Abstract
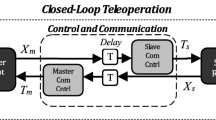
This paper presents an energy-bounding approach for robustly stable bilateral teleoperation over a communication channel with severe variable time delays and packet drops. We extend the energy-bounding algorithm (EBA) for haptic interaction with virtual environments to bilateral teleoperation with remote environments by using an analogy between haptic interaction and teleoperation controls. Robust stability is achieved by both restricting the extra energy that is generated by the sample-and-hold to within the consumable energy in the master device or slave robot and passifying the communication network. Theoretical analyses of transparency are performed for both position and force tracking aspects. Comprehensive test results for various free and contact motions subsequently show that the proposed bilateral EBA can ensure robust stability against fairy large constant/variable round trip time delays (tested for up to 5 sec for free motion and 600 msec for contact motion within the device workspace) as well as for packet losses of up to 90 % during data transmission.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. B. Sheridan, Space teleoperation through time delay: review and prognosis, IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 9(5) (1993) 592–606.
P. F. Hokayem and M. W. Spong, Bilateral teleoperation: An historical survey, Automatica, 42 (2006) 2035–2057.
Y. Tang and M. A. Arteaga, Adaptive control of robot manipulators based on passivity, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 39(9) (1994) 1871–1875.
A. Albu-Schaffer and G. Hirzinger, Parameter identification and passivity based joint control for a 7 DOF torque controlled light weight robot, Proc. of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (2001) 2852–2858.
J. E. Colgate and G. G. Schenkel, Passivity of a class of sampled-data systems: Application to haptic interfaces, Journal of Robotic Systems, 14(1) (1997) 37–47.
B. Hannaford and J.-H. Ryu, Time domain passivity control of haptic interfaces, IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 18(1) (2002) 1–10.
J. -P. Kim and J. Ryu, Robustly stable haptic interaction control using an energy-bounding algorithm, International Journal of Robotic Research, 29(6) (2010) 666–679.
J. Kim, J. -P. Kim, C. Seo and J. Ryu, An energy bounding approach for directional transparency in multiple degree-of-freedom haptic interaction, Proc. of Third Joint Eurohaptics Conference and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems (WorldHaptics2009), (2009) 320–325.
R. J. Anderson and M. W. Spong, Bilateral control of teleoperators with time delay, IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 34(5) (1989) 494–501.
G. Niemeyer and J-J. E. Slotine, Stable adaptive teleoperation, IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 16(1) (1991) 152–162.
G. Niemeyer and J-J. E. Slotine, Telemanipulation with time delays, International Journal of Robotics Research, 23(9) (2004) 873–890.
K. Kosuge, H. Murayama and K. Takeo, bilateral feedback control of telemanipulators via computer network, Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 3 (1996) 1380–1385.
Y. Yokokohji, T. Tsujioka, T. Yoshikawa, Bilateral control with time-varying delay including communication blackout, Proc. of 10th Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems (2002) 285–292.
S. Munir and W. J. Book, Wave-Based Teleoperation with Prediction, Proc. of the American Control Conference, 6 (2001) 4605–4611.
H. Ching and W. J. Book, Internet-based bilateral teleoperation based on wave variable with adaptive predictor and direct drift control, Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 128(1) (2006) 86–93.
N. Chopra, M.W. Spong, R. Ortega and N.E. barabanov, on tracking performance in bilateral teleoperation, IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 22 (2006) 861–866.
J. Artigas, J. Vilanova, C. Preusche and G. Hirzinger, Time domain passivity control-based telepresence with time delay, Proc. of IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Systems (2006) 4205–4210.
J. Artigas, C. Preusche and G. Hirzinger, Time domain passivity for delayed haptic telepresence with energy reference, Proc. of IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Systems (2007) 1612–1617.
J. Artigas, C. Preusche and G. Hirzinger, G. Borghesan, C. Melchiorri, Bilateral energy transfer in delayed teleoperation on the time domain, Proc. of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (2008) 671–676.
J. -H. Ryu and C. Preusche, Stable bilateral control of teleoperators under time-varying communication delay: time domain passivity approach, Proc. of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (2007) 3508–3513.
D. Lee and M. W. Spong, Passive bilateral teleoperation with constant time delay, IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 22(2) (2006) 269–281.
E. Nuno, R. Ortega, N. Barabanov and L. Basanez, A globally stable pd controller for bilateral teleoperators, IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 24(3) (2008) 753–758.
J. -P. Kim, C. Seo and J. Ryu, A preliminary test for bilateral teleoperation using energy bounding algorithm, Proc. of 16th IEEE International Conference on Robot & Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN 2007), (2007) 304–309.
C. Seo, J. Kim, J.-P. Kim, J. H. Yoon and J. Ryu, Stable bilateral teleoperation using the energy-bounding algorithm: basic idea and feasibility tests, IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM 2008), (2008) 335–340.
N. Hogan, Controlling impedance at the man/machine interface, Proc. of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (1989) 1626–1631.
D. A. Lawrence, Stability and transparency in bilateral teleoperation, IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 9(5) 624–637.
Y. Yokokohji and T. Yoshikawa, Bilateral control of master-slave manipulators for ideal kinesthetic coupling-formulation and experiment, IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 10(5) 605–620.
K. W. Ross, J. F. Kurose, Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach Featuring the Internet, Addison-Wesley, 3rd Ed. (2005).
D. W. Weir, J. E. Colgate and M. A. Peshkin, Measuring and increasing Z-width with active electrical damping, Proc. of the Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems (2008) 169–175.
A. H. Gosline, G. Campion and V. Hayward, On the use of eddy current brakes as tunable, fast turn-on viscous dampers for haptic rendering, Proc. of Eurohaptics Conference (2006) 229–234.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper was recommended for publication in revised form by Associate Editor Won Gu Lee
Changhoon Seo received his B.S. degree in Electronics and Electrical Engineering from Pusan National University (PNU), Busan, Korea in 2003, and M.S. degree in Department of Mechatronics from the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Gwangju, Korea in 2005. His research interests include haptic interaction control and bilateral teleoperation control, and haptic interfaces.
Jong-Phil Kim received his B.S. degree in Mechanical Engineering in 1998 from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon, Korea, and M.S. and Ph.D. degrees in Department of Mechatronics from the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Gwangju, Korea, in 2000 and 2007, respectively. He is currently a post-doctoral research fellow in the Image Media Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST). His research interests include haptics, robotics, and teleoperation.
Jaeha Kim received his BS degree in Mechanical & Control Engineering from Handong Global University, Pohang, North Gyeongsang province, Korea in 2006, and MS degree in Department of Mechatronics from the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Gwangju, Korea in 2008. His research interests include stability control of haptic interaction systems and haptic rendering.
Hyo-Sung Ahn received the B.S. and M.S. degrees from Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea in 1998 and 2000, respectively, the M.S. degree in electrical engineering from the University of North Dakota, Grand Forks, in 2003, and the Ph.D. degree in electrical engineering from Utah State University, Logan, in 2006. Since July 2007, he has been an Assistant Professor in the School of Mechatronics, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Gwangju, Korea. Before joining GIST, he was a Senior Researcher with the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute, Daejeon, Korea. He is the author of the research monograph Iterative Learning Control: Robustness and Monotonic Convergence for Interval Systems (Springer-Verlag, 2007). His research interests include control systems, autonomous systems, and aerospace navigation and control.
Jeha Ryu received his B.S. (1982), M.S. (1984) and Ph.D. (1991) degrees from Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Daejeon, Korea and the University of Iowa, USA, respectively, in Mechanical Engineering. He is a professor in the School of Mechatronics, GIST and a member of ASME, KSME, KSAE, and IEEE. More than 120 of his research articles and reports have been published. His research interests include haptic interaction control, haptic modeling and rendering, haptic application for various multimedia systems and teleoperation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, C., Kim, JP., Kim, J. et al. Robustly stable bilateral teleoperation under time-varying delays and data losses: an energy-bounding approach. J Mech Sci Technol 25, 2089–2100 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-011-0523-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-011-0523-8