networks: technologies and design challenges. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 16:1635–1657
Karthiga I, Sankar S, Dhivahar P (2015) A study on routing protocols in wireless body area networks and its suitability for m-Health applications. In Communications and Signal Processing (ICCSP), 2015 International Conference on. pp 1064–1069
Juneja S, Kendre S, Patkar U (2016) Healthcare analysis via wireless sensor network. IJSRSET Journal 2:2395–1990
Kachroo R, Bajaj DR (2015) A novel technique for optimized routing in wireless body area network using genetic algorithm. J Netw Commun Emerg Technol (JNCET), 2, www.jncet.org
Ghamari M, Janko B, Sherratt RS, Harwin W, Piechockic R, Soltanpur C (2016) A survey on wireless body area networks for eHealthcare systems in residential environments. Sensors 16:831
Salayma M, Al-Dubai A, Romdhani I, Nasser Y (2017) Wireless body area network (WBAN): a survey on reliability, fault tolerance, and technologies coexistence. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 50:3
Wolgast G, Ehrenborg C, Israelsson A, Helander J, Johansson E, Manefjord H (2016) Wireless body area network for heart attack detection (education corner). IEEE Antennas Propag Mag 58:84–92
Honeine P, Mourad F, Kallas M, Snoussi H, Amoud H, Francis C (2011) Wireless sensor networks in biomedical: body area networks. In Systems, Signal Processing and their Applications (WOSSPA), 2011 7th International Workshop on, pp 388–391
Sharma R, Ryait HS, Gupta AK (2016) Wireless body area nework–a review
Dangi KG, Panda SP (2014) Challenges in wireless body area network-a survey. In Optimization, Reliabilty, and Information Technology (ICROIT), 2014 International Conference on, pp 204–207
Latré B, Braem B, Moerman I, Blondia C, Demeester P (2011) A survey on wireless body area networks. Wirel Netw 17:1–18
Movassaghi S, Abolhasan M, Lipman J, Smith D, Jamalipour A (2014) Wireless body area networks: a survey. IEEE Commun Surv Tutorials 16:1658–1686
Ha I (2015) Technologies and research trends in wireless body area networks for healthcare: a systematic literature review. Int J Distrib Sens Netw 2015:4
Shehu NM, Adam MM (2016) A survey on thermal aware routing protocols in WBAN. Science (ETEBMS-2016) 5:6
Lai X, Liu Q, Wei X, Wang W, Zhou G, Han G (2013) A survey of body sensor networks. Sensors 13:5406–5447
Hayajneh T, Almashaqbeh G, Ullah S, Vasilakos AV (2014) A survey of wireless technologies coexistence in WBAN: analysis and open research issues. Wirel Netw 20:2165–2199
Ayatollahitafti V, Ngadi MA, bin Mohamad Sharif J, Abdullahi M (2016) An efficient next hop selection algorithm for multi-hop body area networks. PLoS One 11:e0146464
Nadeem Q, Javaid N, Mohammad S, Khan M, Sarfraz S, Gull M (2013) Simple: stable increased-throughput multi-hop protocol for link efficiency in wireless body area networks. In Broadband and Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications (BWCCA), 2013 Eighth International Conference on, pp 221–226
Tauqir A, Javaid N, Akram S, Rao A, Mohammad S (2013) Distance aware relaying energy-efficient: dare to monitor patients in multi-hop body area sensor networks. In Broadband and Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications (BWCCA), 2013 Eighth International Conference on, pp 206–213
Fortino G, Di Fatta G, Pathan M, Vasilakos AV (2014) Cloud-assisted body area networks: state-of-the-art and future challenges. Wirel Netw 20:1925–1938
Adhikary S, Choudhury S, Chattopadhyay S (2016) A new routing protocol for WBAN to enhance energy consumption and network lifetime. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Distributed Computing and Networking, p 40
Sahndhu MM, Javaid N, Imran M, Guizani M, Khan ZA, Qasim U (2015) BEC: a novel routing protocol for balanced energy consumption in Wireless Body Area Networks. In 2015 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), pp 653–658
Ha I (2016) Even energy consumption and backside routing: an improved routing protocol for effective data transmission in wireless body area networks. Int J Distrib Sens Netw 12:1550147716657932
Singh S, Negi S, Uniyal A, Verma SK (2016) Modified new-attempt routing protocol for wireless body area network. In Advances in Computing, Communication, & Automation (ICACCA) (Fall), International Conference on, pp 1–5
Maskooki A, Soh CB, Gunawan E, Low KS (2015) Adaptive routing for dynamic on-body wireless sensor networks. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics 19:549–558
Smail O, Kerrar A, Zetili Y, Cousin B (2016) ESR: energy aware and stable routing protocol for WBAN networks. In 12th International Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC 2016)
Singh K, Singh RK (2015) An energy efficient fuzzy based adaptive routing protocol for wireless body area network. In 2015 I.E. UP Section Conference on Electrical Computer and Electronics (UPCON), pp. 1–6
Chebbo H, Abedi S, Lamahewa TA, Smith DB, Miniutti D, Hanlen L (2012) Reliable body area networks using relays: restricted tree topology. In Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), 2012 International Conference on, pp 82–88
Kaur HP, Goyal K (2015) Cost based efficient routing for wireless body area networks
Ahmad A, Javaid N, Qasim U, Ishfaq M, Khan ZA, Alghamdi TA (2014) RE-ATTEMPT: a new energy-efficient routing protocol for wireless body area sensor networks. Int J Distrib Sens Netw 9:2014
Ahmed S, Javaid N, Yousaf S, Ahmad A, Sandhu M, Imran M et al (2015) Co-LAEEBA: cooperative link aware and energy efficient protocol for wireless body area networks. Comput Hum Behav 51:1205–1215
Hall PS, Hao Y (2006) Antennas and propagation for body centric communications. In 2006 First European Conference on Antennas and Propagation, pp 1–7
Hall PS, Hao Y, Nechayev YI, Alomainy A, Constantinou CC, Parini C et al (2007) Antennas and propagation for on-body communication systems. IEEE Antennas Propag Mag 49:41–58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection: Special Issue on Software Defined Networking: Trends, Challenges and Prospective Smart SolutionsGuest Editors: Ahmed E. Kamal, Liangxiu Han, Sohail Jabbar, and Liu Lu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ullah, Z., Ahmed, I., Razzaq, K. et al. DSCB: Dual sink approach using clustering in body area network. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 12, 357–370 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-017-0587-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-017-0587-z