Abstract
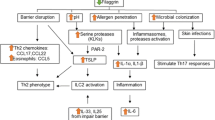
Skin barrier dysfunction caused by endogenous or exogenous factors can lead to various disorders such as xerosis cutis, ichthyoses, and atopic dermatitis. Filaggrin is a pivotal structural protein of the stratum corneum (SC) and provides natural moisturizing factors that play a role in skin barrier functions. Filaggrin aggregates keratin filaments, resulting in the formation of a keratin network, which binds cornified envelopes and collapse keratinocytes to flattened corneocytes. This complex network contributes to the physical strength of the skin. Filaggrin is degraded by caspase-14, calpain 1, and bleomycin hydrolases into amino acids and amino acid metabolites such as trans-urocanic acid and pyrrolidone carboxylic acid, which are pivotal natural moisturizing factors in the SC. Accordingly, filaggrin is important for the pathophysiology of skin barrier disorders, and its deficiency or dysfunction leads to a variety of skin disorders. Here, the roles and biology of filaggrin, related skin diseases, and a therapeutic strategy targeting filaggrin are reviewed. In addition, several drug candidates of different mode of actions targeting filaggrin, along with their clinical efficacy, are discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adham IM, Sallam MA, Steding G, Korabiowska M, Brinck U, Hoyer-Fender S, Oh C, Engel W (2003) Disruption of the pelota gene causes early embryonic lethality and defects in cell cycle progression. Mol Cell Biol 23:1470–1476. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.23.4.1470-1476.2003
Amano W, Nakajima S, Kunugi H, Numata Y, Kitoh A, Egawa G, Dainichi T, Honda T, Otsuka A, Kimoto Y, Yamamoto Y, Tanimoto A, Matsushita M, Miyachi Y, Kabashima K (2015). The Janus kinase inhibitor JTE-052 improves skin barrier function through suppressing signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling. J Allergy Clin Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.03.051
Barresi C, Stremnitzer C, Mlitz V, Kezic S, Kammeyer A, Ghannadan M, Posa-Markaryan K, Selden C, Tschachler E, Eckhart L (2011) Increased sensitivity of histidinemic mice to UVB radiation suggests a crucial role of endogenous urocanic acid in photoprotection. J Invest Dermatol 131:188–194. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2010.231
Baurecht H, Ruhlemann MC, Rodriguez E, Thielking F, Harder I, Erkens AS, Stolzl D, Ellinghaus E, Hotze M, Lieb W, Wang S, Heinsen-Groth FA, Franke A, Weidinger S (2018) Epidermal lipid composition, barrier integrity, and eczematous inflammation are associated with skin microbiome configuration. J Allergy Clin Immunol 141:1668–1676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2018.01.019
Bissonnette R, Papp KA, Poulin Y, Gooderham M, Raman M, Mallbris L, Wang C, Purohit V, Mamolo C, Papacharalambous J, Ports WC (2016) Topical tofacitinib for atopic dermatitis: a phase IIa randomized trial. Br J Dermatol 175:902–911. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.14871
Brown SJ, Mclean WH (2012) One remarkable molecule: filaggrin. J Invest Dermatol 132:751–762. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2011.393
Brown SJ, Kroboth K, Sandilands A, Campbell LE, Pohler E, Kezic S, Cordell HJ, Mclean WH, Irvine A (2012) D. Intragenic copy number variation within filaggrin contributes to the risk of atopic dermatitis with a dose-dependent effect. J Invest Dermatol 132:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2011.342
Bunick CG, Presland RB, Lawrence OT, Pearton DJ, Milstone LM, Steitz TA (2015) Crystal Structure of Human Profilaggrin S100 Domain and Identification of Target Proteins Annexin II, Stratifin, and HSP27. J Invest Dermatol 135:1801–1809. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2015.102
Candi E, Schmidt R, Melino G (2005) The cornified envelope: a model of cell death in the skin. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:328–340. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1619
Clar EJ, Fourtanier A (1981) Pyrrolidone carboxylic acid and the skin. Int J Cosmet Sci 3:101–113. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-2494.1981.tb00275.x
Clausen ML, Edslev SM, Andersen PS, Clemmensen K, Krogfelt KA, Agner T (2017) Staphylococcus aureus colonization in atopic eczema and its association with filaggrin gene mutations. Br J Dermatol 177:1394–1400. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.15470
Clausen ML, Agner T, Lilje B, Edslev SM, Johannesen TB, Andersen PS (2018) Association of Disease Severity With Skin Microbiome and Filaggrin Gene Mutations in Adult Atopic Dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol 154:293–300. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.5440
Czarnowicki T, Krueger JG, Guttman-Yassky E (2017) Novel concepts of prevention and treatment of atopic dermatitis through barrier and immune manipulations with implications for the atopic march. J Allergy Clin Immunol 139:1723–1734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2017.04.004
Dainichi T, Nakano Y, Wakae K, Otsuka M, Muramatsu M, Kabashima K (2019) APOBEC3 regulates keratinocyte differentiation and expression of Notch3. Exp Dermatol 28:1341–1347. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.14019
Dale BA, Resing KA, Lonsdale-Eccles JD (1985) Filaggrin: a keratin filament associated protein. Ann N Y Acad Sci 455:330–342. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb50420.x
Descargues P, Deraison C, Bonnart C, Kreft M, Kishibe M, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Elias P, Barrandon Y, Zambruno G, Sonnenberg A, Hovnanian A (2005) Spink5-deficient mice mimic Netherton syndrome through degradation of desmoglein 1 by epidermal protease hyperactivity. Nat Genet 37:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1493
Elias PM (1983) Epidermal lipids, barrier function, and desquamation. J Invest Dermatol 80:44–49. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.1983.12
Elias PM, Cullander C, Mauro T, Rassner U, Komuves L, Brown BE, Menon GK (1998) The secretory granular cell: the outermost granular cell as a specialized secretory cell. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc 3:87–100. https://doi.org/10.1038/jidsymp.1998.20
Elias PM, Hatano Y, Williams ML (2008) Basis for the barrier abnormality in atopic dermatitis: outside-inside-outside pathogenic mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol 121:1337–1343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2008.01.022
Elkenani M, Nyamsuren G, Raju P, Liakath-Ali K, Hamdaoui A, Kata A, Dressel R, Klonisch T, Watt FM, Engel W, Thliveris JA, Pantakani K, Adham IM (2016) Pelota regulates epidermal differentiation by modulating BMP and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. J Invest Dermatol 136:1664–1671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2016.04.020
Emmert H, Baurecht H, Thielking F, Stolzl D, Rodriguez E, Harder I, Proksch E, Weidinger S (2020) Stratum corneum lipidomics analysis reveals altered ceramide profile in atopic dermatitis patients across body sites with correlated changes in skin microbiome. Exp Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.14185
Feuillie C, Vitry P, Mcaleer MA, Kezic S, Irvine AD, Geoghegan JA, Dufrêne YF (2018) Adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus to corneocytes from atopic dermatitis patients is controlled by natural moisturizing factor levels. MBio. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01184-18
Gutowska-Owsiak D, Schaupp AL, Salimi M, Taylor S, Ogg GS (2011) Interleukin-22 downregulates filaggrin expression and affects expression of profilaggrin processing enzymes. Br J Dermatol 165:492–498. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10400.x
Gutowska-Owsiak D, Schaupp AL, Salimi M, Selvakumar TA, Mcpherson T, Taylor S, Ogg GS (2012) IL-17 downregulates filaggrin and affects keratinocyte expression of genes associated with cellular adhesion. Exp Dermatol 21:104–110. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0625.2011.01412.x
Guttman-Yassky E, Thaci D, Pangan AL, Hong HC, Papp KA, Reich K, Beck LA, Mohamed MF, Othman AA, Anderson JK, Gu Y, Teixeira HD, Silverberg J (2020) I. Upadacitinib in adults with moderate to severe atopic dermatitis: 16-week results from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol 145:877–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2019.11.025
Hashimoto-Hachiya A, Tsuji G, Murai M, Yan X, Furue M (2018) Upregulation of FLG, LOR, and IVL expression by Rhodiola crenulata root extract via aryl hydrocarbon receptor: differential involvement of OVOL1. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061654
He H, Guttman-Yassky EJAK (2019) Inhibitors for Atopic Dermatitis: An Update. Am J Clin Dermatol 20:181–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-018-0413-2
Hoste E, Kemperman P, Devos M, Denecker G, Kezic S, Yau N, Gilbert B, Lippens S, De Groote P, Roelandt R, Van Damme P, Gevaert K, Presland RB, Takahara H, Puppels G, Caspers P, Vandenabeele P, Declercq W (2011) Caspase-14 is required for filaggrin degradation to natural moisturizing factors in the skin. J Invest Dermatol 131:2233–2241. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2011.153
Howell MD, Kim BE, Gao P, Grant AV, Boguniewicz M, Debenedetto A, Schneider L, Beck LA, Barnes KC, Leung DY (2007) Cytokine modulation of atopic dermatitis filaggrin skin expression. J Allergy Clin Immunol 120:150–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2007.04.031
Huang J, Chen D, Yan F, Wu S, Kang S, Xing W, Zeng W, Xie J (2020) JTC-801 alleviates mechanical allodynia in paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 883:173306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173306
Imai Y (2019) Interleukin-33 in atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci 96:2–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2019.08.006
Irvine AD, Mclean WH, Leung DY (2011) Filaggrin mutations associated with skin and allergic diseases. N Engl J Med 365:1315–1327. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1011040
Jin T, Park KY, Seo SJ (2017) Adiponectin upregulates filaggrin expression via SIRT1-mediated signaling in human normal keratinocytes. Ann Dermatol 29:407–413. https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2017.29.4.407
Joo KM, Nam GW, Park SY, Han JY, Jeong HJ, Lee SY, Kim HK, Lim KM (2010) Relationship between cutaneous barrier function and ceramide species in human stratum corneum. J Dermatol Sci 60:47–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2010.07.016
Joo KM, Han JY, Son ED, Nam GW, Chung HY, Jeong HJ, Cho JC, Lim KM (2012) Rapid, simultaneous and nanomolar determination of pyroglutamic acid and cis-/trans-urocanic acid in human stratum corneum by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC)-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of chromatography B Analytical technologies in the biomedical and life sciences, 897:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.04.008
Joo KM, Hwang JH, Bae S, Nahm DH, Park HS, Ye YM, Lim KM (2015) Relationship of ceramide-, and free fatty acid-cholesterol ratios in the stratum corneum with skin barrier function of normal, atopic dermatitis lesional and non-lesional skins. J Dermatol Sci 77:71–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2014.10.001
Kamata Y, Taniguchi A, Yamamoto M, Nomura J, Ishihara K, Takahara H, Hibino T, Takeda A (2009) Neutral cysteine protease bleomycin hydrolase is essential for the breakdown of deiminated filaggrin into amino acids. J Biol Chem 284:12829–12836. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M807908200
Kezic S, O’regan GM, Yau N, Sandilands A, Chen H, Campbell LE, Kroboth K, Watson R, Rowland M, Mclean WH, Irvine AD (2011) Levels of filaggrin degradation products are influenced by both filaggrin genotype and atopic dermatitis severity. Allergy 66:934–940. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1398-9995.2010.02540.x
Kim BE, Bin L, Ye YM, Ramamoorthy P, Leung DYM (2013) IL-25 enhances HSV-1 replication by inhibiting filaggrin expression, and acts synergistically with Th2 cytokines to enhance HSV-1 replication. J Invest Dermatol 133:2678–2685. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2013.223
Kim M, Jeong H, Lee B, Cho Y, Yoon WK, Cho A, Kwon G, Nam KT, Ha H, Lim KM (2019) Enrichment of short-chain ceramides and free fatty acids in the skin epidermis, liver, and kidneys of db/db mice, a type 2 diabetes mellitus model. Biomol Ther. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2018.214
Kiyomatsu-Oda M, Uchi H, Morino-Koga S, Furue M (2018) Protective role of 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ), an endogenous ligand for arylhydrocarbon receptor, in chronic mite-induced dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci 90:284–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2018.02.014
Koseki R, Morii W, Noguchi E, Ishikawa M, Yang L, Yamamoto-Hanada K, Narita M, Saito H, Ohya Y (2019) Effect of filaggrin loss-of-function mutations on atopic dermatitis in young age: a longitudinal birth cohort study. J Hum Genet 64:911–917. https://doi.org/10.1038/s10038-019-0628-y
Kraft M, Worm M (2017) Dupilumab in the treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 13:301–310. https://doi.org/10.1080/1744666X.2017.1292134
Laffet GP, Genette A, Gamboa B, Auroy V, Voegel JJ (2018) Determination of fatty acid and sphingoid base composition of eleven ceramide subclasses in stratum corneum by UHPLC/scheduled-MRM. Metabolomics 14:69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11306-018-1366-4
Leyvraz C, Charles RP, Rubera I, Guitard M, Rotman S, Breiden B, Sandhoff K, Hummler E (2005) The epidermal barrier function is dependent on the serine protease CAP1/Prss8. J Cell Biol 170:487–496. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200501038
List K, Szabo R, Wertz PW, Segre J, Haudenschild CC, Kim SY, Bugge TH (2003) Loss of proteolytically processed filaggrin caused by epidermal deletion of Matriptase/MT-SP1. J Cell Biol 163:901–910. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200304161
Madison KC, Howard EJ (1996) Ceramides are transported through the Golgi apparatus in human keratinocytes in vitro. J Invest Dermatol 106:1030–1035. https://doi.org/10.1111/1523-1747.ep12338596
Man MQ, Hatano Y, Lee SH, Man M, Chang S, Feingold KR, Leung DY, Holleran W, Uchida Y, Elias PM (2008) Characterization of a hapten-induced, murine model with multiple features of atopic dermatitis: structural, immunologic, and biochemical changes following single versus multiple oxazolone challenges. J Invest Dermatol 128:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jid.5701011
Markova NG, Marekov LN, Chipev CC, Gan SQ, Idler WW, Steinert PM (1993) Profilaggrin is a major epidermal calcium-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol 13:613–625. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.13.1.613
Masukawa Y, Narita H, Sato H, Naoe A, Kondo N, Sugai Y, Oba T, Homma R, Ishikawa J, Takagi Y, Kitahara T (2009) Comprehensive quantification of ceramide species in human stratum corneum. J Lipid Res 50:1708–1719. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.D800055-JLR200
Matsui T, Miyamoto K, Kubo A, Kawasaki H, Ebihara T, Hata K, Tanahashi S, Ichinose S, Imoto I, Inazawa J, Kudoh J, Amagai M (2011) SASPase regulates stratum corneum hydration through profilaggrin-to-filaggrin processing. EMBO Mol Med 3:320–333. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201100140
Mclean WH Filaggrin failure - from ichthyosis vulgaris to atopic eczema and beyond. Br J Dermatol 175 Suppl 2, 4–7 (2016).doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.14997
Ming M, Zhao B, Shea CR, Shah P, Qiang L, White SR, Sims DM, He YY Loss of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) disrupts skin barrier integrity and sensitizes mice to epicutaneous allergen challenge. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 135, 936–45 e4 (2015).doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2014.09.035
Mlitz V, Latreille J, Gardinier S, Jdid R, Drouault Y, Hufnagl P, Eckhart L, Guinot C, Tschachler E (2012) Impact of filaggrin mutations on Raman spectra and biophysical properties of the stratum corneum in mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 26:983–990. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04198.x
Murata T, Noguchi PD, Puri RK (1995) Receptors for interleukin (IL)-4 do not associate with the common gamma chain, and IL-4 induces the phosphorylation of JAK2 tyrosine kinase in human colon carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 270:30829–30836. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.51.30829
Murata T, Husain SR, Mohri H, Puri RK (1998) Two different IL-13 receptor chains are expressed in normal human skin fibroblasts, and IL-4 and IL-13 mediate signal transduction through a common pathway. Int Immunol 10:1103–1110. https://doi.org/10.1093/intimm/10.8.1103
Murata T, Taguchi J, Puri RK, Mohri H (1999) Sharing of receptor subunits and signal transduction pathway between the IL-4 and IL-13 receptor system. Int J Hematol 69:13–20
Nakagawa H, Nemoto O, Igarashi A, Nagata T (2018) Efficacy and safety of topical JTE-052, a Janus kinase inhibitor, in Japanese adult patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: a phase II, multicentre, randomized, vehicle-controlled clinical study. Br J Dermatol 178:424–432. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.16014
Nemes Z, Marekov LN, Fesus L, Steinert PM (1999) A novel function for transglutaminase 1: attachment of long-chain omega-hydroxyceramides to involucrin by ester bond formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:8402–8407. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.15.8402
Nettis E, Fabbrocini G, Ortoncelli M, Pellacani G, Argenziano G, Di Leo E, Patruno C, Stingeni L, Foti C, Rongioletti F, Macchia L, Tavecchio S, Napolitano M, Ribero S, Bonzano L, Calabrese G, Di Bona D, Nistico SP, Hansel K, Romita P, Piras V, Carbonara M, Detoraki A, Ferrucci SM (2020) Long-term effectiveness of dupilumab up to 52 weeks in atopic dermatitis in 253 adult patients. Br J Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.19577
Niehues H, Schalkwijk J, Van Vlijmen-Willems I, Rodijk-Olthuis D, Van Rossum MM, Wladykowski E, Brandner JM, Van Den Bogaard EHJ, Zeeuwen P (2017) Epidermal equivalents of filaggrin null keratinocytes do not show impaired skin barrier function. J Allergy Clin Immunol 139:1979–1981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2016.09.016
Osawa R, Akiyama M, Shimizu H (2011) Filaggrin gene defects and the risk of developing allergic disorders. Allergol Int 60:1–9. https://doi.org/10.2332/allergolint.10-RAI-0270
Otsuka A, H, Egawa G, Maekawa A, Fujita T, Nakamizo S, Nakashima C, Nakajima S, Watanabe T, Miyachi Y, Narumiya S, Kabashima K (2014) Possible new therapeutic strategy to regulate atopic dermatitis through upregulating filaggrin expression. J Allergy Clin Immunol 133:139 –139 46 e1–e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2013.07.027
Paller AS, Gold LS, Soung J, Tallman AM, Rubenstein DS, Gooderham M (2020) Efficacy and Patient-reported outcomes from a phase IIb, randomized clinical trial of tapinarof cream for the treatment of adolescents and adults with atopic dermatitis. J Am Acad Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.135
Palmer CN, Irvine AD, Terron-Kwiatkowski A, Zhao Y, Liao H, Lee SP, Goudie DR, Sandilands A, Campbell LE, Smith FJ, O’regan GM, Watson RM, Cecil JE, Bale SJ, Compton JG, Digiovanna JJ, Fleckman P, Lewis-Jones S, Arseculeratne G, Sergeant A, Munro CS, Houate E, Mcelreavey B, Halkjaer K, Bisgaard LB, Mukhopadhyay H, S., and Mclean WH (2006) Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis. Nat Genet 38:441–446. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1767
Park YH, Jang WH, Seo JA, Park M, Lee TR, Park YH, Kim DK, Lim KM (2012) Decrease of ceramides with very long-chain fatty acids and downregulation of elongases in a murine atopic dermatitis model. J Invest Dermatol 132:476–479. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2011.333
Peppers J, Paller AS, Maeda-Chubachi T, Wu S, Robbins K, Gallagher K, Kraus JE (2019) A phase 2, randomized dose-finding study of tapinarof (GSK2894512 cream) for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J Am Academy Dermatol 80(1):89–98.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2018.06.047
Quiroz FG, Fiore VF, Levorse J, Polak L, Wong E, Pasolli HA, Fuchs E (2020) Liquid-liquid phase separation drives skin barrier formation. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aax9554
Rawlings AV, Harding CR (2004) Moisturization and skin barrier function. Dermatol Ther 17(Suppl 1):43–48. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1396-0296.2004.04s1005.x
Resing KA, Thulin C, Whiting K, Al-Alawi N, Mostad S (1995) Characterization of profilaggrin endoproteinase. 1. A regulated cytoplasmic endoproteinase of epidermis. J Biol Chem 270:28193–28198. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.47.28193
Safe S, Jin UH, Park H, Chapkin RS, Jayaraman A (2020) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) Ligands as selective AHR modulators (SAhRMs). Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186654
Sakabe J, Yamamoto M, Hirakawa S, Motoyama A, Ohta I, Tatsuno K, Ito T, Kabashima K, Hibino T, Tokura Y (2013) Kallikrein-related peptidase 5 functions in proteolytic processing of profilaggrin in cultured human keratinocytes. J Biol Chem 288:17179–17189. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.476820
Sandilands A, Sutherland C, Irvine AD, Mclean WH (2009) Filaggrin in the frontline: role in skin barrier function and disease. J Cell Sci 122:1285–1294. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.033969
Scott IR, Harding CR, Barrett JG (1982) Histidine-rich protein of the keratohyalin granules. Source of the free amino acids, urocanic acid and pyrrolidone carboxylic acid in the stratum corneum. Biochim Biophys Acta 719:110–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4165(82)90314-2
Shamsadin R, Adham IM, Engel W (2002) Mouse pelota gene (Pelo): cDNA cloning, genomic structure, and chromosomal localization. Cytogenet Genome Res 97:95–99. https://doi.org/10.1159/000064059
Simpson EL, Sinclair R, Forman S, Wollenberg A, Aschoff R, Cork M, Bieber T, Thyssen JP, Yosipovitch G, Flohr C, Magnolo N, Maari C, Feeney C, Biswas P, Tatulych S, Valdez H, Rojo R (2020) Efficacy and safety of abrocitinib in adults and adolescents with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (JADE MONO-1): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 396:255–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30732-7
Smith FJ, Irvine AD, Terron-Kwiatkowski A, Sandilands A, Campbell LE, Zhao Y, Liao H, Evans AT, Goudie DR, Lewis-Jones S, Arseculeratne G, Munro CS, Sergeant A, O’regan G, Bale SJ, Compton JG, Digiovanna JJ, Presland RB, Fleckman P, Mclean WH (2006) Loss-of-function mutations in the gene encoding filaggrin cause ichthyosis vulgaris. Nat Genet 38:337–342. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1743
Smith SH, Jayawickreme C, Rickard DJ, Nicodeme E, Bui T, Simmons C, Coquery CM, Neil J, Pryor WM, Mayhew D, Rajpal DK, Creech K, Furst S, Lee J, Wu D, Rastinejad F, Willson TM, Viviani F, Morris DC, Moore JT, Cote-Sierra J (2017) Tapinarof is a natural AhR agonist that resolves skin inflammation in mice and humans. J Invest Dermatol 137(10):2110–2119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2017.05.004
Song C, Liu L, Chen J, Hu Y, Li J, Wang B, Bellusci S, Chen C, Dong N (2020) Evidence for the critical role of the PI3K signaling pathway in particulate matter-induced dysregulation of the inflammatory mediators COX-2/PGE2 and the associated epithelial barrier protein Filaggrin in the bronchial epithelium. Cell Biol Toxicol 36(4):301–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-019-09508-1
Sorg O (2014) AhR signalling and dioxin toxicity. Toxicol Lett 230:225–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.10.039
Steven AC, Bisher ME, Roop DR, Steinert PM (1990) Biosynthetic pathways of filaggrin and loricrin—two major proteins expressed by terminally differentiated epidermal keratinocytes. J Struct Biol 104:150–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/1047-8477(90)90071-j
Sutter CH, Rainwater HM, Sutter TR (2020) Contributions of nitric oxide to AHR-ligand-mediated keratinocyte differentiation. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165680
Tsuji G, Hashimoto-Hachiya A, Kiyomatsu-Oda M, Takemura M, Ohno F, Ito T, Morino-Koga S, Mitoma C, Nakahara T, Uchi H, Furue M (2017) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation restores filaggrin expression via OVOL1 in atopic dermatitis. Cell Death Dis 8:e2931. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.322
Tsuji G, Hashimoto-Hachiya A, Yen VH, Miake S, Takemura M, Mitamura Y, Ito T, Murata M, Furue M, Nakahara T (2020) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation downregulates IL-33 expression in keratinocytes via ovo-like 1. J Clin Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9030891
Van Den Bogaard EH, Bergboer JG, Vonk-Bergers M, Van Vlijmen-Willems IM, Hato SV, Van Der Valk PG, Schroder JM, Joosten I, Zeeuwen PL, Schalkwijk J (2013) Coal tar induces AHR-dependent skin barrier repair in atopic dermatitis. J Clin Invest 123:917–927. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI65642
Van Smeden J, Boiten WA, Hankemeier T, Rissmann R, Bouwstra JA, Vreeken RJ (2014) Combined LC/MS-platform for analysis of all major stratum corneum lipids, and the profiling of skin substitutes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1841:70–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.10.002
Vavrova K, Henkes D, Struver K, Sochorova M, Skolova B, Witting MY, Friess W, Schreml S, Meier RJ, Schafer-Korting M, Fluhr JW, Kuchler S (2014) Filaggrin deficiency leads to impaired lipid profile and altered acidification pathways in a 3D skin construct. J Invest Dermatol 134:746–753. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2013.402
Wang S, Qiu L, Meng X, Dang N (2018) Knock-down of filaggrin influences the mitogen-activated protein kinases signaling pathway in normal human epidermal keratinocytes. Med Sci (Paris) 34(Focus issue F1):94–98. https://doi.org/10.1051/medsci/201834f116
Weidinger S, Beck LA, Bieber T, Kabashima K, Irvine A (2018) D. Atopic dermatitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 4:1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-018-0001-z
Yamazaki M, Ishidoh K, Suga Y, Saido TC, Kawashima S, Suzuki K, Kominami E, Ogawa H (1997) Cytoplasmic processing of human profilaggrin by active mu-calpain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 235:652–656. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.1997.6809
Yoneda K, Nakagawa T, Lawrence OT, Huard J, Demitsu T, Kubota Y, Presland RB (2012) Interaction of the profilaggrin N-terminal domain with loricrin in human cultured keratinocytes and epidermis. J Invest Dermatol 132:1206–1214. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2011.460
Zeeuwen PL, Ederveen TH, Van Der Krieken DA, Niehues H, Boekhorst J, Kezic S, Hanssen DA, Otero ME, Van Vlijmen-Willems IM, Rodijk-Olthuis D, Falcone D, Van Den Bogaard EH, Kamsteeg M, De Koning HD, Zeeuwen-Franssen ME, Van Steensel MA, Kleerebezem M, Timmerman HM, Van Hijum SA, Schalkwijk J (2017) Gram-positive anaerobe cocci are underrepresented in the microbiome of filaggrin-deficient human skin. J Allergy Clin Immunol 139:1368–1371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2016.09.017
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (2018R1D1A1B07042919) and the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (Grant No. HP20C0061).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
YJ Kim is the employee of Qmine Co., Ltd, and KM Lim has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y., Lim, KM. Skin barrier dysfunction and filaggrin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 44, 36–48 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01305-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01305-x