Abstract
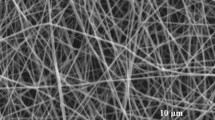
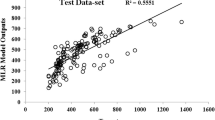
The aim of this work was to evaluate the effective parameters for prediction of the electrospun gelatin nanofibers diameter using artificial neural network (ANN) technique. The various sets of electrospinning process including temperature, applied voltage and polymer and solvent concentrations were designed to produce pure gelatin nanofibers. The obtained results by analyzing Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) images indicated that the produced nanofibers diameter was in the range of 85 to 750 nm. Due to the volume of the data, k fold cross-validation method was used for data setting. Data were divided into the five categories and trained and tested using ANN technique. The results indicated that the network including 4 input variables, 3 hidden layers with 10, 18 and 9 nodes in each layers, respectively, and one output layer had the best performance in the testing sets. The mean squared error (MSE) and linear regression (R) between observed and predicted nanofibers diameter were 0.1531 and 0.9424, respectively. The obtained results demonstrated that the selected neural network model had acceptable performance for evaluating involved parameters and prediction of nanofibers diameter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Q. P. Pham, U. Sharma, and A. G. Mikos, Tissue. Eng., 12, 1197 (2006).
M. I. Lerner, S. G. Psakhie, V. G. Pugachev, V. E. Repin, G. E. Rudenskiy, and N. V. Svarovskaya, U. S. Patent, 8033400 B2 (2011).
X. J. Loh, P. Peh, S. Liao, C. Sng, and J. Li, J. Control. Release, 143, 175 (2010).
S. Hong and G. Kim, Carbohyd. Polym., 83, 940 (2011).
C. J. Thompson, G. G. Chase, A. L. Yarin, and D. H. Reneker, Polymer, 48, 6913 (2007).
R. Faridi-Majidi, H. Ziyadi, N. Naderi, and A. Amani, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 124, 1589 (2012).
P. Gibson, H. Schreuder-Gibson, and D. Rivin, Colloid. Surface. A, 187, 469 (2001).
P. Mazzatorta, E. Benfenati, C. D. Neagu, and G. Gini, J. Chem. Inf. Comp. Sci., 42, 1250 (2002).
A. Feelders, H. Daniels, and M. Holsheimer, Inform. Manag., 37, 271 (2000).
J. Sun and H. Li, Knowl-Based Syst., 21, 1 (2008).
N. Naderi, F. Agend, R. Faridi-Majidi, N. Sharifi-Sanjani, and M. Madani, J. Nanosci. Nanotechno., 8, 2509 (2008).
O. Yördem, M. Papila, and Y. Z. Mencelo lu, Design, 29, 34 (2008).
D. Ba and. H. Boyac, J. Food Eng., 78, 836 (2007).
W. Lou and S. Nakai, Food. Res. Int., 34, 573 (2001).
K. Sarkar, M. B. Ghalia, Z. Wu, and S. C. Bose, J. Mater. Process. Tech., 209, 3156 (2009).
E. Mirzaei, A. Amani, S. Sarkar, R. Saber, D. Mohammadyani, R. Faridi-Majidi, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 125, 1910 (2012).
M. Li, X. Huang, H. Liu, B. Liu, Y. Wu, and X. Deng, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 129, 3297 (2013).
E. Esmaeilzadeh-Gharedaghi, M. A. Faramarzi, M. A. Amini, A. Rouholamini-Najafabadi, S. M. Rezayat, and A. Amani, Pharm. Dev. Technol., 17, 638 (2012).
N. Kathuria, A. Tripathi, K. K. Kar, and A. Kumar, Acta Biomater., 5, 406 (2009).
H. Fong, I. Chun, and D. Reneker, Polymer, 40, 4585 (1999).
D. Li, T. Herricks, and Y. Xia, Appl. Phys. Lett., 83, 4586 (2003).
R. Kohavi, International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Ltd, 14, 1137–1145 (1995).
J. H. He, Y. Q. Wan, and L. Xu, Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 33, 26 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naghibzadeh, M., Adabi, M. Evaluation of effective electrospinning parameters controlling gelatin nanofibers diameter via modelling artificial neural networks. Fibers Polym 15, 767–777 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-014-0767-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-014-0767-x