Abstract
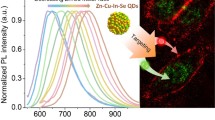
Inorganic nanoparticles have been introduced into biological systems as useful probes for in vitro diagnosis and in vivo imaging, due to their relatively small size and exceptional physical and chemical properties. A new kind of colortunable Gd-Zn-Cu-In-S/ZnS (GZCIS/ZnS) quantum dots (QDs) with stable crystal structure has been successfully synthesized and utilized for magnetic resonance (MR) and fluorescence dual modality imaging. This strategy allows successful fabrication of GZCIS/ZnS QDs by incorporating Gd into ZCIS/ZnS QDs to achieve great MR enhancement without compromising the fluorescence properties of the initial ZCIS/ZnS QDs. The as-prepared GZCIS/ZnS QDs show high T 1 MR contrast as well as “color-tunable” photoluminescence (PL) in the range of 550–725 nm by adjusting the Zn/Cu feeding ratio with high PL quantum yield (QY). The GZCIS/ZnS QDs were transferred into water via a bovine serum albumin (BSA) coating strategy. The resulting Cd-free GZCIS/ZnS QDs reveal negligible cytotoxicity on both HeLa and A549 cells. Both fluorescence and MR imaging studies were successfully performed in vitro and in vivo. The results demonstrated that GZCIS/ZnS QDs could be a dual-modal contrast agent to simultaneously produce strong MR contrast enhancement as well as fluorescence emission for in vivo imaging.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xie, J.; Chen, K.; Huang, J.; Lee, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Chen, X. PET/NIRF/MRI triple functional iron oxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3016–3022.
Lauffer, R. B. Paramagnetic metal complexes as water proton relaxation agents for NMR imaging: Theory and design. Chem. Rev. 1987, 87, 901–927.
Tsai, C. P.; Hung, Y.; Chou, Y. H.; Huang, D. M.; Hsiao, J. K.; Chang, C.; Chen, Y. C.; Mou, C. Y. High-contrast paramagnetic fluorescent mesoporous silica nanorods as a multifunctional cell imaging probe. Small 2008, 4, 186–191.
Mulder, W. J.; Strijkers, G. J.; van Tilborg, G. A.; Griffioen, A. W.; Nicolay, K. Lipid-based nanoparticles for contrast-enhanced MRI and molecular imaging. NMR Biomed. 2006, 19, 142–164.
Bridot, J.-L.; Faure, A.-C.; Laurent, S.; Riviere, C.; Billotey, C.; Hiba, B.; Janier, M.; Josserand, V.; Coll, J.-L.; Vander Elst, L. Hybrid gadolinium oxide nanoparticles: Multimodal contrast agents for in vivo imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 5076–5084.
Zhang, B.; Jin, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Liu, S.; Shi, D. Bioinspired synthesis of gadolinium-based hybrid nanoparticles as MRI blood pool contrast agents with high relaxivity. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 14494–14501.
Gao, J.; Chen, K.; Xie, R.; Xie, J.; Yan, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Peng, X.; Chen, X. In vivo tumor-targeted fluorescence imaging using near-infrared non-cadmium quantum dots. Bioconjugate Chem. 2010, 21, 604–609.
Gao, J.; Chen, K.; Xie, R.; Xie, J.; Lee, S.; Cheng, Z.; Peng, X.; Chen, X. Ultrasmall near-infrared non-cadmium quantum dots for in vivo tumor imaging. Small 2010, 6, 256–261.
Cheon, J.; Lee, J.-H. Synergistically integrated nanoparticles as multimodal probes for nanobiotechnology. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1630–1640.
Jennings, L. E.; Long, N. J. ‘Two is better than one’-probes for dual-modality molecular imaging. Chem. Commun. 2009, 3511–3524.
Kircher, M. F.; Mahmood, U.; King, R. S.; Weissleder, R.; Josephson, L. A multimodal nanoparticle for preoperative magnetic resonance imaging and intraoperative optical brain tumor delineation. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 8122–8125.
Bruchez, M.; Moronne, M.; Gin, P.; Weiss, S.; Alivisatos, A. P. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 1998, 281, 2013–2016.
Chan, W. C.; Nie, S. Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 1998, 281, 2016–2018.
Li, L.; Daou, T. J.; Texier, I.; Kim Chi, T. T.; Liem, N. Q.; Reiss, P. Highly luminescent CuInS2/ZnS core/shell nanocrystals: Cadmium-free quantum dots for in vivo imaging. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 2422–2429.
Cassette, E.; Pons, T.; Bouet, C.; Helle, M.; Bezdetnaya, L.; Marchal, F.; Dubertret, B. Synthesis and characterization of near-infrared Cu-In-Se/ZnS core/shell quantum dots for in vivo imaging. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 6117–6124.
Pons, T.; Pic, E.; Lequeux, N.; Cassette, E.; Bezdetnaya, L.; Guillemin, F.; Marchal, F.; Dubertret, B. Cadmium-free CuInS2/ZnS quantum dots for sentinel lymph node imaging with reduced toxicity. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2531–2538.
Guo, W. Synthesis of Zn-Cu-In-S/ZnS core/shell quantum dots with inhibited blue-shift photoluminescence and applications for tumor targeted bioimaging. Theranostics 2013, 3, 99–108.
Yong, K.-T.; Roy, I.; Hu, R.; Ding, H.; Cai, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Bergey, E. J.; Prasad, P. N. Synthesis of ternary CuInS2/ZnS quantum dot bioconjugates and their applications for targeted cancer bioimaging. Integr. Biol. 2010, 2, 121–129.
Deng, D.; Chen, Y.; Cao, J.; Tian, J.; Qian, Z.; Achilefu, S.; Gu, Y. High-quality CuInS2/ZnS quantum dots for in vitro and in vivo bioimaging. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 3029–3037.
De Trizio, L.; Prato, M.; Genovese, A.; Casu, A.; Povia, M.; Simonutti, R.; Alcocer, M. J.; D’Andrea, C.; Tassone, F.; Manna, L. Strongly fluorescent quaternary Cu-In-Zn-S nanocrystals prepared from Cu1–x InS2 nanocrystals by partial cation exchange. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 2400–2406.
Guo, W.; Chen, N.; Dong, C.; Tu, Y.; Chang, J.; Zhang, B. One-pot synthesis of hydrophilic ZnCuInS/ZnS quantum dots for in vivo imaging. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 9470–9475.
Zhang, J.; Xie, R.; Yang, W. A simple route for highly luminescent quaternary Cu-Zn-In-S nanocrystal emitters. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 3357–3361.
Zhang, W.; Zhong, X. Facile Synthesis of ZnS-CuInS2-alloyed nanocrystals for a color-tunable fluorchrome and photocatalyst. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 4065–4072.
Ding, K.; Jing, L.; Liu, C.; Hou, Y.; Gao, M. Magnetically engineered Cd-free quantum dots as dual-modality probes for fluorescence/magnetic resonance imaging of tumors. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1608–1617.
Wang, S.; Jarrett, B. R.; Kauzlarich, S. M.; Louie, A. Y. Core/shell quantum dots with high relaxivity and photoluminescence for multimodality imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 3848–3856.
Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Yuan, Q.; Lu, L. Fluorescence-enhanced gadolinium-doped zinc oxide quantum dots for magnetic resonance and fluorescence imaging. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1185–1192.
Li, I.-F.; Yeh, C.-S. Synthesis of Gd doped CdSe nanoparticles for potential optical and MR imaging applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 2079–2081.
Liu, Q.; Deng, R.; Ji, X.; Pan, D. Alloyed Mn-Cu-In-S nanocrystals: A new type of diluted magnetic semiconductor quantum dots. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 255706.
Tu, C.; Ma, X.; Pantazis, P.; Kauzlarich, S. M.; Louie, A. Y. Paramagnetic, silicon quantum dots for magnetic resonance and two-photon imaging of macrophages. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2016–2023.
Wang, S.; Jarrett, B. R.; Kauzlarich, S. M.; Louie, A. Y. Core/shell quantum dots with high relaxivity and photoluminescence for multimodality imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 3848–3856.
Park, J.; An, K.; Hwang, Y.; Park, J.-G.; Noh, H.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Park, J.-H.; Hwang, N.-M.; Hyeon, T. Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 891–895.
Zhou, Z.; Huang, D.; Bao, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, G.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Gao, J. A Synergistically enhanced T 1-T 2 dualmodal contrast agent. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 6223–6228.
Zhang, B.; Li, Q.; Yin, P.; Rui, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, D. Ultrasound-triggered BSA/SPION hybrid nanoclusters for liver-specific magnetic resonance imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 2012, 4, 6479–6486.
Zhang, B.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, D. Effective reduction of nonspecific binding by surface engineering of quantum dots with bovine serum albumin for cell-targeted imaging. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16605–16613.
Xie, R.; Rutherford, M.; Peng, X. Formation of high-quality I-III-VI semiconductor nanocrystals by tuning relative reactivity of cationic precursors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5691–5697.
Zhong, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, M.; He, Y.; Ye, J.; He, C.; Yang, C.; Li, Y. Controlled synthesis and optical properties of colloidal ternary chalcogenide CuInS2 nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 6434–6443.
Nam, D. E.; Song, W. S.; Yang, H. Noninjection, one-pot synthesis of Cu-deficient CuInS2/ZnS core/shell quantum dots and their fluorescent properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 361, 491–496.
Chen, B.; Zhong, H.; Zhang, W.; Tan, Z. A.; Li, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhai, T.; Bando, Y.; Yang, S.; Zou, B. Highly emissive and color-tunable CuInS2-based colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals: Off stoichiometry effects and improved electroluminescence performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2081–2088.
Frangioni, J. V. In vivo near-infrared fluorescence imaging. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 626–634.
He, X.; Gao, J.; Gambhir, S. S.; Cheng, Z. Near-infrared fluorescent nanoprobes for cancer molecular imaging: Status and challenges. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 574–583.
Kim, B. H.; Lee, N.; Kim, H.; An, K.; Park, Y. I.; Choi, Y.; Shin, K.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, S. G.; Na, H. B. Large-scale synthesis of uniform and extremely small-sized iron oxide nanoparticles for high-resolution T 1 magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12624–12631.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, W., Yang, W., Wang, Y. et al. Color-tunable Gd-Zn-Cu-In-S/ZnS quantum dots for dual modality magnetic resonance and fluorescence imaging. Nano Res. 7, 1581–1591 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0518-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0518-8