Abstract
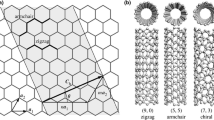
Microfluidic lab-on-a-chip allows chemical and biochemical analysis to be conducted in a miniaturized system. Miniaturized analysis reduces the reagent consumption while decreasing the overall size of the device, but the small dose of the sample make detection more demanding and is more sensitive to adsorption of species on the surface. Integration of carbon nanotubes into microfludic devices is a promising approach. This review addresses recent advances in the application of carbon nanotubes for microfluidic lab-on-a-chip. The literature review shows that carbon nanotubes have been used to achieve superlubrifying microchannels, act as high density nanoporous membranes, electrical transducers mainly in flow sensors and biosensors, and mimics of living systems. In addition, extensive work has been carried out to investigate the tunable mechanical, chemical and electrical properties of carbon nanotubes in order to manipulate and analyse extremely small volumes of fluid effectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen BL, Kichambare PD, Star A (2007) Carbon nanotube field-effect-transistor-based biosensors. Adv Mater 19:1439–1451
Bakajin O, Ben-barak N, Peng J, Noy A (2003) Carbon nanotube based microfluidic elements for filtration and concentration. 7th International Conference on Miniaturized Chemical and Blochemlcal Analysts Systems, October 5–9, 2003, Squaw Valley, Callfornla USA
Balasubramanian K, Burghard M (2006) Biosensor based on carbon nanoubes. Anal Bional Chem 385:452–468
Berthier J, Dubois P, Clementz P, Claustre P, Peponnet C, Fouillet Y (2006) Actuation potentials and capillary forces in electrowetting based microsystems. Sens Actuators A 5346:1–9
Berthier J, Silberzan P (2006) Microfluidics for biotechnology. Artech House, London
Bourlon AB, Wong J, Miko C, Forro L, Bockrath M (2007) A nanoscale probe for fluidic and ionic transport. Nature Nanotech 2:104–107
Cai H, Xu Y, He PG, Fang YZ (2003) Indicator free DNA hybridization detection by impedance measurement based on the DNA-doped conducting polymer film formed on the carbon nanotube modified electrode. Electroanalysis 15:1864–1870
Chopra N, Majumder M, Hinds BJ (2005) Bifunctional carbon nanotubes by sidewall protection. Adv Funct Mater 15:858–864
Choi A, Jeong H, Kim S, Jo S, Jeon S (2007) Electrocatalytic reduction of dioxygen by cobalt porphyrin modified glassy carbon electrode with single-walled carbon nanotubes and nafion in aqueous solutions. Electrochimica Acta. 1–22
Doktycz MJ, Simpson ML (2004) Nanoengineered membranes for controlled transport. U. S. Patent Appl. Pub. US 2004/0173506A1
Feng L, Li S, Li Y, Li H, Zhang L, Zhai J (2002) Super-hydrophobic surfaces: from natural to artificial. Adv Mater 14:1857–1860
Ghosh S, Sood AK, Kumar N (2003) Carbon nanotube flow sensors. Science 299:1042–1044
He P, Xu Y, Fang Y (2006) Applications of carbon nanotubes in electrochemical DNA biosensors-review. Microchim Acta 152:175–186
Hinds BJ, Chopra N, Rantell T, Andrews R, Gavalas V, Bachas LG (2004) Aligned multiwalled carbon nanotube membranes. Science 303:62–65
Holt JK, Park HG, Wang RY, Stadermann M, Artyukhin AB, Grigoropoulos CP, Noy A, Bakajin O (2006) Fast mass transport through sub-2-nanometer carbon nanotubes. Science 312:1034–1037
Journet C, Moulinet S, Ybert C, Purcell ST, Bocquet L (2005) Contact angle measurements on superhydrophobic carbon nanotube forests: effect of fluid pressure. Europhys Lett 71:104–109
Koch M, Evans A, Brunnschweiler A (2000) Microfluidic technology and applications. Baldock, Herts
Lau KKS, Bico J, Teo KBK, Chhowalla M, Amaratunga GAJ, Milne WI, McKinley GH, Gleason KK (2003) Superhydrophobic carbon nanotube forests. Nano Lett 3:1701–1705
Lee Y, Kwon O, Yoon Y, Ryu K (2006) Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on multi-wall carbon nanotubes and its electrochemical properties. Biotech Lett 28:39–43
Li PH (2006) Microfluidic lab-on-a-chip for chemical and biological analysis and discovery. Taylor and Francis
Li J, Cassell A, Delzeit L, Han J, Meyyappan M (2002a) Novel three-dimensional electrodes: electrochemical properties of carbon nanotube ensembles. J Phys Chem B 106:9299–9305
Li S, Li H, Wang X, Song Y, Liu Y, Jiang L (2002b) Super-hydrophobicity of large-area honeycomb-like aligned carbon nanotubes. J Phys Chem B 106:9274–9276
Li C, Currelli M, Lin H, Lei B, Ishikawa FN, Datar R, Cote R, Thompson M, Zhou C (2005) Complementary detection of prostate-specific antigen using In2O3 nanowires and carbon nanotubes. J Am Chem Soc 127:484–485
Li X, Zhu G, Dordick JS, Ajayan PM (2007) Compression-modulated tunable-pore carbon-nanotube membrane filters. Small 3:595–599
Liu J, Chou A, Rahmat W, Paddon-Row WN, Gooding JJ (2005) Achieving direct electrical connection to glucose aligned single walled carbon nanotube arrays. Electroanalysis 17:38–46
Liu H, Zhai J, Jiang L (2006) Wetting and anti-wetting on aligned carbon nanotube films. Soft Matter 2:81–8211
Male KB, Hrapovic S, Liu Y, Wang D, Luong JHT (2004) Electrochemical detection of carbohydrates using copper nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. Anal Chim Acta 516:35–41
Majumder M, Chopra N, Andrews R, Hinds BJ (2005) Enhanced flow in carbon nanotubes. Nature 438:44
Miller SA, Martin CR (2004) Redox modulation of electroosmotic flow in a carbon nanotube membrane. J Am Chem Soc 126:6226–6227
Nednoor P, Gavalas VG, Chopra N, Hinds BJ, Bachas LG (2007) Carbon nanotube based biomimetic membranes: mimicking protein channels regulated by phosphorylation. J Mater Chem 17:1755–1757
Nguyen-Vu TDB, Chen H, Cassell AM, Andrews RJ, Meyyappan M, Li J (2006) Vertically aligned carbon nanofiber arrays: an advance toward electrical–neural interfaces. Small 2:89–94
Pan W, Chen X, Guo M, Huang Y, Yao S (2007) A novel amperometric sensor for the detection of difenidol hydrochloride based on the modification of \({\text{Ru}}\left( {{\text{bpy}}} \right)_3^{2 + } \) on a glassy carbon electrode. Talanta 73:651–655
Patankar NA (2004) Mimicking the lotus effect: influence of double roughness structures and slender pillars. Langmuir 20:8209–8213
Pedano ML, Rivas GA (2004) Adsorption and electrooxidation of nucleic acids at carbon nanotubes paste electrodes. Electrochem Commun 6:10–16
Qu Y, Ouyang MX, Li WJ, Han X (2007) CNTs as ultra-low-powered aqueous flow sensor microfluidic systems. 1st Annual IEEE International Conference on Nano/Molecular Medicine and Engineering, August 06, 2007
Roy S, Vedala H, Choi W (2006) Vertically aligned carbon nanotube probes for monitoring blood cholesterol. Nanotechnology 17:514–518
Sood AK, Ghosh S (2004) Carbon nanotube flow sensor device and method. U. S. Patent, US 6,718.834
Star A, Joshi V, Han TR, Altoe MV, Gruner G, Stoddart JF (2004) Electronic detection of the enzymatic degradation of starch. Org Lett 6:2089–2092
Sun T, Liu H, Song W, Wang X, Jiang L, Li L, Zhu D (2004) Responsive aligned carbon nanotubes. Angew Chem Int Ed 43:4663–4666
Sun T, Wang G, Liu H, Feng L, Jiang L, Zhu D (2003) Control over the wettability of an aligned carbon nanotube film. J Am Chem Soc 125:14996–14997
Valentini F, Orlanducci S, Terranova MK, Amine A, Palleschi G (2004) Carbon nanotubes as electrode materials for the assembling of new electrochemical biosensors. Sensor Actuators B 100:117–125
Wang J (2005) Carbon-nanotube based electrochemical biosensors: a review. Electroanalysis 17:7–14
Wang J, Musameh M (2003) Carbon nanotube/teflon composite electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Anal Chem 75:2075–2079
Wang J, Chen G, Wang M, Chatrathi MP (2004) Carbon-nanotube/copper composite electrodes for capillary electrophoresis microchip detection of carbohydrates. Analyst 129:512–515
Wang Y, Li Q, Hu S (2005) A multiwall carbon nanotubes film-modified carbon fiber ultramicroelectrode for the determination of nitric oxide radical in liver mitochondria. Bioelectrochemistry 65:135–142
Wang Z, Ci L, Nayak S, Ajayan PM, Koratkar N (2007) Polarity-dependent electrochemically controlled transport of water through carbon nanotube membranes. Nano Lett 7:697–702
Whitby M, Quirke N (2007) Fluid flow in carbon nanotubes and nanopipes. Nature Nanotech 2:87–94
Xu D, Liu H, Yang L, Wang Z (2006) Fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces with non-aligned alkyl-modified multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Carbon 44:3226–3231
Yao D, Cao H, Wen S, Liu D, Bai Y, Zheng W (2006) A novel biosensor for sterigmatocystin constructed by multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWNT) modified with aflatoxin–detoxifizyme (ADTZ). Bioelectrochem 68:126–133
Ye J, Wen Y, Zhang W, Cui H, Xu G, Sheu F (2005) Electrochemical biosensing platforms using phthalocyanine-functionalized carbon nanotube electrode. Electroanalysis 17:89–96
Yun YH, Dong Z, Shanov V, Schulz MJ (2007) Electrochemical impedance measurement of prostate cancer cells using carbon nanotube array electrodes in a microfluidic channel. Nanotechnology 18:1–7
Zeng Y, Huang Y, Jiang J, Zhang XB, Tang C, Shen G, Yu R (2007) Functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with poly(amidoamine) dendrimer for mediator-free glucose biosensor. Electrochem Commum 9:185
Zhang Y, He J, Xiao P, Gong Y (2007) Flow sensing characteristic of thin film based on multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Int J Mod Phys B 21:3473–3476
Zhou X, Moran-Mirabal JM, Craighead HG, McEuen PL (2007) Supported lipid bilayer/carbon nanotube hybrids. Nature Nanotech 2:185–190
Zhu L, Xiu Y, Xu J, Tamirisa PA, Hess DW, Wong CP (2005) Superhydrophobicity on two-tier rough surfaces fabricated by controlled growth of aligned carbon nanotube arrays coated with fluorocarbon. Langmuir 21:11208–11212
Acknowledgement
C. L. acknowledges the ORS Award from the Cambridge Trust and the support of Downing College Cambridge.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choong, CL., Milne, W.I. & Teo, K.B.K. Review: carbon nanotube for microfluidic lab-on-a-chip application. Int J Mater Form 1, 117–125 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12289-008-0379-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12289-008-0379-3