Abstract
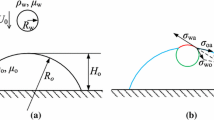
Compound and simple droplets have been studied and appeared in many life applications, e.g., drug processing and microfluidic systems. Many studies have been conducted on the thermocapillary effects on simple droplets, but similar studies on compound droplets are quite rare. Filling this missing gap, this paper presents the front-tracking-based simulation results of the thermocapillary effects on compound droplets in a certain limited domain. The compound droplet consists of a single inner core that is initially concentric with the outer one. Various dimensionless parameters including Reynolds number from 1 to 50, Marangoni number from 1 to 100, droplet radius ratio from 0.3 to 0.8, and viscosity ratios from 0.1 to 6.4 are varied to reveal their influences on the migration of a compound droplet from cold to hot regions. Initially, the inner droplet moves faster than the outer one, and when the leading surface of the inner droplet touches the outer one, the inner and outer droplets migrate at the same speed. The effects of these parameters on the compound droplet eccentricity are also considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Wang, H. Jing and Y. Wang, Possible effects of complex internal structures on the apparent viscosity of multiple emulsions, Chem. Eng. Sci., 135 (2015) 381–392.
L. Zhang, J. Aoki and B. G. Thomas, Inclusion removal by bubble flotation in a continuous casting mold, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 37(3) (2006) 361–379.
D. R. Uhlmann, Glass processing in a microgravity environment, MRS Online Proceedings Library, 9(1) (1981) 269–278.
T. S. Sammarco and M. A. Burns, Thermocapillary pumping of discrete drops in microfabricated analysis devices, AIChE Journal, 45(2) (1999) 350–366.
M. R. de Saint Vincent, R. Wunenburger and J.-P. Delville, Laser switching and sorting for high speed digital microfluidics, Appl. Phys. Lett., 92(15) (2008) 154105.
B. Sobac, A. Rednikov, S. Dorbolo and P. Colinet, Self-propelled Leidenfrost drops on a thermal gradient: a theoretical study, Phys. Fluids, 29(8) (2017) 082101.
N. O. Young, J. S. Goldstein and M. J. Block, The motion of bubbles in a vertical temperature gradient, J. Fluid Mech., 6(3) (1959) 350–356.
R. S. Subramanian, Slow migration of a gas bubble in a thermal gradient, AlChE Journal, 27(4) (1981) 646–654.
H. Haj-Hariri, A. Nadim and A. Borhan, Effect of inertia on the thermocapillary velocity of a drop, J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 140(1) (1990) 277–286.
R. Balasubramaniam and A.-T. Chai, Thermocapillary migration of droplets: an exact solution for small marangoni numbers, J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 119(2) (1987) 531–538.
N. Shankar and R. S. Subramanian, The stokes motion of a gas bubble due to interfacial tension gradients at low to moderate Marangoni numbers, J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 123(2) (1988) 512–522.
J. Szymczyk and J. Siekmann, Numerical calculation of the thermocapillary motion of a bubble under microgravity, Chem. Eng. Commun., 69(1) (1988) 129–147.
R. Balasubramaniam and J. E. Lavery, Numerical simulation of thermocapillary bubble migration under microgravity for large reynolds and marangoni numbers, Numer. Heat Tr. A-Appl., 16(2) (1989) 175–187.
Z. Yin, P. Gao, W. Hu and L. Chang, Thermocapillary migration of nondeformable drops, Phys. Fluids, 20(8) (2008) 082101.
J. C. Chen and Y. T. Lee, Effect of surface deformation on thermocapillary bubble migration, AIAA Journal, 30(4) (1992) 993–998.
S. W. J. Welch, Transient thermocapillary migration of deformable bubbles, J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 208(2) (1998) 500–508.
H. J. Keh and L. S. Chen, Droplet interactions in thermocapillary migration, Chem. Eng. Sci., 48(20) (1993) 3565–3582.
R. Sun and W.-R. Hu, The thermocapillary migrations of two bubbles in microgravity environment, J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 255(2) (2002) 375–381.
S. Nas and G. Tryggvason, Thermocapillary interaction of two bubbles or drops, Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 29(7) (2003) 1117–1135.
S. S. Kalichetty, T. Sundararajan and A. Pattamatta, Thermocapillary migration and interaction dynamics of droplets in a constricted domain, Phys. Fluids, 31(2) (2019) 022106.
T. V. Vu, H. Takakura, J. C. Wells and T. Minemoto, Production of hollow spheres of eutectic tin-lead solder through a coaxial nozzle, J. Solid Mech. Mater. Eng., 4(10) (2010) 1530–1538.
K. D. Bhagat, T. V. Vu, J. C. Wells, H. Takakura, Y. Kawano and F. Ogawa, Production of hollow germanium alloy quasispheres through a coaxial nozzle, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 58(6) (2019) 068001.
J. M. Kendall, M. C. Lee and T. G. Wang, Metal shell technology based upon hollow jet instability, J. Vac. Sci. Technol., 20(4) (1982) 1091–1093.
J. H. Nadler, T. H. Sanders Jr. and J. K. Cochran, Aluminum hollow sphere processing, Mater. Sci. Forum, 331–337 (2000) 495–500.
M. Iqbal, N. Zafar, H. Fessi and A. Elaissari, Double emulsion solvent evaporation techniques used for drug encapsulation, Int. J. Pharm., 496(2) (2015) 173–190.
J. Yang, Q. Zhou, Z. Huang, Z. Gu, L. Cheng, L. Qiu and Y. Hong, Mechanisms of in vitro controlled release of astaxanthin from starch-based double emulsion carriers, Food Hydrocoll. (2021) 106837.
S.-H. Hu, R.-H. Fang, Y.-W. Chen, B.-J. Liao, I.-W. Chen and S.-Y. Chen, Photoresponsive protein-graphene-protein hybrid capsules with dual targeted heat-triggered drug delivery approach for enhanced tumor therapy, Adv. Funct. Mater., 24(26) (2014) 4144–4155.
T. V. Vu, L. V. Vu, B. D. Pham and Q. H. Luu, Numerical investigation of dynamic behavior of a compound drop in shear flow, J. Mech. Sci. Technol., 32(5) (2018) 2111–2117.
G. Tryggvason, B. Bunner, A. Esmaeeli, D. Juric, N. Al-Rawahi, W. Tauber, J. Han, S. Nas and Y.-J. Jan, A front-tracking method for the computations of multiphase flow, J. Comput. Phys., 169(2) (2001) 708–759.
H. Liu, Y. Zhang and A. J. Valocchi, Modeling and simulation of thermocapillary flows using lattice Boltzmann method, J. Comput. Phys., 231(12) (2012) 4433–4453.
G. Tryggvason, R. Scardovelli and S. Zaleski, Direct Numerical Simulations of Gas-Liquid Multiphase Flows, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2011).
T.-V. Vu, T. V. Vu, C. T. Nguyen and P. H. Pham, Deformation and breakup of a double-core compound droplet in an axisymmetric channel, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 135 (2019) 796–810.
M. Lu, J. Lu, Y. Zhang and G. Tryggvason, Numerical study of thermocapillary migration of a bubble in a channel with an obstruction, Phys. Fluids, 31(6) (2019) 062101.
T. V. Vu and P. H. Pham, Numerical study of a compound droplet moving toward a rigid wall in an axisymmetric channel, Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow, 82 (2020) 108542.
Y. Chen, X. Liu and M. Shi, Hydrodynamics of double emulsion droplet in shear flow, Appl. Phys. Lett., 102(5) (2013) 051609.
C. Zhou, P. Yue and J. J. Feng, Deformation of a compound drop through a contraction in a pressure-driven pipe flow, Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 34(1) (2008) 102–109.
S. Tasoglu, G. Kaynak, A. J. Szeri, U. Demirci and M. Muradoglu, Impact of a compound droplet on a flat surface: a model for single cell epitaxy, Phys. Fluids, 22(8) (2010) 082103.
Acknowledgments
This research is funded by the Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development under grant number 107.03-2019.307.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Vinh T. Nguyen is a Ph.D. student of the Graduate University of Science and Technology, Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, Hanoi, Vietnam. He received his M.S. in Mechanical Engineering from the Keio University, Japan. His research interests include aerospace structures, multiphase and free surface flows, heat transfer, and numerical methods.
Truong V. Vu is a Lecturer of the Faculty of Vehicle and Energy Engineering, Phenikaa University, Hanoi, Vietnam. He received his Ph.D. in Integrated Science and Engineering from the Ritsumeikan University, Japan. His research interests include multiphase and free surface flows, phase change heat transfer, and numerical methods.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, V.T., Vu, T.V., Nguyen, P.H. et al. Thermocapillary migration of a fluid compound droplet. J Mech Sci Technol 35, 4033–4044 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-021-0816-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-021-0816-5