Abstract
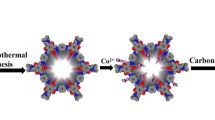
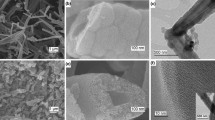
Highly efficient metal-free, carbon-based, bi-functional electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) have attracted increased attention for use in electrochemical energy conversion systems, owing to their low cost and high activity. In this work, N-doped carbon nanocages (N-CCs) with a porous self-supported architecture and high specific surface area are synthesized by a facile interfacial assembly synthetic route. The materials are comprehensively characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, nitrogen adsorption–desorption experiments, X-ray diffraction, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Cyclic voltammetry, chronoamperometry, and linear sweep voltammetry demonstrate that the as-prepared N-CC could serve as an effective metal-free electrocatalyst with excellent catalytic activity, long-term operation durability, and excellent methanol tolerance for the ORR in alkaline media. In the presence of 3 mM methanol, the half wave potential of the N-CCs for the ORR is 190 mV; this is more positive than that of the commercial Pt/C electrocatalyst. Meanwhile, the N-CCs also show an OER activity comparable to that of the commercial Ru/C electrocatalyst, revealing their bifunctional property.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chu, S.; Majumdar, A. Opportunities and challenges for a sustainable energy future. Nature 2012, 488, 294–303.
Shao, M. H.; Chang, Q. W.; Dodelet, J.-P.; Chenitz, R. Recent advances in electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3594–3657.
Kudo, A.; Miseki, Y. Heterogeneous photocatalyst materials for water splitting. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 253–278.
Mao, S.; Wen, Z. H.; Huang, T. Z.; Hou, Y.; Chen, J. H. High-performance bi-functional electrocatalysts of 3D crumpled graphene-cobalt oxide nanohybrids for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 609–616.
Xu, Y. X.; Sheng, K. X.; Li, C.; Shi, G. Q. Highly conductive chemically converted graphene prepared from mildly oxidized graphene oxide. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7376–7380.
Nie, Y.; Li, L.; Wei, Z. D. Recent advancements in Pt and Pt-free catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2168–2201.
Ma, R. G.; Ren, X. D.; Xia, B. Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, C.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J. J.; Wang, J. C. Novel synthesis of N-doped graphene as an efficient electrocatalyst towards oxygen reduction. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 808–819.
Su, C. Y.; Cheng, H.; Li, W.; Liu, Z. Q.; Li, N.; Hou, Z. F.; Bai, F. Q.; Zhang, H. X.; Ma, T. Y. Atomic modulation of FeCo–nitrogen–carbon bifunctional oxygen electrodes for rechargeable and flexible all-solid-state zinc-air battery. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602420.
Cai, J.; Zheng, P.; Mahmood, Q. Effect of cathode electron acceptors on simultaneous anaerobic sulfide and nitrate removal in microbial fuel cell. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 947–954.
Ma, M.; You, S. J.; Wang, W.; Liu, G. S.; Qi, D.P.; Chen, X. D.; Qu, J. H.; Ren, N. Q. Biomass-derived porous Fe3C/t ungsten carbide/graphitic carbon nanocomposite for efficient electrocatalysis of oxygen reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32307–32316.
Zhu, C. Z.; Fu, S. F.; Song, J. H.; Shi, Q. R.; Su, D.; Engelhard, M. H.; Li, X. L.; Xiao, D. D.; Li, D. S.; Estevez, L. et al. Self-assembled Fe-N-doped carbon nanotube aerogels with single-atom catalyst feature as high-efficiency oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Small 2017, 13, 1603407.
Li, J. J.; Zhang, Y. M.; Zhang, X. H.; Huang, J. Z.; Han, J. C.; Zhang, Z. H.; Han, X. J.; Xu, P.; Song, B. S,N dual-doped graphene-like carbon nanosheets as efficient oxygen reduction reaction electrocatalysts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 398–405.
He, Y. F.; Gehrig, D.; Zhang, F.; Lu, C.B.; Zhang, C.; Cai, M.; Wang, Y. Y.; Laquai, F.; Zhuang, X. D.; Feng, X. L. Highly efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction based on 1D ternary doped porous carbons derived from carbon nanotube directed conjugated microporous polymers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 8255–8265.
Xu, W.; Wu, Z. C.; Tao, S. W. Recent progress in electrocatalysts with mesoporous structures for application in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 16272–16287.
Ma, R.G.; Xia, B. Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, P. X.; Chen, Y. F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J. C. Ionic liquid-assisted synthesis of dual-doped graphene as efficient electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. Carbon 2016, 102, 58–65.
Zhang, J. T.; Zhao, Z. H.; Xia, Z. H.; Dai, L. M. A metalfree bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reactions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 444–452.
Che, G. L.; Lakshmi, B. B.; Fisher, E. R.; Martin, C. R. Carbon nanotubule membranes for electrochemical energy storage and production. Nature 1998, 393, 346–349.
Kongkanand, A.; Kuwabata, S.; Girishkumar, G.; Kamat, P. V. Single-wall carbon nanotubes supported platinum nanoparticles with improved electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction reaction. Langmuir 2006, 22, 2392–2396.
Maldonado, S.; Morin, S.; Stevenson, K. J. Structure, composition, and chemical reactivity of carbon nanotubes by selective nitrogen doping. Carbon 2006, 44, 1429–1437.
Nagaiah, T. C.; Kundu, S.; Bron, M.; Muhler, M.; Schuhmann, W. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes as a cathode catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction in alkaline medium. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 338–341.
Mo, Z. Y.; Zheng, R. P.; Peng, H. L.; Liang, H. G.; Liao, S. J. Nitrogen-doped graphene prepared by a transfer doping approach for the oxygen reduction reaction application. J. Power Sources 2014, 245, 801–807.
Wang, H. T.; Wang, W.; Xu, Y. Y.; Dong, S.; Xiao, J. W.; Wang, F.; Liu, H. F.; Xia, B. Y. Hollow nitrogen-doped carbon spheres with Fe3O4 nanoparticles encapsulated as a highly active oxygen-reduction catalyst. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 10610–10617.
Trogadas, P.; Ramani, V.; Strasser, P.; Fuller, T. F.; Coppens, M. O. Hierarchically structured nanomaterials for electrochemical energy conversion. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 122–148.
Bai, Z. Y.; Yang, L.; Guo, Y. M.; Zheng, Z.; Hu, C. G.; Xu, P. L. High-efficiency palladium catalysts supported on ppymodified C60 for formic acid oxidation. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1752–1754.
Yang, S. D.; Dong, J.; Yao, Z. H.; Shen, C. M.; Shi, X. Z.; Tian, Y.; Lin, S. X.; Zhang, X. G. One-pot synthesis of graphene-supported monodisperse pd nanoparticles as catalyst for formic acid electro-oxidation. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4501.
Ali, M.; Jha, M.; Das, S. K.; Saha, S. K. Hydrogen-bondinduced microstructural transition of ionic micelles in the presence of neutral naphthols: Ph dependent morphology and location of surface activity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 15563–15571.
Yu, Q. Y.; Hui, J. F.; Wang, P. P.; Xu, B.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, X. Hydrothermal synthesis of mesoporous silica spheres: Effect of the cooling process. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 7114–7120.
Valle-Vigón, P.; Sevilla, M.; Fuertes, A. B. Mesostructured silica–carbon composites synthesized by employing surfactants as carbon source. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2010, 134, 165–174.
Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, H. H.; Hu, Y.; Shi, G. Q.; Dai, L. M.; Qu, L. T. Nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots with oxygen-rich functional groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15–18.
Qu, L. T.; Liu, Y.; Baek, J. B.; Dai, L. M. Nitrogen-doped graphene as efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction in fuel cells. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1321–1326.
Yu, J. S.; Kang, S.; Yoon, S. B.; Chai, G. Fabrication of ordered uniform porous carbon networks and their application to a catalyst supporter. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 9382–9383.
Gong, K. P.; Du, F.; Xia, Z. H.; Durstock, M.; Dai, L. M. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube arrays with high electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction. Science 2009, 323, 760–764.
Wan, K.; Tan, A. D.; Yu, Z. P.; Liang, Z. X.; Piao, J. H.; Tsiakaras, P. 2D nitrogen-doped hierarchically porous carbon: Key role of low dimensional structure in favoring electrocatalysis and mass transfer for oxygen reduction reaction. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 209, 447–454.
Gorlin, Y.; Jaramillo, T. F. A bifunctional nonprecious metal catalyst for oxygen reduction and water oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13612–13614.
Liu, Y. Y.; Jiang, H. L.; Zhu, Y. H.; Yang, X. L.; Li, C. Z. Transition metals (Fe, Co, and Ni) encapsulated in nitrogendoped carbon nanotubes as bi-functional catalysts for oxygen electrode reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1694–1701.
Faisal, S. N.; Haque, E.; Noorbehesht, N.; Zhang, W. M.; Harris, A. T.; Church, T. L.; Minett, A. I. Pyridinic and graphitic nitrogen-rich graphene for high-performance supercapacitors and metal-free bifunctional electrocatalysts for ORR and OER. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17950–17958.
Jiang, H.; Wang, Y. Q.; Hao, J. Y.; Liu, Y. S.; Li, W. Z.; Li, J. N and P co-functionalized three-dimensional porous carbon networks as efficient metal-free electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction. Carbon 2017, 122, 64–73
Yu, H. J.; Shang, L.; Bian, T.; Shi, R.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Zhao, Y. F.; Zhou, C.; Wu, L. Z.; Tung, C. H.; Zhang, T. R. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon nanosheets templated from g-C3N4 as metal-free electrocatalysts for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5080–5086.
Tao, L.; Wang, Q.; Dou, S.; Ma, Z. L.; Huo, J.; Wang, S. Y.; Dai, L. M. Edge-rich and dopant-free graphene as a highly efficient metal-free electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 2764–2767.
Men, B.; Sun, Y. Z.; Li, M. J.; Hu, C. Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L. A.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y. M.; Wan, P. Y.; Pan, J. Q. Hierarchical metal-free nitrogen-doped porous graphene/carbon composites as an efficient oxygen reduction reaction catalyst. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1415–1423.
Yazdi, A. Z.; Roberts, E. P. L.; Sundararaj, U. Nitrogen/sulfur co-doped helical graphene nanoribbons for efficient oxygen reduction in alkaline and acidic electrolytes. Carbon 2016, 100, 99–108.
Hu, C. G.; Dai, L. M. Multifunctional carbon-based metalfree electrocatalysts for simultaneous oxygen reduction, oxygen evolution, and hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604942.
Zhao, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Kamiya, K.; Nakanishi, S.; Hashimoto, K. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials as non-metal electrocatalysts for water oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2390.
Czerw, R.; Terrones, M.; Charlier, J. C.; Blase, X.; Foley, B.; Kamalakaran, R.; Grobert, N.; Terrones, H.; Tekleab, D.; Ajayan, P. M. et al. Identification of electron donor states in N-doped carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2001, 1, 457–460.
Hou, Z. F.; Wang, X. L.; Ikeda, T.; Terakura, K.; Oshima, M.; Kakimoto, M.-A. Electronic structure of N-doped graphene with native point defects. Phys. Rev. B 2013, 87, 165401.
Cheng, Y. H.; Tian, Y. Y.; Fan, X. Z.; Liu, J. G.; Yan, C. W. Boron doped multi-walled carbon nanotubes as catalysts for oxygen reduction reaction and oxygen evolution reactionin in alkaline media. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 143, 291–296.
Cheng, N. Y.; Liu, Q.; Tian, J. Q.; Xue, Y. R.; Asiri, A. M.; Jiang, H. F.; He, Y. Q.; Sun, X. P. Acidically oxidized carbon cloth: A novel metal-free oxygen evolution electrode with high catalytic activity. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 1616–1619.
Tian, J. Q.; Liu, Q.; Asiri, A. M.; Alamry, K. A.; Sun, X. P. Ultrathin graphitic C3N4 nanosheets/graphene composites: Efficient organic electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 2125–2130.
Qu, K. G.; Zheng, Y.; Dai, S.; Qiao, S. Z. Graphene oxidepolydopamine derived N, S-codoped carbon nanosheets as superior bifunctional electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction and evolution. Nano Energy 2016, 19, 373–381.
Cheng, Y.; Xu, C. W.; Jia, L. C.; Gale, J. D.; Zhang, L. L.; Liu, C.; Shen, P. K.; Jiang, S. P. Pristine carbon nanotubes as non-metal electrocatalysts for oxygen evolution reaction of water splitting. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2015, 163, 96–104.
Acknowledgements
This research was sponsored by Key Technologies R&D Program of Shaanxi Province (Nos. 2014K10-06 and 2015XT-18), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51373092 and 21543012), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Nos. GK201503038 and GK201501002), Program for Key Science & Technology Innovation Team of Shaanxi Province (No. 2015KCT-13), and the 111 Project (No. B14041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, N., Weng, Q., Shi, Y. et al. N-doped carbon nanocages: Bifunctional electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. Nano Res. 11, 1905–1916 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1808-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-017-1808-8