Abstract
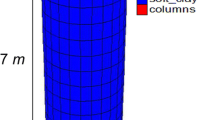
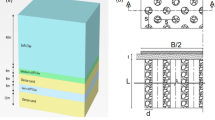
A method is proposed to evaluate settlement of soft clay reinforced with stone columns. Finite element analyses were carried out using 15-noded triangular elements with PLAXIS. A drained analysis was carried out using Mohr–Coulomb’s criterion for soft clay, stones, and sand. The stress due to column installation has been considered in the analysis. At the interface between the stone column and soft clay, interface elements have been used. The settlement ratio (SR) of the soil has been estimated using the equivalent secant modulus. The results are compared with those available in the literature, and the advantages of the numerical analysis were highlighted. Based on the results of this analysis, the SR decrease with compaction surrounding soft soil, but decrease of SR is mainly due to a stiffer column material in soft clay.
مجردة
ويقترح طريقة لتقييم تسوية الطين الطري معززة مع الأعمدة الحجرية. تحليلات العنصر المحدود نفذت باستخدام 15 – العقدة العناصر الثلاثية مع.PLAXIS ويشير تحليل استنزفت نفذ باستخدام موهر - كولومب معيارا لينة الطين والحجارة والرمال. الإجهاد بسبب تركيب عمود تم النظر في التحليل. في الواجهة بين العمود الحجر والطين الطري، عناصر واجهة قد استخدمت. النتائج العددية قد أظهرت أن نسبة التسوية (SR) للتربة قدرت باستخدام معامل يعادل القاطع. وتتم مقارنة النتائج مع تلك المتاحة في الأدب والمزايا التي تتمتع بها التحليل العددي وسلط الضوء. استنادا إلى نتائج هذا التحليل ، فإن الانخفاض SR مع انضغاط التربة المحيطة بها لينة، ولكن بانخفاض قدره SRويرجع ذلك أساسا إلى صلابة المادة العمود في الطين الطري.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboshi H, Ichimoto E, Harada K, Emoki M (1979) The composer—a method to improve the characteristics of soft clays by inclusion of large diameter sand columns. Proc., Int. Conf. on Soil Reinforcement., E.N.P.C., 1, Paris 211–216
Ambily AP, Grandhi SR (2007) Behavior of stone columns based on experimental and FEM analysis. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng ASCE 133(4):405–415
Balaam NP, Booker JR (1981) Analysis of rigid rafts supported by granular piles. Int J Num Anal Methods Geomech 5:379–403
Balaam NP, Poulos HG, Brown PT (1978) Settlement analysis of soft clays reinforced with granular piles. Proc., 5th Asian Conf. on Soil Engineering, Bangkok, Thailand, 81–92
Brinkgreve RB, Vermeer PA (1998) Plaxis-finite element code for soil and rocks analysis. Version 8.2 Rotterdam Brookfield, AA. Balkema
Christian JT, Carrier WD (1978) Janbu, Bjerrum and Kjaernsli’s chart reinterpreted. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 15:123–128
Elkasabgy MA (2005) Performance of stone columns reinforced grounds. M.Sc. Thesis, Zagazig University, Faculty of Engineering at Shobra, Cairo
Elshazly HA, Hafez D, Mosaad M (2006) Back calculating vibro-installation stresses in stone columns reinforced grounds. J Ground Improve 10(2):47–53
Elshazly H, Elkasabgy M, Elleboudy A (2007) Effect of inter-column spacing on soil stresses due to vibro-installed stone columns: interesting findings. Geotech Geol Eng (2008) 26:225–236
Etezad M (2006) Geotechnical Performance of Group of Stone Columns. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Montreal Quebec
Greenwood DA (1970) Mechanical improvement of soils below ground surfaces. Proc., Ground Engineering Conf., Institution of Civil Engineers, London, 11–22
Guetif Z, Bouassida M, Debats JM (2007) Improved soft clay characteristics due to stone column installation. Comput Geotech 34(2007):104–111
Han J, Ye SL (1992) Settlement analysis of buildings on the soft clays stabilized by stone columns, Proc., Int. Conf. on Soil Improvement and Pile Found., 118, 446–451
Han J, Ye SL (2001) Simplified method for consolidation rate of stone column reinforced foundation. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 127(7):597–603
Hu W, Wood D M, Stewart W (1977) Ground improvement using stone column foundation: results of model tests. Proc., Int. Conf. on Ground Improvement Techniques, Macau, 247–256
Hughes JMO, Withers NJ, Greenwood DA (1976) A field trial of reinforcing effect of stone column in soil. Proc., Ground Treatment by Deep Compaction, Institution of Civil Engineers, London, 32–44
Lee JS, Pande GN (1998) Analysis of stone column reinforced foundations. Int J Numer Anal Meth Geomech 22:1001–1020
Mitchell JK, Huber TR (1985) Performance of a stone column foundation. J Geotech Engrg 111(2):205–223
Pitt J M, White DJ, Gaul A, Hoevelkamp K (2003) Highway applications for rammed aggregate piers in Iowa soils, Iowa DOT Project TR-443, CTRE Project 00-60, USA.
Poorooshasb HB, Meyerhof GG (1996) Analysis of behavior of stone columns and lime columns. Comput Geotech 20(1):47–70
Priebe HJ (1976) Abschactzung des setzungsverhaltns eiens durch stopfverdichtung verbesserten baugrundees. Die Bautechnik 54:160–162 (in german)
Priebe HJ (1995) The design of vibro replacement. Ground engineering 28:31–37
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahmatkesh, A., Choobbasti, A.J. Settlement evaluation of soft clay reinforced with stone columns using the equivalent secant modulus. Arab J Geosci 5, 103–109 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0145-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-010-0145-y