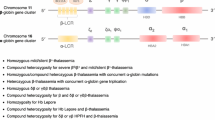
Abstract
Thalassemia is a common genetic disorder. It has been estimated that in India nearly 5 crore people are thalassemia carriers. They are asymptomatic and are detected on blood tests. These people are at same risk of developing iron deficiency anemia as general population and need iron therapy in the presence of iron deficiency anemia. Nearly 12,000 children with thalassemia major (Homozygous state) are born every year. These children often present with significant anemia along with hepatosplenomegaly during infancy and require early diagnosis and institution of therapy with repeated blood transfusions and chelation therapy. Adequate dose of chelation therapy is essential to maintain serum ferritin around 1000 ng/ml. With present protocol of management, thalassemic children have near normal life. Bone marrow transplantation offers cure for these children; results of bone marrow transplantation are best when performed below 7 y of age.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohanty D, Colah RB, Gorakshakar AC, et al. Prevalence of β-thalassemia and other haemoglobinopathies in six cities in India: a multicenter study. J Community Genet. 2013;4:33–42.
Choudhry VP. Anemia. In: Choudhury N, Bharucha ZS, editors. A textbook on laboratory and clinical transfusion medicine. Good clinical transfusion practices, vol. 3. New York: Nova; 2016. p. 1–34.
Weatherall DJ. Haemoglobin and the inherited disorders of globin synthesis. In: Hoffbrand, Catovsky, Tuddenham, editors. Postgraduate hemotology. 5th ed. Hoboken: Blackwell Publishers; 2005. p. 85–103.
Choudhry VP, Aroa JS. Thalassemia. In: Gupta P, Menon PSN, Ramji S, Lodha R, editors. PG textbook of pediatrics, vol. 2. New Delhi: Jaypee Health Science; 2015. p. 1556–64.
Trompeter S, Cohen A. Blood transfusion. In: Cappellini MD, Cohen A, Porter J, Taher A, Viprakasit V, editors. Guidelines for the clinical management of transfusion dependent thalassemia. 3rd ed. Cyprus: Thalassemia International Federation Publication; 2014. p. 28–41.
Choudhry VP, Pati HP, Saxena A, et al. Deferiprone, efficacy and safety. Indian J Pediatr. 2004;71:213–6.
Taher AT, Musallam KM, Cappellini MD, Weatherall DJ. Optimal management of β-thalassemia intermedia. Br J Hematol. 2011;152:512–23.
Chandy M. Stem cell transplantation in India. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2008;42:S81–4.
Borgna-Pignatti C. The life of patients with thalassemia major. Haematologica. 2010;95:345–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhry, V.P. Thalassemia Minor and Major: Current Management. Indian J Pediatr 84, 607–611 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-017-2325-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-017-2325-1