Abstract
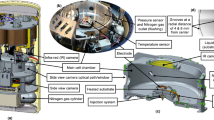
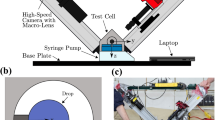
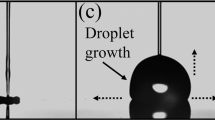
We present in this paper the results obtained from a parabolic flight campaign regarding the contact angle and the drop interface behavior of sessile drops created under terrestrial gravity (1g) or in microgravity (μg). This is a preliminary study before further investigations on sessile drops evaporation under microgravity. In this study, drops are created by the mean of a syringe pump by injection through the substrate. The created drops are recorded using a video camera to extract the drops contact angles. Three fluids have been used in this study : de-ionized water, HFE-7100 and FC-72 and two heating surfaces: aluminum and PTFE. The results obtained evidence the feasibility of sessile drop creation in microgravity even for low surface tension liquids (below 15 mN m − 1) such as FC-72 and HFE-7100. We also evidence the contact angle behavior depending of the drop diameter and the gravity level. A second objective of this study is to analyze the drop interface shape in microgravity. The goal of the these experiments is to obtain reference data on the sessile drop behavior in microgravity for future experiments to be performed in an French-Chinese scientific instrument (IMPACHT).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aussillous, P.: Les gouttes enrobees, pp. 30–33. Ph.D. thesis, Universite Paris VI (2002)
Bernardin, J.D., Mudawar, I., Walsh, C.B., Franses, E.I.: Contact angle temperature dependence for water droplets on practical aluminum surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 40(5), 1017–1033 (1997)
Bigioni, T.P., Lin, X.M., Nguyen, T.T., Corwin, E.I., Witten, T.A., Jaeger, H.M.: Kinetically driven self assembly of highly ordered nanoparticle monolayers. Nat. Mater. 5, 265–270 (2006)
Bourges-Monnier, C., Shanahan, M.: Influence of evaporation on contact angle. Langmuir 11, 2820–2829 (1995)
Chandra, S., Di Marzo, M., Qiao, Y.M., Tartarini, P.: Effect of liquid solid contact angle on droplet evaporation. Fire Saf. J. 27, 141–158 (1996)
Frassy, J., Lecot, C., Delattre, C., Soucemarianadin, A.: Droplet evaporation on solid substrates of different wetting behaviour. SHF Microfluidics 2006 (2006)
Gajewski, A.: Contact angle and sessile drop diameter hysteresis on metal surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 51, 4628–4636 (2008)
Grandas, L.: Evaporation d’une goutte sessile: etude experimentale des transferts de chaleur et de masse. Ph.D. thesis, Universite de Provence (2004)
Grandas, L., Reynard, C., Santini, R., Tadrist, L.: Experimental study of the evaporation of a sessile drop on a heat wall. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 44(2), 137–146 (2005)
Kulinich, S.A., Farzaneh, M.: Effect of contact angle hysteresis on water droplet evaporation from super-hydrophobic surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 4056–4060 (2009)
Letellier, P., Mayaffre, A., Turmine, M.: Drop size effect on contact angle explained by nonextensive thermodynamics. Young’s equation revisited. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 314, 604–614 (2007)
Ning, Q., Zhu, Z.Q., Li X.T., Yu, Q., Yuan, Z.F.: Determine the surface tension and contact angle of drop by image processing method. Chin. J. Space Sci. 28, 74–79 (2008)
Panwar, A.K., Barthwal, S.K., Ray, S.: Effect of evaporation on the contact angle of a sessile drop on solid substrates. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 17(10), 1321–1329 (2003)
Ponter, A.B., Boyes, A.P.: The relation between contact angle and drop size for water at its boiling point for a pressure range 50–760 Torr. Can. J. Chem. 50, 2419 (1972)
Rotenberg, Y., Boruvka, L., Neumann, A.W.: Determination of surface tension and contact angle from the axisymmetric fluid interfaces. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 93, 169–183 (1983)
Takata, Y., Hidaka, S., Cao, J.M., Nakamura, T., Yamamoto, H., Masuda, M., Ito, T.: Effect of surface wettability on boiling and evaporation. Energy : (Oxford) 30(2–4), 209–220 (2005)
Whyman, G., Bormashenko, E.: Oblate spheroid model for calculation of the shape and contact angles of heavy droplets. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 331, 174–177 (2009)
Yekta-Fard, M., Ponter, A.B.: The influence of vapor environment and temperature on the contact angle drop size relationship. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 126, 134–140 (1989)
Zhang, N., Chao, D.F.: Flow visualization in evaporating liquid drops and measurement of dynamic contact angles and spreading rate. J. Flow Vis. Image Process. 8(2–3), 303–312 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brutin, D., Zhu, Z., Rahli, O. et al. Sessile Drop in Microgravity: Creation, Contact Angle and Interface. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 21 (Suppl 1), 67–76 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-009-9132-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-009-9132-x