Abstract
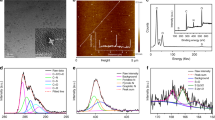
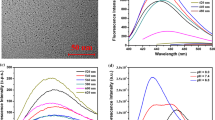
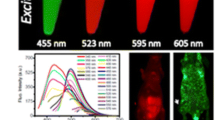
C dots (CDs) have shown great potential in bioimaging and phototherapy. However, it is challenging to manipulate their fluorescent properties and therapeutic efficacy to satisfy the requirements for clinic applications. In this study, we prepared S, Se-codoped CDs via a hydrothermal method and demonstrated that the doping resulted in excitation wavelength-independent near-infrared (NIR) emissions of the CDs, with peaks at 731 and 820 nm. Significantly, the CDs exhibited a photothermal conversion efficiency of ~58.2%, which is the highest reported value for C nanostructures and is comparable to that of Au nanostructures. Moreover, the CDs had a large two-photon absorption cross section (~30,045 GM), which allowed NIR emissions and the photothermal conversion of the CDs through the two-photon excitation (TPE) mechanism. In vitro and in vivo tests suggested that CDs can function as new multifunctional phototheranostic agents for the TPE fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy of cancer cells.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, G. Y.; Roy, I.; Yang, C. H.; Prasad, P. N. Nanochemistry and nanomedicine for nanoparticle-based diagnostics and therapy. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2826–2885.
Lucky, S. S.; Soo, K. C.; Zhang, Y. Nanoparticles in photodynamic therapy. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 1990–2042.
Lim, E. K.; Kim, T.; Paik, S.; Haam, S.; Huh, Y. M.; Lee, K. Nanomaterials for theranostics: Recent advances and future challenges. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 327–394.
Lovell, J. F.; Liu, T. W. B.; Chen, J.; Zheng, G. Activatable photosensitizers for imaging and therapy. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2839–2857.
Cheng, L.; Wang, C.; Feng, L. Z.; Yang, K.; Liu, Z. Functional nanomaterials for phototherapies of cancer. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10869–10939.
Yuan, Y. Y.; Zhang, C. J.; Xu, S. D.; Liu, B. A self-reporting AIE probe with a built-in singlet oxygen sensor for targeted photodynamic ablation of cancer cells. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1862–1866.
Yuan, Y. Y.; Zhang, C. J.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Xu, S. D.; Zhang, R. Y.; Wu, J. E.; Tang, B. Z.; Liu, B. Light-up probe for targeted and activatable photodynamic therapy with realtime in situ reporting of sensitizer activation and therapeutic responses. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 6586–6595.
Jin, C. S.; Lovell, J. F.; Chen, J.; Zheng, G. Ablation of hypoxic tumors with dose-equivalent photothermal, but not photodynamic, therapy using a nanostructured porphyrin assembly. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2541–2550.
Yang, X.; Yang, M. X.; Pang, B.; Vara, M.; Xia, Y. N. Gold nanomaterials at work in biomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10410–10488.
Wang, K. K.; Zhang, Y. F.; Wang, J.; Yuan, A. H.; Sun, M. J.; Wu, J. H.; Hu, Y. Q. Self-assembled IR780-loaded transferrin nanoparticles as an imaging, targeting and PDT/PTT agent for cancer therapy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27421.
Pang, X. J.; Wang, J. P.; Tan, X. X.; Guo, F.; Lei, M. Z.; Ma, M.; Yu, M.; Tan, F. P.; Li, N. Dual-modal imagingguided theranostic nanocarriers based on indocyanine green and mTOR inhibitor rapamycin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 13819–13829.
Shi, C. H.; Wu, J. B.; Pan, D. F. Review on near-infrared heptamethine cyanine dyes as theranostic agents for tumor imaging, targeting, and photodynamic therapy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 050901.
Li, N.; Zhao, P. X.; Astruc, D. Anisotropic gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, applications, and toxicity. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1756–1789.
Xu, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, L. H.; He, Y.; Shi, J. Y.; Tang, B.; Fan, C. H. Nanoscale optical probes for cellular imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 2650–2661.
Ge, J. C.; Lan, M. H.; Zhou, B. J.; Liu, W. M.; Guo, L.; Wang, H.; Jia, Q. Y.; Niu, G. L.; Huang, X.; Zhou, H. Y. et al. A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4596.
Ge, J. C.; Jia, Q. Y.; Liu, W. M.; Guo, L.; Liu, Q. Y.; Lan, M. H.; Zhang, H. Y.; Meng, X. M.; Wang, P. F. Red-emissive carbon dots for fluorescent, photoacoustic, and thermal theranostics in living mice. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4169–4177.
Cao, L.; Meziani, M. J.; Sahu, S.; Sun, Y. P. Photoluminescence properties of graphene versus other carbon nanomaterials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 171–180.
Morimoto, Y.; Horie, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Shinohara, N.; Shimada, M. Inhalation toxicity assessment of carbon-based nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 770–781.
Lim, S. Y.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Q. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381.
Baker, S. N.; Baker, G. A. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6726–6744.
Zeng, J.; Goldfeld, D.; Xia, Y. N. A plasmon-assisted optofluidic (PAOF) system for measuring the photothermal conversion efficiencies of gold nanostructures and controlling an electrical switch. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 4169–4173.
Ji, M. W.; Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Z. Z.; Huang, L.; Liu, J. J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, L.; Yu, Y. X.; Hao, W. C. et al. Structurally well-defined Au@Cu2-xS core–shell nanocrystals for improved cancer treatment based on enhanced photothermal efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3094–3101.
Song, J. B.; Wang, F.; Yang, X. Y.; Ning, B.; Harp, M. G.; Culp, S. H.; Hu, S.; Huang, P.; Nie, L. M.; Chen, J. Y. et al. Gold nanoparticle coated carbon nanotube ring with enhanced Raman scattering and photothermal conversion property for theranostic applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7005–7015.
Hu, Y.; Wang, R. Z.; Wang, S. G.; Ding, L.; Li, J. C.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X. L.; Shen, M. W.; Shi, X. Y. Multifunctional Fe3O4 @ Au core/shell nanostars: A unique platform for multimode imaging and photothermal therapy of tumors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28325.
Li, D.; Han, D.; Qu, S. N.; Liu, L.; Jing, P. T.; Zhou, D.; Ji, W. Y.; Wang, X. Y.; Zhang, T. F.; Shen, D. Z. Supra-(carbon nanodots) with a strong visible to near-infrared absorption band and efficient photothermal conversion. Light: Sci. Appl. 2016, 5, e16120.
Hu, S. L.; Trinchi, A.; Atkin, P.; Cole, I. Tunable photoluminescence across the entire visible spectrum from carbon dots excited by white light. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2970–2974.
Tang, L. B.; Ji, R. B.; Li, X. M.; Bai, G. X.; Liu, C. P.; Hao, J. H.; Lin, J. Y.; Jiang, H. X.; Teng, K. S.; Yang, Z. B. et al. Deep ultraviolet to near-infrared emission and photoresponse in layered N-doped graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6312–6320.
Wu, L.; Luderer, M.; Yang, X. X.; Swain, C.; Zhang, H. Y.; Nelson, K.; Stacy, A. J.; Shen, B. Z.; Lanza, G. M.; Pan, D. J. Surface passivation of carbon nanoparticles with branched macromolecules influences near infrared bioimaging. Theranostics 2013, 3, 677–686.
Shen, Y. Z.; Shuhendler, A. J.; Ye, D. J.; Yu, J. J.; Chen, H. Y. Two-photon excitation nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6725–6741.
Cao, L.; Wang, X.; Meziani, M. J.; Lu, F. S.; Wang, H. F.; Luo, P. G.; Lin, Y.; Harruff, B. A.; Veca, L. M.; Murray, D. et al. Carbon dots for multiphoton bioimaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11318–11319.
Fowley, C.; McHale, A. P.; McCaughan, B.; Fraix, A.; Sortino, S.; Callan, J. F. Carbon quantum dot-NO photoreleaser nanohybrids for two-photon phototherapy of hypoxic tumors. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 81–84.
Wang, J.; Zhang, Z. H.; Zha, S.; Zhu, Y. Y.; Wu, P. Y.; Ehrenberg, B.; Chen, J. Y. Carbon nanodots featuring efficient FRET for two-photon photodynamic cancer therapy with a low fs laser power density. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 9372–9381.
Li, J. L.; Bao, H. C.; Hou, X. L.; Sun, L.; Wang, X. G.; Gu, M. Graphene oxide nanoparticles as a nonbleaching optical probe for two-photon luminescence imaging and cell therapy. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 1830–1834.
Lan, M. H.; Wu, J. S.; Liu, W. M.; Zhang, W. J.; Ge, J. C.; Zhang, H. Y.; Sun, J. Y.; Zhao, W. W.; Wang, P. F. Copolythiophene-derived colorimetric and fluorometric sensor for visually supersensitive determination of lipopolysaccharide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6685–6694.
Guo, X.; Wang, C. F.; Yu, Z. Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, S. Facile access to versatile fluorescent carbon dots toward lightemitting diodes. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2692–2694.
Kozák, O.; Sudolská, M.; Pramanik, G.; Cígler, P.; Otyepka, M.; Zboril, R. Photoluminescent carbon nanostructures. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 4085–4128.
Yang, S. W.; Sun, J.; Li, X. B.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Z. Y.; He, P.; Ding, G. Q.; Xie, X. M.; Kang, Z. H.; Jiang, M. H. Large-scale fabrication of heavy doped carbon quantum dots with tunable-photoluminescence and sensitive fluorescence detection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 8660–8667.
Brouwer, A. M. Standards for photoluminescence quantum yield measurements in solution (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 2213–2228.
Yang, F.; Zhao, M. L.; Zheng, B. Z.; Xiao, D.; Wu, L.; Guo, Y. Influence of pH on the fluorescence properties of graphene quantum dots using ozonation pre-oxide hydrothermal synthesis. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 25471–25479.
Zhao, S. J.; Lan, M. H.; Zhu, X. Y.; Xue, H. T.; Ng, T.-W.; Meng, X. M.; Lee, C.-S.; Wang, P. F.; Zhang, W. J. Green synthesis of bifunctional fluorescent carbon dots from garlic for cellular imaging and free radical scavenging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17054–17060.
Turro, N. J. Modern Molecular Photochemistry; University Science Books: Mill Valley, CA, 1991.
Englman, R.; Jortner, J. The energy gap law for radiationless transitions in large molecules. J. Mol. Phys. 1970, 18, 145–164.
Lan, M. H.; Zhang, J. F.; Zhu, X. Y.; Wang, P. F.; Chen, X. F.; Lee, C. S.; Zhang, W. J. Highly stable organic fluorescent nanorods for living-cell imaging. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 2380–2389.
Sharma, A.; Gadly, T.; Gupta, A.; Ballal, A.; Ghosh, S. K.; Kumbhakar, M. Origin of excitation dependent fluorescence in carbon nanodots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 3695–3702.
Xu, Q. F.; Zhou, Q.; Hua, Z.; Xue, Q.; Zhang, C. F.; Wang, X. Y.; Pan, D. Y.; Xiao, M. Single-particle spectroscopic measurements of fluorescent graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10654–10661.
Khan, S.; Gupta, A.; Verma, N. C.; Nandi, C. K. Timeresolved emission reveals ensemble of emissive states as the origin of multicolor fluorescence in carbon dots. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 8300–8305.
Singh, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Bhupathiraju, N. V. S. D. K.; Arianna, G.; Tiwari, K.; Drain, C. M. Glycosylated porphyrins, phthalocyanines, and other porphyrinoids for diagnostics and therapeutics. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10261–10306.
Pu, S. C.; Yang, M. J.; Hsu, C. C.; Lai, C. W.; Hsieh, C. C.; Lin, S. H.; Cheng, Y. M.; Chou, P. T. The empirical correlation between size and two-photon absorption cross section of CdSe and CdTe quantum dots. Small 2006, 2, 1308–1313.
Liu, Q.; Guo, B. D.; Rao, Z. Y.; Zhang, B. H.; Gong, J. R. Strong two-photon-induced fluorescence from photostable, biocompatible nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for cellular and deep-tissue imaging. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2436–2441.
Kong, B.; Zhu, A. W.; Ding, C. Q.; Zhao, X. M.; Li, B.; Tian, Y. Carbon dot-based inorganic–organic nanosystem for two-photon imaging and biosensing of pH variation in living cells and tissues. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 5844–5848.
Peng, X. J.; Yang, Z. G.; Wang, J. Y.; Fan, J. L.; He, Y. X.; Song, F. L.; Wang, B. S.; Sun, S. G.; Qu, J. L.; Qi, J. et al. Fluorescence ratiometry and fluorescence lifetime imaging: Using a single molecular sensor for dual mode imaging of cellular viscosity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6626–6635.
Fan, M.; Yao, J.; Tung, C.-H. Molecular Photochemistry and Materials Science; Chinese Science Publishing & Media Ltd.: Beijing, 2008. (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the General Research Fund of Hong Kong (No. 11338516), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51572269 and 51672230).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
12274_2017_1528_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Two-photon-excited near-infrared emissive carbon dots as multifunctional agents for fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, M., Zhao, S., Zhang, Z. et al. Two-photon-excited near-infrared emissive carbon dots as multifunctional agents for fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy. Nano Res. 10, 3113–3123 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1528-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1528-0